Vaccinations ADS and ADS-M are widely used in pediatrics. They are given to children after 6 years of age or are administered to those children who have not tolerated immunization with the pertussis component well. Often parents confuse ADS and ADS-M with each other, as well as with DPT. These vaccinations have significant differences.
If a child has had a severe reaction to the DPT vaccine, the DPT vaccine should be considered as an alternative. It causes less adverse reactions and is better tolerated by the body. The main difference between the vaccinations is the absence of the pertussis component in ADS and ADS-M.
The importance of tetanus vaccination
A distinctive feature of tetanus is that it is not the bacterium itself that disrupts the functioning of the central nervous system, but the toxin that it produces.
The second distinctive feature is that the development of the disease is almost asymptomatic, which does not allow timely initiation of drug treatment.
And the third is a very short incubation period and rapid development of the disease, which can kill a person within two weeks.
Failure to immunize the body in time can lead to dire consequences.
For children and adolescents, tetanus vaccination is a mandatory scheduled procedure, according to the vaccination schedule.
An adult, from the age of 18, independently determines for himself the need for immunization of the body.
Over the past five years, not a single case of infection of a child has been recorded in Russia. While adults still face this terrible disease and more than a third of cases are fatal.
Where can you get vaccinated against coronavirus?
Having found out who is contraindicated for coronavirus vaccination, patients want to know where they can get vaccinated. There is no vaccine yet that has proven highly effective in clinical trials. However, many of them are in the final stage of testing. Scientists plan to launch mass vaccination in 2021. Developed countries are already lining up, distributing vaccine supplies among themselves.
You can't get vaccinated today. However, many countries conduct voluntary vaccination as part of the third phase of clinical trials. Volunteers who have undergone a thorough medical examination are vaccinated in accordance with the established procedure. Thus, 40 thousand volunteers were vaccinated in Moscow. Specialists continuously monitor their condition. Governments of countries and ministries of health post on the official website all the information for those who want to be among the first: where to get vaccinated against coronavirus, how to sign up for voluntary testing.
When and where to get a tetanus shot: schedule
For infants, three-time vaccination is used. The injection is given intramuscularly into the thigh. The baby does not yet understand the importance of immunization, so he just needs to be distracted, and then encouraged and praised.
For preschool children and adolescents, the injection is given into the shoulder or under the shoulder blade. Parents are informed in advance about revaccination and receive written permission from one of them.
After adulthood, revaccination is necessary every 10 years.
If more than 5 years have passed since the last administration of the toxoid and severe contamination of the damaged skin has occurred, then an unscheduled anti-tetanus injection is necessary. Carrying out such a procedure also applies to planned pregnancy, or upcoming participation in hostilities.
This preventative precaution is carried out due to the fact that in many people the properties of toxoid disappear after 5 years.
Vaccination calendar in Russia for children of the first year of life
Why are people afraid of the coronavirus vaccine?
Is it necessary to get vaccinated against coronavirus, what will happen if you don’t get vaccinated - popular questions asked to doctors. The vaccines being developed have not yet been fully studied. Because of this, many patients are afraid of dying from the coronavirus vaccine. The created variants of vaccination against coronavirus, which are undergoing research, will be improved in the future (vaccination against coronavirus). Many do not want to be test subjects, preferring to wait until an effective vaccine against coronavirus is developed.
Preparation for injection, assessment of contraindications
Before administering tetanus serum, an examination in a clinic and the direct permission of the attending physician are required.
If we are talking about a child, he is examined by a pediatrician. Examines the skin, listens to the functioning of the heart and lungs, examines the throat, and measures body temperature.
A finger blood test may be prescribed. Since many diseases have a long incubation period, their presence in the body can only be determined by the number of leukocytes in the blood.
Contraindications:
- history of reactions to previous tetanus vaccinations;
- liver and kidney pathologies;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- respiratory viral infections;
- acute allergic diseases;
- individual antigen intolerance;
- elevated temperature;
- pathologies of the central nervous system.
It is not recommended to vaccinate after taking hormonal medications or antibiotics. The period between taking the drugs and the injection should be at least three weeks.
How does vaccination work?
Traditionally, one of the following drugs is used:
- ADS – vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria;
- ADSm – ADS with a reduced dose of tetanus toxoid;
- DPT – for whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus.
Pentaxim - vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, polio and Hib infection
Tetanus serum is included in the DTP, vaccination is carried out in accordance with the National Preventive Vaccination Calendar. It also includes immunization against whooping cough and diphtheria.
According to the schedule, in the first year of life, infants are administered three tetanus toxoids:
- The first DTP is given to children three months old. It does not provide full immune protection - at least twice the application is necessary.
- The second is from 4 to 5 months.
- The third - in six months. After the third injection, the baby’s body is 100% protected.
The vaccination schedule provides for five-time immunization of children.
Preschoolers 7 years old and adolescents 16 years old receive it according to routine vaccination.
Types of vaccines
The tetanus vaccine itself has the same composition, however, it can be contained either in an isolated state (isolated vaccine) or in combination with other active components against diphtheria and whooping cough (combined vaccine).
There is also a variant of a combined vaccine against diphtheria and tetanus, but the most common is the three-component vaccine - DTP.
The third subtype of vaccination is emergency vaccination.
Combination vaccine
The combined type is so named because it contains two or one more active component, designed to develop immunity to other diseases (in this case, diphtheria and whooping cough).
This type of vaccine, in turn, is divided into two subtypes:
- low dose;
- full.
The low-dose type of vaccination is intended for vaccination of children over 6 years of age and adults, and the full-dose type is intended for children from 3 months to 6 years. This is due to the composition of the vaccine and side effects (as a rule, adult children and people tolerate this drug less well).
Isolated vaccine
An isolated subtype, usually in a low-dose formulation, is used for repeated vaccination of adults after they reach adulthood.
In terms of the composition of the active substance and effectiveness, it is no different from the combined one.
In addition, this subtype is also used for emergency vaccination.
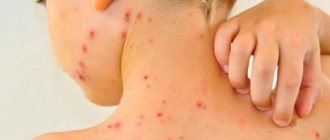
Possible adverse reactions
As a rule, the drug is well tolerated, without causing deterioration or complications. It is more difficult for a child’s body to cope with the load after vaccination, so in children side effects occur more often and the symptoms are more obvious and last longer.
Post-vaccination reactions in children
DTP is the most powerful drug for a child’s body.
According to statistics, every third child experiences a reaction to a tetanus vaccine, with possible symptoms such as:
- increased body temperature;
- slight malaise;
- lack of appetite;
- compaction and pain at the injection site;
- increased salivation.
Such symptoms can be observed for no more than 4 days. Then everything goes away.
If, after a tetanus vaccination, uncharacteristic symptoms are observed: strabismus, the appearance of red spots on the body, severe pain, difficulty breathing, an increase in redness of the injection site by 10 cm or more, a temperature above 39°C - you must immediately consult a doctor or call an emergency room. help.
Reaction to vaccination in adults
The mature, stronger body of an adult tolerates such loads more easily and quickly. Mild symptoms may occur:
- deterioration of general condition - feeling tired and exhausted;
- manifestation of hyperactivity or, conversely, passivity;
- lack of appetite;
- increase in body temperature.
Perforation symptoms appear for no more than two days and go away on their own.
Vaccination calendar for children and adults
Coronavirus vaccination - side effects
All patients who voluntarily were vaccinated against coronavirus as part of a large drug trial were given a special diary. It includes information about your well-being, a sudden change in condition, if:
- temperature increase;
- chills;
- headache;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- labored breathing;
- flickering of flies before the eyes.
Such side effects from the coronavirus vaccine require special medical supervision. If they occur, you must immediately inform your doctor. Some states have developed special mobile applications to facilitate the collection of information about possible side effects of vaccination. This helps to obtain systematic information.
How to avoid unpleasant consequences?
No specialist can give a 100% guarantee that there will be no post-vaccination reaction, since each patient reacts individually.
But with the help of simple rules it is possible to minimize or even avoid side effects after vaccination.
Actions before vaccination:
- It is recommended to spend more time outdoors.
- Medical examination and testing.
- 2 days before the injection, do not visit crowded places.
- Avoid contact with infectious and contagious people.
- Before and after the injection, do not introduce new foods with high allergens into the diet.
Everyone handles this load differently. Typically, side effects are extremely rare.
How often do you get a tetanus shot?
Before reaching adulthood, a child receives 5 vaccines. The sixth dose may be additional. It is especially recommended before planning your first pregnancy, or before entering military service. But this does not guarantee protection for the rest of your life.
Not many people know that tetanus toxoid provides immunization for only 10 years .
For this reason, revaccination is necessary every decade.
A person needs about 10-12 anti-inflammatory injections throughout his life.
Immunization of children
Vaccination of children takes place at an early stage, in several stages.
The first stage, the primary vaccination itself, takes place in three vaccinations with an interval of 1.5 months up to the age of one year (3-4.5-6).
Next, revaccination is carried out, which also takes place in three vaccinations, with only one difference - an increased interval between vaccines.
The first - at 18 months, the second at 6 or 7 years, the third at 14 years (in some cases at 16 years).
As stated earlier, a full vaccine is recommended for children under 6 years of age, while once they reach 6 years of age, a low-dose vaccine is used, as for adults.
It is worth noting that upon reaching six years of age, active components aimed at developing immunity against whooping cough are excluded from the general DTP vaccine. This vaccine is called ADS.
Vaccine compatibility with alcohol
Let's start with the fact that not a single laboratory assistant will agree to inject a drunk person.
It is not recommended to drink alcohol after receiving tetanus toxoid. This is due to the fact that after the administration of the serum, the immune system deteriorates, the body weakens, and the additional burden in the form of alcohol poisoning can negatively affect the patient.
In addition, post-vaccination reactions can occur even without drinking alcohol. Adding alcohol will worsen the situation and cause side effects.
When should you get a tetanus vaccine after an injury, cut or injury?
Injuries, cuts or wounds received in unsterile conditions are always a reason for tetanus immunoprophylaxis in the absence of reliable facts about the person’s vaccination against the disease.
The best option for choosing a further treatment regimen is to determine the titer of tetanus antitoxin in the blood serum within 1-2 hours after injury.
Unfortunately, such an analysis requires a good laboratory, which is not possible in primary care.
The following categories of patients are subject to emergency tetanus immunoprophylaxis:
- people who have received injuries with a violation of the integrity of the skin, mucous membranes, as well as penetrating wounds of the abdominal cavity;
- persons with frostbite and 2-4 degree burns;
- women after out-of-hospital births or clandestine abortions;
- patients with animal, snake, and spider bites;
- people suffering from gangrene with soft tissue necrosis, long-term abscesses, and the like.
The following are not vaccinated against tetanus:
- patients in whom, during emergency immunological control, a sufficient titer of tetanus antitoxin in the blood serum was determined (at least 160);
- children with documented evidence of routine tetanus vaccination;
- adults who have documented evidence of a course of tetanus immunization prophylaxis at least 5 years ago.
The state of tetanus immunity should be assessed by specialists immediately after the patient visits a medical institution.