Hepatitis is a viral inflammation of the liver. The transition of the disease to the chronic phase threatens a person with kidney failure or even cirrhosis. Hepatitis has 3 subtypes - A, B, C.
And if A is not so destructive, then B and C are very dangerous for the liver. Vaccination against hepatitis B is an indispensable tool for combating one of the most dangerous infectious diseases today.
Due to the increased likelihood of infection, babies are vaccinated on the first day of their life. But, unfortunately, the immune system gradually weakens while fighting the virus. Therefore, scheduled revaccinations are carried out.
When is vaccination against hepatitis B given?
This is the first vaccination in a newborn's life.
Then the second vaccination is carried out within a month, and the third – six months later. But for children at risk, the vaccination schedule looks like this: the first vaccination according to the schedule, the second – after one month, the third – after two months (from the start of immunovaccination), the fourth – after a year. One of the distinctive features of the hepatitis B vaccine is the absence of age limits for its use .
For those vaccinated who are on hemodialysis (a special method of blood purification), the vaccine is administered in double doses four times. This is explained by the fact that the antibodies from the injected drug lose their potency due to the nature of the procedure.
Such patients are prescribed frequent revaccinations (usually no more than three) in order to obtain a response from the immune system (or to make the body immune to the drug).
There is a separate emergency vaccination against hepatitis B. It can be carried out, for example, when traveling abroad soon. The vaccination schedule in this case looks like this: the first day, the seventh day and the twenty-first day. In addition, a separate revaccination is prescribed after a year.
It must be remembered that the optimal vaccination schedule for hepatitis B can only be drawn up by the attending physician. After all, it is he who is able to take into account all the characteristics of the vaccinator’s body.
Treatment
Medical intervention when diagnosing hepatitis B is to keep the patient comfortable and monitor the body's nutritional levels. After all, hepatitis is often accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea.
In addition, Interferon injections are used in therapy. Therapy for this disease helps slow the development of cirrhosis and improves survival. In many areas where medicines are not available, this type of treatment is difficult.
Liver cancer is fatal in most cases. It often develops in people of productive age. In developing countries, the death of a person diagnosed with this type occurs a couple of months after the disease is detected. If we are talking about a high-income country, chemotherapy combined with surgery can prolong the patient’s life by several years. Patients with cirrhosis sometimes undergo a liver transplant, but no one gives guarantees for a complete recovery.
Is it necessary to get vaccinated or not?
Viral hepatitis can be considered one of the most unpredictable infectious diseases. First it affects the liver, then moves to the skin, blood vessels and digestive system, ending with the nervous system.
Viral hepatitis B is a disease that can be fatal
More than 770,000 people die each year from hepatitis B disorders. That is why vaccination is an extremely important means of prevention.
This explains the mandatory immunization of children. But adults can also undergo hepatitis vaccination if they wish.
In particular, vaccination is indicated for those who are at risk:
- persons who have contact with a virus carrier;
- health workers and medical students;
- oncohematological patients;
- previously unvaccinated persons who have encountered hepatitis B;
- and those for whom blood transfusions are indicated on an ongoing basis.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the importance of vaccination against hepatitis B for schoolchildren. According to the current legislation of the Russian Federation, a person entering a school institution must receive a number of preventive vaccinations. These include the hepatitis vaccine.
In addition, schoolchildren are vaccinated against hepatitis B at the age of thirteen. The only contraindication here is a severe allergic reaction to baker's yeast (plus all products containing it).
Vaccination is possible only on a voluntary basis. But in no case should we neglect the importance of its implementation.
Methods of infection with hepatitis
Any genotype of infection provides a special route of transmission from a sick organism to a healthy one. Hepatitis A can be transmitted through handshakes and the oral-fecal route. Therefore, the countries most affected by the virus are those with low sanitary and epidemiological conditions. Often, unwashed hands become the main carrier of infection that affects the filtering organ of people.
Hepatitis B is transmitted in different ways:
- Using one syringe (drug addiction).
- Eating dirty food.
- Sharing a shared object with an infected person.
- Vertical path (from mother to child during birth).
- Poorly processed medical instruments for medical procedures (especially common in dental offices).
- Sexual intercourse with an infected person.
- Untreated, dirty water.
Hepatitis C spreads among the population through contact with the blood of a patient. It is impossible to become infected through handshakes or communication.
Does vaccination protect against viral disease?
Any modern means for preventing hepatitis B infection are created thanks to innovative research in genetic engineering.
Such vaccines are produced almost entirely (90-95%) from antigen and only 5-10% from other components. The sole purpose of the existence of such drugs is to prevent the human body from protecting itself from a viral disease called hepatitis B. And it is worth noting that they cope with their function quite well.
In 2001, WHO formulated a task for health authorities of all world countries: to find a way to control the spread of this serious infection through organized immunization and updating the vaccination calendar.
Over the past 30 years, 7 of the most effective vaccines have been developed to combat hepatitis B. Each of them is based on an envelope protein known as HBsAg.
To date, the vaccine is being actively improved and vaccinated in 180 countries.
Indications for use
Vaccination is necessary for people who have constant direct contact with a carrier of the infection or have contracted hepatitis. In addition, indications for injection are:
- A job that involves contact with people.
- Traveling to a place with poor sanitary and epidemiological conditions.
- Short-term movement to a country with widespread hepatitis A infection.
- Living in a place where there is an increased risk of infection.
Before leaving for a country with unfavorable conditions, vaccination is carried out approximately 14 days in advance so that immunity has time to develop.
Composition of vaccination preparations
Hepatitis vaccines used in the Russian Federation deserve more attention. Today there are six varieties of the drug. They are made by different companies, but all are created by modifying the cells of the yeast organism.
All vaccines have a fairly similar composition:
- traces of yeast proteins;
- adjuvant (immune booster) in the form of aluminum hydroxide;
- envelope protein of the virus (namely HBsAg). It is the antibody, the main component of the drug;
- preservative thiomersal.
However, not all vaccines contain preservatives.
Hepatitis B drugs registered in Russia include:
- H-B-VAX II. Made in the USA. It is a recombinant agent;
- Sci-B-Vac . Manufacturer – Israel;
- Engerix-V . British development;
- Recombinant yeast vaccine . Produced in Russia by Combiotech and Microgen;
- Eberbiovak . Manufacturer: Cuba.
It is worth noting that the Euvax vaccine is now banned for sale in Russia. It caused some deaths in Vietnam.
DESCRIPTION OF THE MEDICINE
Hepatitis B recombinant yeast vaccine is a protein sorbed on aluminum hydroxide (HBsAg), synthesized by a recombinant yeast strain and containing antigenic determinants of the surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus.
Appearance: A homogeneous suspension of white, grayish tint, without visible foreign inclusions, which separates when standing into a colorless transparent liquid and a loose precipitate of white with a grayish tint, easily breaking when shaken.
Immunobiological properties
A course of vaccination leads to the formation of specific antibodies to the hepatitis B virus in a protective titer in more than 90% of vaccinated people.
Names of imported and Russian vaccines against hepatitis B: which one is better to choose
When choosing a vaccine against hepatitis B, many people cannot decide which one to take: domestic or foreign. It's worth considering the pros and cons of each.
First, we will talk about Russian vaccinations, since vaccination in state clinics (and maternity hospitals) is carried out using domestic means. These drugs are budgetary and supplied at the expense of the state.
Vaccine Regevak B
The largest and most famous Russian vaccine manufacturers can be called Combiotech with Binnopharm, and the vaccines themselves include:
- Bubo-M;
- Regevak;
- Combiotech;
- Bubo-Kok et al.
But if desired, you can also use foreign-made drugs. In this case, immunovaccination should be completed in private clinics.
The range of foreign drugs for the prevention of hepatitis B is wider:
- H-B-VAX II and Sci-B-Vac (described above);
- Shanvak-B, manufactured in India;
- polyvaccine Infanrix hexa. Belgian production;
- Euvax B from South Korea;
- Eberbiovak NV. Manufacturer – Cuba;
- Engerix from Belgium.
But which ones should you choose? There is no clear answer here.
Both domestic and imported vaccines form a fairly stable immunity to the hepatitis virus. However, there is still a difference. Foreign vaccines are more convenient and faster to administer and have individual containers.
In addition, they rarely cause undesirable symptoms: increased temperature of the vaccinator, decreased appetite, swelling and redness of the vaccination site.
Latest epidemics
In an area where hepatitis B is common, approximately 20% of local residents may be carriers of the virus. For the most part, this is the situation in the countries of the African continent, in Asia, in the Eastern Mediterranean, and on individual islands of the Pacific Ocean. The same situation occurs in the Caribbean.
It is noteworthy that hepatitis B infection occurs very quickly. So, if you drop just a drop of infected blood into a bucket of water, and then, after wetting the needle, inject yourself with it, infection will occur with a 100% probability.
Do I need to get tested before immunization?
All vaccination procedures require pre-tests and immunization against hepatitis B is no exception. What is required here is:
- HBsAg blood test;
- analysis for antibodies to HBsAg and HBcAg.
Your attending physician can provide more detailed information about the test procedure. The list of necessary tests may vary slightly in different clinics. However, there are a number of general rules that should be followed by those who decide to undergo immunization.
First of all, vaccinations should be scheduled in advance. The upcoming need for vaccination is announced several days before the procedure. To avoid experiencing the full severity of side effects, it is better to get vaccinated before the weekend.
Then the body will not experience additional stress and will be able to fully focus on building immunity. You should not plan an active holiday with friends after vaccination. It is also not recommended to visit crowded places again.
It is best to work with your doctor to determine an appropriate hepatitis B immunization schedule. He will tell you about all the nuances and give the most useful advice.
Instructions for use of vaccines
Like any other vaccination, the hepatitis B vaccine has its own rules for use that must be followed.
Injection site
The drug is administered intramuscularly. However, vaccination sites for adults and children differ. If the first vaccination is given in the deltoid muscle on the shoulder, then the second (up to three years of age) the injection is given in the thigh area.
The fact is that the child’s muscles in this area are already quite developed. Other sites are not suitable for injection.
The subcutaneous method is unacceptable; it not only sharply reduces the effectiveness of the vaccine, but also threatens the formation of a lump that can take a very long time to dissolve. An injection into the buttock is also prohibited. This is fraught with inflammation at the injection site and the danger of the needle getting into the sciatic nerve.
Fortunately, modern vaccines are constantly being improved and rarely cause serious side effects.
Dosage for children and adults
There is a fairly wide range of vaccines to combat hepatitis B. And each of them has its own dosage. However, their injected volumes are quite similar.
For example, the recombinant hepatitis B vaccine has the following indicators:
- single vaccination for people under 19 years of age – half a milliliter (equal to 10 mcg of HBsAg);
- for those over 19 years of age - one milliliter (that is, 20 mcg of HBsAg).
A separate category of hemodialysis patients is distinguished. They are prescribed a dosage of 2 milliliters (as much as 40 mcg of HBsAg).
Interval between vaccinations
The intervals between administered vaccines are declared by the National Vaccination Calendar. According to it, it is permissible to administer vaccines during the day to different parts of the body and with different syringes (the rule does not apply to vaccines against tuberculosis and jaundice).
And if the hepatitis B vaccine was not given along with others, then it can be carried out any day after the previous vaccination. This rule is followed in maternity hospitals.
The vaccine administration interval here is only a few days. For other vaccinations designed for separate use, the break is usually at least a month.
What to do if deadlines are missed?
Naturally, it is not recommended to violate the vaccination schedule. But anything can happen in life, and there is no need to refuse to continue vaccination. The introduction of the second dose of the vaccine can be delayed by a maximum of one month, and the third by twelve months. If the vaccine was administered within these time intervals, the process of acquiring immunity will proceed without complications.
If these time intervals have been violated, it is recommended that the next doses of the drug be administered according to the vaccination calendar (the interval between vaccinations must be at least a month).
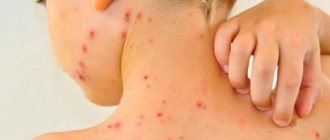
Side effects and complications
In most cases, adults tolerate the hepatitis B vaccine well.
Some people, due to the characteristics of their body, may experience various complications:
- pain at the injection site, in the joints, muscle areas and in the abdomen;
- nausea, general weakness;
- skin itching, urticaria. Possible swelling;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- fainting, feeling of lack of air and many others.
But if such symptoms are not very pronounced and disappear after a few hours, then there is no particular cause for concern. However, consulting a doctor and warning the medical staff conducting vaccinations will not hurt.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to yeast and other components of the vaccine;
- Severe reaction (temperature above 40 C, swelling, hyperemia >8 cm in diameter at the injection site) or complication (exacerbation of chronic diseases) to the previous administration of the drug. Routine vaccination is postponed until the end of acute manifestations of the disease or exacerbation of chronic diseases. For mild ARVI, acute intestinal and other diseases, vaccinations can be carried out after the temperature has normalized.
How to issue a refusal?
If a decision is made not to be vaccinated, a refusal should be issued. How to do it? If an adult vaccinator receives an invitation from the clinic, you can simply ignore it and not show up at the appointed time. There will be no punishment for this.
You can write a refusal in the maternity hospital. It’s not too late to do this both before and after childbirth. The refusal is written on the form that the nurse will give you; the form is free to fill out.
Then the paper is glued to the card. Do not forget to notify the neonatologist at the maternity hospital about your decision. At school or kindergarten, the refusal is written personally to the director and the nurse must be notified.
Fill out the vaccination waiver in 2 copies. One will go to be signed by the head of the relevant institution, where it remains, and the second will be in your hands. Make sure that the refusal indicates the incoming number and details of the person registering your document.
CLAIMS
All cases of increased reactogenicity or development of post-vaccination complications should be reported to:
- Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare;
- The Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia and the Federal State Institution GISC named after. L.A. Tarasevich Rospotrebnadzor with subsequent sending of medical documentation: 121002, Moscow, lane. Sivtsev - Vrazhek, 41, tel., fax +7;
- Manufacturer's address: JSC NPK "Combiotech", 117997, Moscow, Miklukho-Maklaya str., 16/10, building 71, tel./fax +7 (495) 330-74-29.
Price and reviews
In our country (according to the law), children and adults (up to 55 years old) are provided with a free hepatitis vaccination course. Immunization is carried out in the clinic at the place of residence.
Engerix B vaccine
If a person does not qualify for the free procedure, then vaccination can be done in private clinics. The price of the entire course will be 1000-1300 rubles.
If you decide to buy the drug yourself, then the prices for the vaccine (for 1 ampoule) are as follows:
- Biovac – 155-220 rubles;
- Regevak – 150-270 rubles;
- Engerix – 200-320 rub.
Reviews about vaccination against hepatitis B:
- Oksana, 33 years old . I am a doctor myself, and vaccination is required for us on schedule. I and all my relatives are vaccinated, because every day I see the terrible consequences people have if they become infected. I think it’s better to survive a reaction after vaccination than to suffer from complications;
- Valery, 41 years old . I sincerely don’t understand why people are afraid to get vaccinated against this terrible infection, because you can catch it anywhere. In addition, today everyone can choose a drug for themselves, and the price is not high. I got vaccinated as an adult. The cause was the death of a friend from liver cirrhosis;
- Christina, 28 years old . As for hepatitis B, we vaccinated our son back in the maternity hospital. I knew in advance that they would ask my consent on this matter, so I studied this topic in advance. And nowhere have I found information that after this vaccine anyone felt ill or had serious consequences. But it provides a guarantee against hepatitis. Therefore, I decided - let’s get vaccinated, besides, you can get infected anywhere, and you won’t even know, because the disease can be asymptomatic.
Symptoms
The usual incubation period for hepatitis B is 75 days. Sometimes it increases to 180 days. The virus is detected a month or two after infection.
An acute infection usually does not show itself as anything special. Usually the person does not suffer from any symptoms. But some people report yellowing of the skin, dark urine, fatigue, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. A certain number of infected people have acute liver failure, sometimes leading to death. For some, hepatitis B leads to chronic liver infection. As a result, the body begins to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.