Epidemiology
Epidemiological data on dolichosigma are as follows:
- in 80% of cases of dolichosigma in children are caused by cessation of neural migration in the intestine and disruption of innervation;
- an asymptomatic disease that does not bother patients is diagnosed in 15% of people;
- damage to the entire length of the intestine occurs in 1% of victims;
- among newborns, only 1 in 5000 children have this pathology;
- the disease is 4 times more common in boys;
- family history of the disease is observed in 7% of cases;
- In 3 - 5% of victims, the pathology is associated with developmental defects, for example, Down syndrome.
Reasons for the development of dolichosigma
The exact reasons for this anomaly have not yet been identified. Sometimes congenital pathology is the result of exposure to radiation, toxins, and various chemical and physical factors during fetal development. Dolichosigma can also develop if a woman has an infectious disease during pregnancy. The correct development of the fetus can be disrupted by the use of certain medications by a pregnant woman.
Acquired dolichosigma rarely appears in children. The reasons will be the following:
- long-term constipation, processes of fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines after prolonged dysbiosis or prolonged infection, frequent food poisoning;
- disturbance of intestinal motor activity due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive consumption of meat products, carbohydrate diet;
- persistent nervous tension and stress.
Nutrition Basics
The diet for dolichosigma should be as close as possible to table No. 3 (according to Pevzner), where the diet is aimed at eliminating constipation and reducing gas formation.
In adults
The diet for dolichosigma in adults implies compliance with the following rules:
- inclusion in food of a sufficient amount of foods containing dietary fiber (fruits and vegetables, cereals);
- exclusion of foods that increase gas formation in the intestines (fried foods, whole milk, legumes);
- reducing the consumption of animal fats - they weaken the motility of the digestive tract; products containing them can be replaced with vegetable oils;
- cooking food preferably by steaming or by boiling, baking;
- exclude dishes that irritate the intestine (its inner layer) - spicy, smoked;
- eating food is recommended in unground form (meat, fish - chopped or in pieces);
- Most fruits and vegetables should be eaten raw;
- It is advisable to bring the number of meals closer to 5-6 rubles. in a day;
- meals must be consumed in small portions;
- compliance with the drinking regime - fluid consumption per day should be within one and a half to two liters.
An important aspect of the diet for dolichosigma is the equal time intervals between meals - they should average 3-4 hours. Each intake of food into the digestive system increases intestinal motility, which helps eliminate constipation.
In children
The diet for dolichosigma in children is basically no different from nutritional recommendations for adults. The child’s diet also includes foods rich in plant fiber, and the consumption of proteins and fats of animal origin is limited. An important part of treatment is the restoration of intestinal microflora (taking probiotics).
For children who are breastfed naturally, all nutritional rules must be followed by the nursing mother. The mother's consumption of recommended foods also has a beneficial effect on the child's intestinal function.
Formula-fed babies need:
- include fermented milk products in the diet (for children under one year old - adapted formulas, for older children - baby yoghurts);
- periodically feed the child pureed fruits and vegetables, give juices with pulp;
- introduce complementary foods in a timely and gradual manner.
If nutritional recommendations are ineffective for eliminating constipation, the child is prescribed milk formulas with lactulose, vegetable oils and fructo-oligosaccharides (Humana bifidus, Nutrilon Omneo).
A diet for dolichosigma in older children implies:
- eating food by steaming;
- inclusion of vegetable salads in vegetable oil in the diet;
- adequate fruit consumption;
- The basis of the drinking regime should be fortified drinks (berry fruit drinks, dried fruit compotes).
If a child develops excessive gas, food should be served in crushed form. You should also limit the amount of foods containing simple carbohydrates (sweets, pasta, jam, etc.) in your food.
The mechanism of development of the disease and its manifestations (pathogenesis)
Congenital or acquired increase in the length of the sigmoid colon underlies the pathogenesis. If there are concomitant pathologies, fibrosis of the intestinal tissue often occurs; as a result, connective tissue replaces normal intestinal tissue. Hyperemia and swelling appear. Muscle fibers grow, as a result of which the intestinal walls are abundantly saturated with tissue fluid.
All this disrupts intestinal contraction and weakens its tone. A decrease in contraction processes makes it difficult for feces to pass through the intestines, resulting in constipation. Due to the constant presence of feces in the intestine, the innervation of cells is disrupted, stagnation, pain and intoxication develop.
Symptoms
Symptoms occur as the intestines fill with feces and the body becomes intoxicated. The intensity of the disease is directly proportional to the degree of morphological and functional disorders in the intestine.
In comparison with other gastrointestinal pathologies, dolichosigma is represented by bright characteristic symptoms. Here are a few of them:
- Sick children experience constipation for many days. As it progresses, the desire to defecate is suppressed, and stool masses become denser. Dense feces often cause damage to the rectal mucosa, so blood appears during bowel movements. In severe cases, it becomes impossible to have a bowel movement without an enema;
- pain with dolichosigma is localized in the navel area and is spasmodic in nature. Painful sensations occur on the left side and disappear immediately after defecation;
- this pathology also causes severe flatulence, persistent bloating and rumbling;
- Constant constipation leads to intoxication of the body, so the child experiences weakness and nausea, appetite disappears, and the skin becomes gray and a rash appears on it. Urinary incontinence may occur.
Dolichosigma in a child
Dolichosigma is a pathology associated with abnormal lengthening of the intestine, leading to the development of problems with bowel movements. Symptoms include bloating, pain in the abdomen, and a tendency to constipation. Timely therapy helps restore the function of the digestive tract and avoid the development of complications. Below we will talk about all this in more detail.
Dolichosigma in children can be congenital or acquired. Doctors are not always able to determine the nature of this condition. The reasons for the appearance of additional two or three loops in the sigmoid colon may be:
- heredity;
- influence during intrauterine development of infections, chemicals taken by the mother;
- lack of movement;
- passion for meat dishes and carbohydrates;
- stressful situations.
Fermentation processes in the intestines lead to the development of a pathological condition in adults.
Dolichosigma in a child is usually congenital and is often diagnosed at the age of 3-4 years. During a study of children suffering from constipation, approximately 30% were found to have this pathology.
Normal indicators
Normally, the length of the sigmoid colon in newborns is 20 cm. In children aged 1 year, this figure is 30 cm, in adolescence - 39 cm.
A deviation from the norm is considered to be an increase in the length of the examined section of the intestine to 48 cm or higher. However, not all experts consider this condition to be a defect, and if you feel normal, treatment may not be prescribed.
Therapy is carried out if there are signs of deterioration in the child’s health and worsening symptoms.
Classification
The classification of the sigmoid colon is based on its location in the peritoneum and size. She may be:
- single-loop;
- two-loop;
- multi-loop.
Dolichosigma with two or more loops is considered pathological. At the same time, it should be excessively mobile and easily move in the abdominal cavity.
There are 3 stages of disease development:
- Compensation. At this stage, the patient experiences constipation and discomfort in the abdominal area for two to three days. Defecation occurs after introducing certain foods into the diet, eliminating heavy foods and taking a mild laxative. The child feels fine.
- Subcompensation. Bowel movements occur irregularly. There are complaints of pain in the abdominal cavity. The use of special drugs does not always give the desired effect, so parents give the child a cleansing enema.
- Decompensation. At this stage, multiple symptoms of the disease develop. Manifestations include pain, refusal to eat, nausea, and skin rash. Upon examination, an increase in the thickness of the rectum is determined, which is caused by gases. In some cases, there are signs of obstruction. A siphon enema is used for emptying.
Symptoms
Dolichosigma of the intestine in a child is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Long-term constipation. They occur in six-month-old children during the introduction of complementary foods. The change in stool is due to an increase in the volume of stool and its consistency. Problems with bowel movements can appear as early as three years of age. The absence of an act of emptying is observed for 3 days, followed by an extension of this period. This condition leads to aggravation of morphological symptoms.
- Change in stool consistency. It becomes dense, large, often takes the shape of a fir cone and has an unpleasant odor. An increase in the size of the masses leads to injury to the rectal mucosa and bleeding.
- Pain syndrome. The child complains of unpleasant sensations in the navel area and the left side of the abdominal cavity. Bloating occurs when overeating or during exercise and disappears after defecation. The cause of discomfort is intestinal spasms and the development of an inflammatory process in its walls.
- Dysfunction of the digestive tract. During the examination, dyskinesia, gastritis, colitis and disturbances of intestinal microflora are detected.
- Intoxication. As a result of prolonged constipation, a large amount of toxins begins to enter the blood. This phenomenon causes the development of anemia and irritable bowel syndrome.
Diagnostics
During an external examination of a child with megacolon, the doctor discovers a change in skin tone and tightness in the peritoneal area. Rectal palpation reveals an emptiness in the rectum. The specialist collects information about nutrition, what symptoms and treatment were previously carried out.
Diagnostics includes a series of studies. The specialist issues a referral for laboratory tests. Megadolichosigma requires differentiation from colitis, peptic ulcer disease, enterobiasis, and appendicitis. Hardware techniques are used without fail.
Laboratory research
Blood tests require some preparation on the part of the patient.
48 hours before collection, it is recommended to limit the consumption of fatty foods, smoked and spicy foods. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach.
After sleep, the child can drink some boiled water. Lemonade and juices should not be given to children before visiting the laboratory. The feces are collected in a clean container early in the morning.
Blood analysis
General and biochemical blood tests may reveal minor deviations from normal levels in the presence of the initial stage of the disease. If there are no symptoms and the child is in good health, the indicators are often unchanged.
Stool analysis
Examination of stool helps to identify blood, worm eggs, and fats. Thanks to the analysis, it is possible to confirm or refute the presence of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, enzyme deficiency, and parasitic invasion.
Hardware Research
Before conducting an instrumental examination, doctors recommend doing an enema. On the day of visiting a medical facility, it is necessary for the child to carry out hygienic measures: thoroughly rinse the anal area with warm soapy water.
The choice of hardware technique depends on the degree of symptoms. X-rays of the intestine are not performed in childhood.
Ultrasound
Examination of the digestive tract using ultrasound is safe and is used in the diagnosis of children from birth. Thanks to this technique, it is possible to determine the degree of elongation and the number of loops.
Colonoscopy
The colonoscopy procedure allows the specialist to detect changes in the mucous membranes of the sigmoid colon and determine its functional abilities. A small camera is inserted into the anus. All information is displayed on the monitor.
Medication methods
Spastic pain syndrome can be treated with the help of drugs “Drotaverine”, “No-Shpa”, which have an antispasmodic effect. If peristalsis is weak, the child is prescribed Proserin.
Before using medications, parents should carefully study the instructions for use. It is important to fully comply with the dosages prescribed by your doctor. If side effects occur, you must stop taking the medication and consult a specialist.
Diet
Diet is key if a child has dolichosigma. The basis of your diet should be foods with a lot of fiber.
It is important for parents to ensure that their child drinks at least a liter of liquid. Water deficiency increases the likelihood of developing constipation.
Authorized Products
With dolichosigma, the children's diet should contain:
- vegetables;
- greenery;
- fruits;
- whole grain baked goods.
The daily menu must include:
- vegetable oil;
- kefir;
- yogurt;
- cream;
- bran.
Prohibited Products
If you are prone to constipation, pain and inflammation, it is not recommended to use:
- carbonated drinks;
- baking;
- fast food;
- smoked products;
- marinades.
Physiotherapy
If a child has pain, the doctor prescribes an abdominal massage. It is carried out by a specialist in a medical facility or at home. If you are prone to constipation, a course of electrophoresis and colon hydrotherapy is carried out.
If possible, doctors recommend undergoing a course of treatment in sanatoriums in the cities of Zheleznovodsk and Truskavets. In advance, a special card is issued for the child, in which all the data on the studies performed and a list of identified diseases are recorded.
The presence of an elongated sigmoid colon in a child is not always a pathology and requires therapeutic measures.
Treatment is prescribed when symptoms of dysfunction of the lower digestive tract are detected. Following the diet and all doctor’s recommendations helps prevent the development of complications.
Source: https://easymed-nn.ru/bolezni/narusheniya/dolihosigma-u-rebenka.html
Features of dolichosigma in young children
A child with dolichosigma becomes lethargic, capricious, cries all the time and refuses to eat. The main symptom is constipation with gradually increasing frequency. This is usually due to the transition to mixed feeding or the introduction of complementary foods, which entails a change in the consistency of stool and an increase in its quantity.
Most affected children have functional disorders of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract: diverticular disease, colitis, dysbacteriosis, pancreatitis, biliary dyskinesia, chronic gastroduodenitis, etc.
Stages
There are three stages of abnormal elongation of the sigmoid colon.
Dolichosigma
Dolichosigma is an abnormal increase in the length of the sigmoid colon and its mesentery, leading to impaired motility and bowel movement. Dolichosigma is manifested by chronic constipation, flatulence, and recurrent abdominal pain.
In the diagnosis of dolichosigma, the main role is played by irrigography and radiography of the passage of barium through the large intestine; auxiliary - rectosigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, etc. For dolichosigma, diet, massage, exercise therapy, and physiotherapy are prescribed; for prolonged constipation - laxatives and enemas.
In case of chronic intestinal obstruction, dolichosigmoid resection is performed.
Dolichosigma is an anomaly in the structure of the sigmoid colon, consisting in its elongation without changing the diameter of the lumen and wall thickness.
The elongated sigmoid colon often has increased mobility, which is accompanied by impaired formation and passage of feces.
The frequency of dolichosigma in the population reaches 25%, however, it is assumed that due to the blurred clinical manifestations and the complexity of diagnosis, the pathology is not detected in all cases. In pediatrics, dolichosigma is found in 40% of children suffering from constipation.
Normally, in an adult, the length of the sigmoid colon loop is on average 24-46 cm: such a colon is regarded as normosigma. When the length of the sigmoid colon is less than 24 cm, they speak of brachysigma, and when the length is more than 46 cm, they speak of dolichosigma. The combination of elongation of the sigmoid colon with its expansion and thickening of the walls is designated as megadolichosigma.
Dolichosigma
Dolichosigma can be a congenital or acquired condition in which the sigmoid colon has 2-3 additional loops. The etiological cause of dolichosigma is unclear.
It is assumed that congenital disorder of growth and fixation of the sigmoid colon may be associated with heredity; exposure to unfavorable environmental, physical, and chemical factors on the fetus; infectious diseases of the expectant mother, taking certain medications by the pregnant woman.
Acquired dolichosigma occurs as a result of digestive disorders associated with the processes of prolonged fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines.
This usually affects people over 45-50 years of age who lead a sedentary lifestyle, are engaged in sedentary work, abuse meat and carbohydrates, and often experience stress.
At the same time, some authors believe that dolichosigma is always a congenital anomaly, and digestive problems only cause the manifestation of clinical manifestations given the existing anatomical prerequisites.
To date, proctology has not resolved the question of whether dolichosigma should be considered a malformation of the colon or an individual variant of the norm. On the one hand, dolichosigma occurs in 15% of completely healthy children, which gives grounds to consider it a variant of the norm.
On the other hand, elongation of the sigmoid colon is often accompanied by organic and functional disorders of the distal colon, which makes one think about a developmental anomaly. It is likely that dolichosigma is a kind of background for the development of clinical pathology.
Morphological examination of the intestinal walls in dolichosigma reveals structural disorders caused by intestinal stasis and chronic inflammation: sclerotic changes in the mesentery, hypertrophy of muscle fibers, myofibrosis, damage to the intramural nerve ganglia, degeneration of the mucous membrane. Thus, in the intestinal wall with dolichosigma, secondary degenerative changes take place, leading to disruption of its motor function.
Taking into account the position of the intestine in the abdominal cavity and its size, the S-shaped, single-loop, double-loop and multi-loop sigmoid colon are distinguished. Dolichosigma is usually considered an elongated two-loop or multi-loop sigmoid colon, which has pathological mobility, moves freely in the abdominal cavity and retains additional loops after bowel movement.
Clinical variants of dolichosigma can be variable. During the course of the disease, three forms are distinguished, which are also considered as successive stages of dolichosigma:
- The compensation stage is characterized by periodic constipation lasting up to 3 days and abdominal pain. Bowel movement is achieved by following a special diet and taking mild laxatives. The child's general health remains normal.
- The subcompensation stage occurs with constant constipation, flatulence and abdominal pain. Taking laxatives to regulate bowel movements is ineffective, which forces parents to resort to regular cleansing enemas.
- The decompensation stage is the most severe clinical form of dolichosigma. Constipation lasts 7 or more days, abdominal pain is a constant concern. The colon is swollen and enlarged due to the accumulation of gases and feces. Intoxication is pronounced: lack of appetite, nausea, pustular rashes on the skin. Symptoms of intestinal obstruction may occur. Only siphon enemas are effective for bowel movements.
Clinical manifestations of dolichosigma are caused by morpho-functional changes in the colon, as well as chronic fecal intoxication. The timing of the development of dolichosigma symptoms depends on the degree of elongation of the sigmoid colon, changes in its tone and motility, and the compensatory capabilities of the child’s body.
The leading manifestation of dolichosigma is persistent constipation, which in most cases develops in children aged 6 months - 1 year. This is usually associated with the introduction of complementary foods or the transfer of the child to mixed (artificial) feeding, which entails an increase in the quantity and change in the consistency of stool.
In 30-40% of children, constipation appears at the age of 3-6 years. Initially, constipation is episodic, there is no stool for 2-3 days; subsequently, the frequency and duration of constipation increases. Long-term constipation is accompanied by intestinal dilatation, worsening morphological changes, and a decrease in the reflex to defecate.
Some children with dolichosigma experience encopresis.
The feces in patients with dolichosigma are dense, large in diameter, and sometimes resemble a “fir cone”; often has a foul odor. Damage to the rectal mucosa during the passage of solid feces can cause the appearance of scarlet blood in the stool.
Characteristic clinical signs of dolichosigma are recurrent pain in the left iliac or periumbilical region, flatulence.
These phenomena intensify after a heavy meal or physical activity and disappear or decrease after bowel movement.
Pain syndrome with dolichosigma is associated with a reflex spasm of the intestine, cicatricial changes in the sigmoid mesentery, and an inflammatory process in the intestinal wall.
In most children with dolichosigma, dysfunctions of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract are detected: chronic gastroduodenitis, biliary dyskinesia, pancreatitis, dysbacteriosis, colitis, diverticular disease, etc. Frequent companions of dolichosigma in adults are hemorrhoids and varicose veins.
Due to a long absence of bowel movements, a child with dolichosigmoid may form fecal stones, develop fecal autointoxication, anemia, and irritable bowel syndrome.
One of the serious complications of dolichosigma is intestinal obstruction due to nodulation, volvulus, kinks, and intussusception of the sigmoid colon.
In these cases, a picture of an acute abdomen develops.
Examination of a child suffering from dolichosigma reveals underweight, retarded physical development, and pale skin. Palpation of the abdominal cavity reveals intestinal loops filled with feces. A digital rectal examination reveals an empty rectum, even if the child has not had stool for a long time.
The decisive instrumental method in the diagnosis of dolichosigma is irrigography, during which the elongation of the sigmoid colon is revealed, the presence of additional loops in the form of a “figure eight”, “double-barrel”, “knot”, “snail”, etc. MSCT of the colon allows you to study its location in detail , shape, contours, length, lumen width, haustration, presence of additional loops.
To assess the motor-evacuation function of the colon in a patient with dolichosigma, barium passage radiography, electromyography, and sphincterometry are performed.
Endoscopy in children (rectosigmoscopy, colonoscopy), ultrasonography of the large intestine, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, radiography of the abdominal cavity are of auxiliary importance in the diagnosis of dolichosigma.
Among laboratory methods, a coprogram is used; stool analysis for dysbiosis, occult blood, helminth eggs; clinical and biochemical blood tests.
Dolichosigma in children should be differentiated from ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, enterobiasis, chronic appendicitis, and Hirschsprung's disease. For this purpose, the child should be consulted by a pediatric gastroenterologist, pediatric coloproctologist, and pediatric surgeon.
At any stage of dolichosigma, treatment begins with complex conservative therapy.
The leading role in therapeutic measures is given to the normalization of the digestive tract through diet - fractional meals, consumption of foods rich in fiber (vegetables, whole grain bread, bran, fruits, berries, herbs), fermented milk products, vegetable oils, etc. In some cases, laxatives are prescribed and microenemas, however, with dolichosigma it is extremely important to form a reflex to spontaneous defecation.
For spastic pain, antispasmodics (drotaverine, platyphylline) are prescribed; for intestinal hypotension - prozerin, massage of the anterior abdominal wall, exercise therapy, electrical stimulation of the colon, colon hydrotherapy, acupuncture. Patients with dolichosigma benefit from courses of vitamin therapy (B6, B12, C, E), bacterial preparations (probiotics and prebiotics), and treatment in sanatoriums in Zheleznovodsk and Truskavets.
Indications for surgical treatment of dolichosigma in children are extremely rare.
Surgical treatment is indicated for intestinal obstruction, failure of conservative therapy, persistent constipation, progressive fecal intoxication, the presence of unstraightened loops and kinks of the intestine.
With dolichosigma, resection of the sigmoid colon is performed. In the case of predominant damage to the distal sigmoid colon, proctosigmoidectomy is the operation of choice.
Usually, if all medical recommendations are followed, it is possible to achieve regular independent bowel movements and an acceptable quality of life. As the child grows, many disorders can be compensated; in some cases, the problem of dolichosigma worries patients even in adulthood.
In the latter case, lifelong adherence to the diet and quality of nutrition is necessary, to exclude the development of nutritional, psychogenic and other types of constipation.
Children with dolichosigmoid need observation by a pediatrician, pediatric gastroenterologist, periodic courses of conservative therapy, and examination of the condition of the large intestine.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/children/dolichosigma
Diagnostics
Correct diagnosis is important to determine effective treatment.
Numerous research methods are used to diagnose the disease.
Taking a life history and physical examination of the patient
During the interview, the doctor must obtain the following information about the patient:
- diet and diet;
- degree of exposure to stress;
- intensity of neuropsychic stress;
- information about the immunization performed;
- data on previous illnesses and food poisoning;
- information about concomitant diseases and allergic reactions;
- time of appearance of the first symptoms and the nature of their manifestation;
- subjective feelings and complaints at the moment;
- factors that alleviate or aggravate the condition;
- information about the treatment undertaken and medications taken.
The specialist then examines the patient. The abdomen, intestines and area of the sigmoid colon are carefully palpated. Percussion tapping is carried out on the areas where the compaction is found. Using the method of auscultation, sounds observed in the intestine are heard, this will allow one to determine the approximate direction of the dynamic processes occurring in the intestine.
The information obtained will allow you to make an approximate diagnosis. To confirm it, additional instrumental and laboratory studies should be carried out.
Laboratory research
A number of tests must be performed to make a diagnosis. In general blood and urine tests, you can see signs demonstrating the stage and nature of the pathology: the presence of inflammation, infection, intoxication. Biochemical analysis will show the characteristics of metabolism and the main processes occurring in the body. A stool occult blood test will reveal internal diseases. The presence of blood hidden in feces may indicate the presence of cancer at an early stage.
The coprogram provides information about the quality of food digestion. Examination of feces for helminth eggs is also mandatory. Analysis for dysbacteriosis is carried out if necessary.
Use of instrumental research methods
The results of instrumental methods will allow us to make a final diagnosis.
Only irrigography can detect an increase in the length of the sigma. Before starting the procedure, a barium enema is administered.
Ultrasound can be used to examine intestines clogged with dense feces. It is impossible to perform a CT scan on young children because they cannot remain motionless for a long time.
Using a thin pediatric probe, a colonoscopy is performed under short-term anesthesia, if necessary for differential diagnosis. This procedure makes it possible to examine the colon and assess the degree of damage to the mucosa.
Dolichosigma of the intestines in a child: what is it, what are the symptoms, how to treat?
Young children often have a problem when going to the toilet is a real torment.
This fact worries moms and dads greatly, since the reason for stool retention does not always lie in a temporary difficulty in passing feces.
If constipation is persistent and the child feels pain during bowel movements, the presence of dolichosigma can be suspected, and this requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
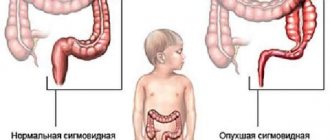
What it is
Dolichosigma is an abnormal elongation of the large intestine, its sigmoid part. This anomaly causes disruption of motility and natural cleansing of the colon.
The increased length of the intestine has great mobility, which leads to disruption of the formation and movement of feces.
Lengthening, the intestine with the pathology under consideration has the same circumference and the same wall thickness.
This pathology is quite common, but due to the complexity of its diagnosis, it is not always detected. Dolichosigma is found in 40% of children who suffer from constipation.
Types of pathology
Depending on the factors that caused the pathology, there are 2 forms of dolichosigma:
- congenital – formed during the mother’s pregnancy, when the baby’s intestines develop with abnormalities;
- acquired - appears when several new loops appear in the intestines, which is usually caused by poor nutrition, which disrupts the process of digestion of food, which begins to rot and ferment in the intestines.
Pathology has 3 stages:
- Compensated – expressed by periodic constipation with short breaks of 3–4 days. The longest duration of stool retention is 5 days. The child’s health is normal, except for discomfort in the abdominal area.
- Subcompensated – represented by more frequent constipation with a long duration. At the same time, the abdomen hurts greatly, bloating is observed, and gases are formed. Laxatives do not have the desired effect.
- Decompensated – occurs with incessant abdominal pain. Due to retention of feces in the intestines, the abdomen swells and increases in size. Characteristic is the gradual development of intoxication of the body. The child feels unwell and refuses to eat. Nausea, vomiting and even ulcers on the skin may occur.
Causes of pathology
There are a number of reasons:
- heredity at the genetic level;
- pregnancy with complications (infectious diseases, etc.);
- fetal development in poor environmental conditions;
- the use of dangerous drugs while carrying a child;
- exposure to radiation;
- strong ultraviolet irradiation;
- poor child nutrition, consumption of foods containing preservatives, pesticides and other harmful additives, as well as fatty foods that are poorly digested;
- lack of physical activity.
Symptoms in children
The main symptom of this disease is constipation. More often they appear in babies under one year of age due to an increase in the volume and density of feces due to the introduction of mixed nutrition. In 3% of children, this symptom appears later - from 3 to 6 years. The duration and severity of constipation increases over time.
Other symptoms of long bowel:
- hard feces of large diameter;
- presence of blood in the stool;
- abdominal pain, especially on the left side and in the navel area;
- flatulence;
- associated ailments of the digestive system such as gastritis, colitis and pancreatitis;
- presence of bad breath;
- cracks in the corners of the lips;
- brittle nails.
Laboratory methods
Laboratory methods for determining diagnosis include various types of tests. The child will need to donate blood and stool.
Tests to diagnose an enlarged sigmoid colon:
- UAC;
- blood chemistry;
- coprogram (analysis of the physical and chemical properties of feces, as well as various components and inclusions of various origins);
- stool occult blood test;
- fecal analysis for helminth eggs.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental diagnostics are as follows:
- ultrasound examination;
- X-ray of the intestines;
- irrigography (allows you to determine the condition of the cells and walls of the intestine, determine its size, position and shape);
- colonoscopy (mainly used to diagnose the disease in adults);
- sigmoidoscopy (examination using a tubular device - a sigmoidoscope, which is inserted rectally).
Treatment methods
Treatment for dolichasigma prescribed by a doctor can be conservative (medication) or more radical with surgery. The type of treatment is determined by the clinical manifestations, as well as the stage of development of the disease and the characteristics of the child’s body. Folk remedies can also help, but they should only be used on the recommendation of a specialist.
Conservative treatment
Treatment with medications is prescribed depending on the stage of the disease. Dolichosigma is treated comprehensively; in the presence of concomitant diseases, additional therapy is also carried out.
For abdominal pain, medications are used:
- "No-shpa";
- "Platifillin";
- "Prozerin";
- "Dibazol".
Medicines can be used in the form of tablets or injections. The duration of treatment is 14 - 17 days, then a break is taken for 1.5 - 2 months and, if necessary, they are resumed. In addition, the child takes B vitamins, medications that help populate the intestines with beneficial bacteria, and undergoes physical therapy with abdominal massage.
Surgery
If there is no positive result from drug treatment, surgical intervention is resorted to. The operation involves resection of the dolichosigma and its removal.
After surgery and a rehabilitation period, problems such as constipation and increased gas formation disappear. However, for this, the little patient must follow all the rules and recommendations of the attending physician.
Folk remedies
To treat enlarged sigmoid colon, the following folk remedies are used:
- Mineral water to saturate the body with the trace elements and minerals it needs. With its help, digestion is improved.
- Fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk) help improve stomach function. You can drink them in the morning and before bed.
- Beet salad with vegetable oil and prunes. You can use boiled and fresh beets. These products have a laxative effect.
- A mixture of honey, prunes and dried apricots is a remedy that helps to improve bowel movements. In combination with dairy products, the effect will be felt immediately.
Diet is very important in the treatment of the pathology in question, when coarse, fatty and spicy foods, as well as sweets, white bread and pastries are excluded from the patient’s diet. Active consumption of fermented milk drinks, fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meat and fish is recommended.
Preventive measures
To prevent the formation of long intestines in children, the following rules must be followed:
- compliance with healthy eating standards;
- sufficient physical activity;
- drinking enough water;
- use of vitamins;
- children's abdominal massage.
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Prevention of dolichosigma is of paramount importance.
Source: https://RosMedPlus.ru/bolezni/gastro/dolihosigma-kishechnika-u-rebenka-lechenie.html
Treatment
Treatment of dolichosigma is a very complex process and includes two main directions: therapeutic (conservative) treatment and surgery.
First, conservative methods are used (medicines, massage, diet, physical therapy, etc.). Surgery is performed solely as a last resort.
Traditional medicine methods are often added to traditional means of therapy, but they complement and do not cancel the above methods of treatment.
Conservative treatment
Diet
To achieve effectiveness from treatment, the digestion process should be carried out. There are certain rules for choosing products and their consumption:
- The child should drink up to 3 liters of fluid per day. Kvass and carbonated drinks should be avoided, as such liquids cause constipation. They help strengthen and compact stool in the intestines. Water with lemon has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Lemon oxidizes the environment, as a result of which feces liquefy and easily exit the body.
- Cereals: wheat, rice, buckwheat, semolina - should be removed from the diet.
- The consumption of flour products (pasta, confectionery, baked goods) has a negative effect on the healing process. Therefore, they should be removed from the diet.
- Meat and animal fats are contraindicated.
- Instead of forbidden strong tea and coffee, it is recommended to give your child at least 200 ml of low-fat kefir daily.
- It is allowed to give the child chocolate. But its consumption is not recommended to be combined with other foods, and it is also forbidden to eat it less than an hour before or after a meal. If you eat chocolate at the same time as other foods, constipation will occur, which will further worsen the child’s condition.
- You should not give your child solid food; all hard foods must be thoroughly steamed.
- The child should be fed in small portions 4 to 5 times a day.
Drug treatment
When the diet does not produce results, it is necessary to give the child pharmaceutical drugs. Before taking them, you should first consult with a specialist, as complications may arise, and an overdose will lead to the development of side effects: intestinal irritation and increased intestinal motility.
Laxatives
These drugs give results at the initial stage of pathology development. They are effective at the early stage of dolichosigma development. The appointment is carried out in strict accordance with medical indications and the age of the child.
The glycerin-based drug is available in the form of suppositories for rectal administration. It has a beneficial effect on intestinal motility and softens fecal matter. Can be used from birth. The best time to use is in the morning.
The drug in the form of rectal suppositories is allowed to be administered to children from two years of age. The medicine has an irritating effect on the intestinal walls, thereby normalizing its motility.
Allowed for children over 4 years old. Produced in the form of tablets and drops. The laxative effect of the drug is based on several mechanisms of action; as a result, the time interval between bowel movements decreases, the stool softens and leaves the body without difficulty.
Probiotics
An imbalance in flora often accompanies constipation. The quantitative and species composition of microflora changes. This has a negative effect on the condition, possibly worsening constipation, which leads to even greater inflammation. An imbalance leads to the growth of pathogenic flora. The free space in the intestines is occupied by a fungus, resulting in the development of candidiasis. Inflammatory and infectious processes move to other organs. Often intestinal dysbiosis is accompanied by an imbalance of the microflora of the genitourinary and respiratory systems. Long-term disruption reduces immunity, and the development of autoimmune pathologies is possible.
To normalize microbiocenosis, it is necessary to take probiotics. The appointment is carried out in strict accordance with the regimen prescribed by the doctor. Treatment should be completed only after consultation with specialists. Recommended products: bifidum, lactobacterin, yoghurt with bacterial starters.
How does intestinal dolichosigma manifest in a child?
The digestive system of a small child, due to its immaturity, may experience certain disruptions in its functioning. This is manifested by various kinds of problems, in particular, bowel dysfunction (constipation).
Constipation in young children is a fairly common ; they occur even with minor changes in diet (replacing formula milk, changing the diet of a nursing mother).
If constipation occurs on a regular basis, this can lead to the development of pathological conditions such as intestinal dolichosigma.
This phenomenon occurs in approximately 40% of young children . We will talk about the symptoms and treatment of intestinal dolichosigma in a child in the article.
Concept and characteristics
Dolichosigma of the intestine is a change in the length of the sigmoid section of the organ , while the thickness of its walls and the size of the lumen remain unchanged.
Depending on the clinical manifestations, this phenomenon is not always considered a pathology.
If the child does not experience pain or any discomfort, the lengthening of the sigmoid intestine can be considered simply a feature of it . If the baby feels pain and malaise, we are talking about a pathological phenomenon.
With lengthening of the sigmoid intestine, the mobility of the organ increases, which leads to impaired intestinal motility and causes certain problems with the movement of feces. One of the main signs of the disease develops - constipation .
How does Hirschsprung's disease manifest in children? Find out about this from our article.
Classification of pathology
Depending on why the disease occurred, it is customary to distinguish 2 forms: congenital and acquired. Congenital dolichosigma occurs during the prenatal period of fetal development, when abnormalities in the formation of the child’s intestines occur.
The acquired form appears when several new loops form in the intestine. This is due, in most cases, to improper nutrition of the baby, a disruption of the digestive process, when rotting and fermentation of food occurs in the intestines.
There is an opinion that there is no acquired form of pathology, the disease manifests itself in all children from birth, but occurs in a latent form and does not manifest itself in any way.
Poor nutrition of a child leads to the development of pathology and the appearance of symptoms. However, this statement has not been proven.
There are also several stages of development of the disease.
| Stage | Characteristics |
| Compensated | Constipation in a child occurs periodically, with intervals of several days. The maximum duration of constipation is 4-5 days. The patient feels discomfort in the abdominal area, but otherwise his health remains normal. To eliminate periodic constipation, it is necessary to use enemas and take laxatives. |
| Subcompensated | Constipation at this stage occurs more often and lasts longer. The child feels severe pain, bloating and increased gas formation appear. Taking laxatives does not give the desired effect. |
| Decompensated | The painful sensations are constant. Feces are retained in the intestines, causing them to swell and increase in size. Intoxication of the body gradually develops. Characteristic symptoms appear, such as the appearance of ulcers on the skin, significant malaise, lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting. |
Causes
The main reason contributing to the appearance and development of the pathology has not been identified to date.
However, a number of negative factors have been identified that negatively affect the condition of the intestines and can lead to the occurrence of dolichosigma.
These factors include:
- Diseases of various natures suffered by a woman during the period of bearing a child.
- Use of certain medications during pregnancy.
- Hereditary predisposition, when one or both parents had problems with the digestive system.
- Poor quality child nutrition, consumption of foods containing preservatives, pesticides, and other harmful additives.
- Eating fatty foods that are difficult to digest.
- Lack of physical activity.
How to treat biliary dyskinesia in children? Read about it here.
Symptoms and manifestations
A child suffering from intestinal dolichosigma experiences the following manifestations of the disease:
- Painful sensations in the abdomen , and the child cannot determine exactly where it hurts; the pain is felt throughout the abdomen and has no clear localization. Painful sensations become more intense with prolonged constipation.
- The main symptom of the disease is constipation , the inability to have normal bowel movements. The duration of constipation may vary, depending on the stage of development of the disease. So, if in the initial stages the duration of constipation was only a few days, as the pathology progresses it increases. In severe cases, the child cannot have a bowel movement for a month.
- Signs of intoxication of the body (rashes, nausea, vomiting). These symptoms occur due to the accumulation of feces and gases in the intestines, which are toxic to the body. The inability to remove them leads to the development of poisoning.
- Bloating, rumbling.
- Increased gas formation .
- Lack of appetite , general malaise.
Diagnostic methods
Due to the fact that the disease does not always manifest itself with pronounced symptoms , special diagnostic methods become important to accurately determine the presence of pathology.
| Laboratory methods | Instrumental diagnostics |
|
|
You will find recommendations for treating diarrhea in a child on our website.
Treatment
Depending on the clinical manifestations, the stage of development of the pathology, and the characteristics of the little patient’s body, conservative or radical treatment of dolichosigma is prescribed.
Conservative
Non-surgical treatment methods may vary.
First of all, dietary correction is indicated.
There are basic rules regarding eating and choosing appropriate foods:
- It is important to ensure that the child consumes a sufficient amount of fluid (at least 2-3 liters per day). In this case, it is necessary to exclude carbonated drinks, since their consumption only aggravates the problem. Allowed drinks include lightly sweetened water with lemon, weak green tea, and regular drinking water.
- The diet should be fractional , that is, it is recommended to give the baby small portions. Breaks between feedings are no more than 3 hours.
- It is best to give preference to soft foods that are easy to digest. Solid foods are best crushed (for example, in the form of purees).
There are foods that should not be given to a child suffering from dolichosigma. These products include:
- fatty meat and animal fats;
- cereals and cereal porridges (especially rice and semolina);
- baked goods, flour and pasta;
- sweets.
But the consumption of fruits, vegetables, lean fish, dairy and fermented milk products, on the contrary, is encouraged.
Non-surgical therapy
To achieve the fastest therapeutic effect , in addition to diet, the child is prescribed other treatment methods.
| Drug therapy | Physiotherapy |
It is necessary to take the following groups of drugs:
| The most common physiotherapy procedures include:
|
Indications for surgery
In some cases, the child is prescribed surgery .
This is necessary in such circumstances as:
- Lack of proper results with conservative treatment.
- Deterioration of the child's condition with frequent relapses of the disease, the possibility of intestinal obstruction.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia ; the scope of surgical intervention may vary, depending on the age and characteristics of the child’s body, the stage and manifestations of the disease.
Recommendations of Dr. Komarovsky
Pediatric doctor E. O. Komarovsky believes that first of all, it is necessary to pay attention to the general condition of the child during constipation. If the baby feels well and has no complaints, then there is no need to worry.
You can give your child a laxative (allowed for his age), and also slightly adjust the baby’s diet .
If constipation is accompanied by severe pain, it is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease or its relapse, you must adhere to the following rules:
- follow the principles of healthy eating;
- move more;
- consume enough fluid (water);
- take vitamin preparations (courses);
- give the child a belly massage.
Dolichosigma is a disease that has very unpleasant symptoms , depending on the stage of its development.
The pathology requires treatment, which consists of following a specially designed diet, taking medications, and using other treatment methods.
In some cases, when the child's condition worsens significantly, surgical treatment is indicated .
Diet for constipation in children from 1 year to 7 years in this video:
We kindly ask you not to self-medicate. Make an appointment with a doctor!
Source: https://pediatrio.ru/d/dolihosigma/kishechnika-u-rebenka.html
Developmental defects: dolichosigma
Among all the malformations of the digestive system, dolichosigma is considered a fairly frequently recorded anomaly. This is an overly elongated sigmoid section of the intestine. This malformation, depending on its severity, provokes problems with the active movement of feces through the intestines. A longer stay of food gruel inside the colon forms fecal dehydration, causing chronic constipation and problems with bowel movements.
Sometimes, if the developmental defects are not severely expressed, there are no digestive problems at an early age and as the child grows, the anomaly can be detected during examinations for other reasons or forms constipation against the background of dietary errors and overeating.
Reasons for development, role of nutrition
Similar intestinal malformations, for example, dolichosigma, form in the early period of intrauterine life. Many scientists consider the presence of dolichosigma not a defect, but a variant of the normal structure of the intestine, in which poor nutrition of a child can provoke problems with stool.
According to researchers, real digestive disorders are typical only for a quarter of children with such an anomaly. The rest of the children develop quite fully, without complaints, even against the backdrop of significant errors in nutrition. Elongation of the intestine is considered to be the result of problems during early pregnancy, when the intestinal tube is formed. Often the cause of problems in the future is poor nutrition, parents’ mistakes in feeding complementary foods and expanding the children’s diet.
Manifestations of pathology: abdominal pain, flatulence, problems with stool
Often the first manifestations occur in children; parents note dry, fragmented stools, absence of bowel movements for 2-3 days, followed by painful bowel movements. Another typical complaint is periodic abdominal pain, which has the character of cramps. Most often, abdominal pain is localized below the navel, closer to the womb or wings of the ilium. Constipation becomes more frequent as you switch from breast milk to formula or when complementary foods are introduced. Most children suffer from constipation after their second birthday, as their diet expands. Stool problems are accompanied by abdominal pain, with cramping or distension, which goes away after defecation, bloating, the passage of foul gases, nausea with vomiting against the background of prolonged stool retention. Digestive disorders lead to deterioration in the absorption of nutritional components and vitamins, minerals, and immunity suffers. The child may have a protruding belly, while he is thin, and an unpleasant odor of breath with a coating on the tongue is typical. Children are pale, with dark circles under their eyes, with brittle and dull hair and nails, and often have anemia.
Stages of pathology: severity of constipation
The pathology has three stages, depending on the manifestations and severity of constipation. At the compensated stage, episodes of constipation appear in severe cases, in practically healthy children against the background of errors in nutrition. During examination, radiography reveals elongation of the sigmoid intestine. Abdominal pain is rare, usually accompanies constipation and disappears after a bowel movement or enema. There are no changes in physical development, the volume of the abdomen is not increased.
The subcompensated form manifests itself as constipation, lasting up to two days, then the stool passes in large volumes on its own. Constipation is more pronounced with a deficiency of plant fiber in the diet, against the background of abuse of fast food and dense foods. Stool disorders occur frequently, flatulence appears, stool is retained, which forces parents to give the baby enemas. The abdomen is swollen in the area of its lower part, an increase in its size is typical.
The decompensated stage leads to almost daily constipation; stool may not pass for up to 4-5 days, which leads to severe abdominal pain, bloating, and vomiting. Against the background of this course of pathology, the physical development of the child suffers significantly; it is important to actively treat the pathology.
The diagnosis is made after a comprehensive examination, including the use of contrast radiography, which reveals elongation of the sigmoid colon.
Long intestine in a child: symptoms and treatment
Constipation is a common problem in childhood; it is often temporary and associated with the child’s eating habits.
But when difficulties in emptying become systematic, it is worth paying special attention to this issue; such a manifestation may indicate a number of diseases.
One of the possible problems is pathology of the sigmoid intestine or dolichosigma.
What is dolichosigma intestinalis
Dolichosigma in a child
By the term “dolichosigma,” doctors mean a pathological change in the sigmoid colon associated with its abnormal lengthening.
The peculiarity of this state of the intestinal section is the absence of changes in wall thickness and lumen size.
The problem lies in the fact that the altered sigmoid area becomes more mobile, which creates certain difficulties in the formation and transportation of feces.
Doctor's note: this situation can be regarded as a feature of the intestinal structure, but if the patient feels unwell and painful, the lengthening is described as a disease. Considering this fact, every child with such a pathology should be monitored by a doctor on an ongoing basis so that any negative changes that arise can be promptly identified and eliminated.
The anomaly is diagnosed in every fourth child, but taking into account the blurred clinical manifestations, this figure is probably much higher. It is usually not difficult to recognize the presence of a problem in a baby - with careful monitoring of his condition, pathology can be identified in the early years.
Types of disease
Depending on the reasons provoking the problem, dolichosigma can be congenital or acquired.
Some experts suggest that the acquired form does not exist as such, the child has the disease from birth, and improper care for him only provokes the development of the disease.
Stages of disease development
During the development process, the disease goes through several stages, each of which is characterized by its own special symptomatic manifestations.
Prohibited foods for dolichosigma in the photo
Parents should pay attention to what physical qualities the food they prepare has. Solid foods should be excluded or steamed as much as possible. The nutrition of a baby with an intestinal disease should be fractional, and the number of meals should be stretched to 4-5, and the portions should be small.
Due to restrictions in the nutritional system, the child must take medications that strengthen the immune system, including vitamin complexes. It is especially important for a child’s body to receive vitamins B6, B12, C and E. Thanks to these complexes, the process of food processing improves, and the process of natural bowel movements is facilitated.
The prescription of antispasmodics and painkillers for increasing pain syndrome for each child is determined individually by the attending physician. These medications may include drotaverine and platyphylline.
Massage also helps relieve spasms and reduce the intensity of pain, and physical therapy also has a beneficial effect on blood flow to the intestines.
These are not only stimulating procedures - they help strengthen muscle structures, which makes it possible to prevent and treat constipation.
A set of exercises for constipation in a child
As part of drug treatment, it is worth highlighting the following groups of drugs to improve the patient’s condition:
- means for reducing the volume of feces;
- herbal enemas;
- prokinetics;
- complex laxatives.
Effective physiotherapeutic procedures include:
- laser therapy;
- acupuncture;
- electrical stimulation of the intestines through rectal and external influence.
Surgical
Treatment through surgery is carried out only with the following features of the disease:
- conservative therapy does not have significant results, and the patient’s vital signs decrease;
- The child’s condition worsens due to relapses leading to intestinal obstruction. In this case, the interventions are classified as planned;
The scope of surgical intervention for children is determined by the general condition of the patient, the size of the pathological elongation, as well as the nature of the disease.
Possible complications and consequences
Without timely measures to eliminate dolichosigma, the child’s condition can significantly worsen due to the development of complications. The following consequences may occur:
- significant weight loss, exhaustion;
- changes in normal blood composition, anemia;
- the appearance of foci of purulent lesions on the skin;
- intestinal obstruction;
- hardening of feces and the formation of fecal stones, which can no longer leave the body on their own;
- poisoning with toxic substances – fecal intoxication.
Despite the fact that it has not yet been precisely established in medical circles whether dolichosigma is a pathology, a child with such a problem requires careful monitoring and systematic visits to the doctor for examinations and medical tests. When symptoms develop, it is very important to react in time, otherwise unpleasant and dangerous complications may follow.
Source: https://lechenie-i-simptomy.ru/dlinnyy-kishechnik-u-rebenka-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Treatment methods, are medications and enemas indicated?
First of all, children with persistent constipation should be shown to a pediatrician, who will refer them for consultation with a surgeon. Initially, the diet is adjusted, foods with a laxative effect and fiber are added to it, the daily routine is normalized, and physical exercises that activate peristalsis are prescribed.
Medications with a mild laxative effect (containing lactulose) may be prescribed. Doses are selected according to age, strictly individually, so that regular and non-compacted stools are formed.
If the situation is more severe, hospitalization is indicated; in stationary conditions, medications with a stimulating, tonic effect are used in courses, supplemented with B vitamins. In addition to medications and non-drug effects, it is acceptable to use electrical stimulation of the intestines, as well as subsequent rehabilitation in a sanatorium.
According to strict indications, surgical correction of pathology is used in the presence of persistent and stubborn constipation that is not eliminated by medications and dietary changes. Also, surgery is prescribed when the expansion of the intestinal walls progresses, when its muscles and nerve ganglia are damaged. Usually a part of the intestine is resected, sometimes it is excised completely within the changed tissue.