Children get sick more often during the cold season. Many parents, after their child gets sick, begin self-medication because they believe it is a cold. However, the use of folk remedies may not be effective at all, since often a cold turns out to be a completely different disease - a sore throat. You can cure a child’s sore throat on your own, but it is not recommended.
If you make any mistakes during treatment or do not take into account the characteristics of the body, there is a considerable probability of negative consequences for its health. Rheumatism may develop or the kidneys may become inflamed. In some cases, improper treatment leads to the fact that a 4-year-old child manages to cure a sore throat, but at the same time the activity of the entire cardiovascular system is disrupted. To prevent such consequences, you need to know how to properly treat a sore throat.
Types of sore throat in children
There are several types of sore throat. And the approach to treatment depends on which subtype the child has. In the vast majority of situations, the disease in children is of bacterial origin. In any case, you need to go to the hospital as soon as possible. Let's take a closer look at the specifics of each variety:
Catarrhal
This form is considered the mildest clinical form of inflammation. Occurs in children from six months. The causative agent in 80% of cases is the bacterium group A streptococcus or (less often) staphylococcus, or a respiratory group virus. With timely use of medications, it can be successfully treated with conservative treatment. This form will last about three to five days. In 94-95% of cases it proceeds without complications. It begins acutely, with pain and discomfort in the throat and other accompanying symptoms, including enlargement of the palatine tonsils, the formation of a pale gray film on them, and hyperthermia.
Lacunarnaya
This form is severe and very dangerous. Inflammation of the tonsils is accompanied by severe disturbances in the child’s general well-being and in half of the cases requires hospitalization. Occurs in children from one year of age. The most common pathogens are also group A streptococci. In addition to damage to the mucous membrane of the tonsils, purulent discharge occurs in their ducts (lacunae), the mark on the thermometer can rise to 40 degrees and is accompanied by intoxication and convulsions, which is especially dangerous.
Follicular
A form of sore throat of moderate severity, affecting both infants and older children. The main symptoms are similar to the previous subtypes: hyperthermia up to 39 degrees, sore throat of varying severity, enlarged tonsils. Follicular tonsillitis can be distinguished from others by the fact that small white or yellowish pustules form on the tonsils. The danger of this form lies in possible complications, including the formation of abscesses, infectious arthritis of the joints, rheumatic fever, and even meningitis.
In addition to the division into the listed types, it is also classified into bacterial, viral and fungal. Bacterial tonsillitis is characterized by the formation of white pustules the size of a millet grain on the tonsils.
Interestingly, the modern medical community believes that removing the tonsils will not reduce the risk of infection. This will provide only a slightly different progression of tonsillitis.
Signs of illness
Before starting to treat any disease, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis. A preliminary examination can be carried out by the child's parents.
If the surface of the tonsils is inflamed and has a bright red color with a white coating, treatment should be started immediately.
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The inflammatory process causes pain when swallowing;
- Body temperature rises. It can reach up to 39 degrees;
- Your head starts to hurt;
- General weakness occurs;
- The voice may change timbre and become hoarse;
- Lymph nodes enlarge;
- The mouth smells unpleasant.
Even if all of the above signs of the disease are present, you should not self-medicate.
After all, only specific medications will effectively affect the causative agent of the disease. And they can only be prescribed by a medical specialist.
Causes, main ways of contracting tonsillitis
The key factor in the appearance of childhood sore throat, regardless of its type, is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the child’s body, such as streptococci and staphylococci (bacterial tonsillitis). When they enter the oral cavity, they primarily affect the palatine tonsils (tonsils). If the immune system cannot cope on its own, the tonsils become inflamed, thereby becoming a source of infection.
It is important to prevent bacteria from entering the child's body. Infection occurs not only through contact with a carrier of the infection, but also through household items, dishes and even kisses from parents. Hypothermia, stress, overwork, high humidity, and significant errors in the child’s diet also contribute to the inflammatory process. Harmful bacteria may not manifest themselves for a long time, remaining in the nasopharynx and waiting for a favorable moment to reproduce.
Even ordinary caries can cause a sore throat, since it is a source of inflammation and promotes the proliferation of microbes.
It is interesting that psychologists talk about another possible factor of the disease, hidden in its psychosomatic nature. This is the inability to express your opinion and express your emotions, which causes mental discomfort. Figuratively speaking, the child “swallows” his resentment, fear and other negative emotions. After all, some parents often carelessly utter phrases such as “don’t make noise”, “don’t cry”, “shut up”, without even suspecting that this may have consequences for the child.
The essence of the pathological process
The term “angina” in medicine refers to a pathological condition that manifests itself:
- inflammation and swelling of the tonsils;
- severe pain that intensifies during swallowing.
Viral tonsillitis is considered a common name for acute tonsillitis in a child, which develops due to infection and active functioning of a viral infection. The disease almost always occurs against the background of acute respiratory illnesses and directly depends on the type of pathogen. In the absence of proper treatment and/or the addition of bacterial microflora, the disease can take a purulent form: follicular or lacunar.
Symptoms and complaints of sore throat in children
The first pronounced signs of tonsillitis begin to appear in most children five to seven days after infection, and in some - within a few hours. It is important to recognize and identify them in time. The following symptoms are characteristic and indicative of angina:
- My throat starts to hurt. The tearing sensation becomes more unbearable when swallowing, but its severity may vary;
- with a sore throat, fever appears (hyperthermia up to 40 degrees), breathing becomes difficult;
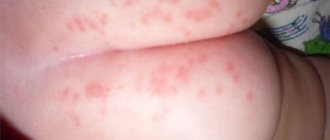
- the throat and tonsils are red and enlarged; with lacunar tonsillitis, a whitish-yellowish coating forms on the tonsils. With follicular - yellowish inflamed follicles are visible;
- swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, under the jaw;
- severe weakness and fatigue. A clinical picture of asthenovegetative syndrome is observed;
- intoxication of the body.
Beginning sore throat without fever
Despite the fact that hyperthermia is a constant and one of the most pronounced symptoms of tonsillitis in a child, tonsillitis without hyperthermia also exists, although it is extremely rare. Clinically, such a sore throat can manifest itself either mildly or quite noticeably. If a child has uncharacteristic signs of deterioration in his general condition and breathing problems, his pharynx should be examined. If she and the tonsils are red and covered with a whitish-yellow coating, you need to call a doctor.
A sore throat without fever can be of combined origin, when the palatine tonsils are affected either by streptococci and staphylococci at the same time, or by bacteria from the sinuses (with advanced sinusitis), or by microbes from dental caries, or by fungi.
Often, a sore throat without fever is accompanied by difficulty breathing and swelling of the oropharynx, which can lead to suffocation in the child.
Manifestation of sore throat with fever
Most often, hyperthermia is an integral sign of angina. Already “on the verge” of a sore throat, the body temperature is rapidly rising, the throat hurts, the tonsils and lymph nodes become inflamed. With purulent forms, the temperature may increase to 40 degrees Celsius.
Sore throat - what is it?
Tonsils are an obstacle to the path of microorganisms into the organs of the lower respiratory system. Microbes accumulate on the surface of the tonsils, multiply and cause a dangerous disease for children - tonsillitis. The disease is often diagnosed in children attending kindergarten or school. Sore throat in a one-year-old child occurs in an acute, severe form and requires mandatory hospitalization. When the first symptoms of the disease appear (lethargy, refusal to eat), you must call a doctor.
Tonsillitis begins with a sudden rise in temperature, severe pain or discomfort, and a tingling sensation in the throat. Nearby lymph nodes enlarge, parents can feel them themselves. Sore throat is a very highly contagious disease and quickly spreads in children's groups by air and droplets, through household items and toys.
Parents note that with a sore throat, the child snores in his sleep. This occurs due to problems breathing through the nose (runny nose) and swelling of the throat. With frequent colds, the adenoids and tonsils remain enlarged and breathing becomes difficult.
Note: If a child’s temperature has risen sharply or symptoms of intoxication have appeared, it is necessary to visit a pediatrician as soon as possible to prescribe a complex of therapy; self-medication and the use of traditional methods are prohibited.
In young children
Up to one year of age, sore throat is extremely rare, the tonsils have not yet fully developed, and the immunity of a one-year-old child is just developing. Therefore, angina progresses much faster and is more difficult. At 2 months, sore throat poses a great danger to the child’s health, because his immunity has not yet fully developed. Sore throat in an 8-month-old child or a 9-month-old child is no less dangerous. The disease in a one-year-old child or younger is already an indication for the prescription of antibiotics.
It is recommended to treat bacterial tonsillitis in a hospital setting for up to three years. Children 2 and 3 years old have difficulty with sore throat. A two- and three-year-old child has difficulty rinsing the mouth and swallowing tablets, so doctors limit themselves to prescribing the use of absorbable lozenges, suspensions and syrups. At 4 years old, some children can already swallow a tablet whole.
The table below discusses the specifics of the disease depending on the age group of the child:
| Progression of the disease | Possible complications | Antibiotics | Hospitalization | |
| Child under one year old | Heavy. The child has not yet developed his own immunity and there are many contraindications to taking medications |
| Antibiotics are prescribed without fail | Shown anyway |
| After a year | A faster recovery is possible, a more extensive list of approved medications. In a three-year-old child and older, the immune system becomes stronger |
| Recovery is possible without the use of antibiotics | Required in half percent of cases |
Local therapy for purulent sore throat
Purulent sore throat in children should also be treated with local remedies.
- Throat sprays.
- Tablets with antiseptics for resorption.
- Rinse products.
To remove purulent plaque, doctors recommend that parents soak a cotton pad in medications such as Lugol, Stomatodin and peroxide with a small amount of water and lubricate the sore tonsils with it.
If the child is 3 years old or less, then the following rules should be taken into account when taking local medications:
- It is not worth treating such babies with sprays.
The thing is that small children cannot hold their breath when injecting. You shouldn’t even try to use such remedies, as they can cause laryngospasm. Doctors advise parents to direct the stream of medicine not into the throat, but onto the cheek of a child under 3 years of age. And for infants, it is better to treat their favorite pacifier with sprays. This method of treating purulent tonsillitis in infants is the safest.
- Doctors also do not recommend giving absorbent tablets to children under 3 years of age. In this case, there is a high risk of asphyxia by a foreign body.
- Only those children who are already 2 years old should gargle with various means.
Compliance with these rules is mandatory when treating the above-described illness in very young children. If they are not followed, complications may arise that will subsequently be very difficult to deal with.
A few more rules that must be taken into account when using local products:
- Before using this or that product, be sure to read the instructions very carefully. Medicines should be used only according to age recommendations.
- Some medications can cause an allergic reaction in your baby. Therefore, you need to very carefully monitor the baby’s reaction to this or that drug.
- Topical medications should be used only after meals.
You should rinse your mouth every 3 hours. After using topical remedies, do not drink or eat for 30 minutes. If you do not follow this rule, then you should not even hope that the symptoms of purulent sore throat in children will soon go away.
- Iodinol and Lugol should not be used to treat the above-described illness in infants.
The thing is that such products can greatly irritate the throat mucosa
They should also be used very carefully to treat children who are only 1 year old. They should treat the oral cavity no more than once a day.
In older children
The highest rate of streptococcal sore throat infection is in the age group of 5 to 10 years. This is partly due to the child’s social activity: he just started school and began to go out more often, as a result of which the chances of catching an infection become much greater.
The table below presents data on the permissibility of using certain medications for a child from five to thirteen years of age (without taking into account possible allergic reactions).
| Ibuprofen | Amoxiclav | Viferon, Kipferon | Nimesulide | Tsetrin | Tonsilgon | |
| 5 years | The medication is prohibited for children under 12 years of age. You can use baby Paracetamol (not until one month old) | Acceptable as a suspension | + | For children under 12 years of age, the drug Nimulid is available in the form of a suspension. | The medication is not approved for children 5 years of age and younger. You can use Suprastin | + |
| 6 years | + | + | + | + | ||
| 7 years | + | + | + | + | ||
| 8 years | + | + | + | + | ||
| 9 years | + | + | + | + | ||
| 10 years | + | + | + | + | ||
| 11 years | + | + | + | + | ||
| 12 years | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 13 years | + | + | + | + | + | + |
Development and course of the disease in children by day
In young children, the course of sore throat has its own characteristics, since their body is not yet strong and any damage to the body without timely help can lead to complications. Let's consider the course of the disease in a child who has a moderate form of tonsillitis. The duration of its cure takes on average one week.
| Days | Symptoms |
| First | Beginning stage. There is a fever, a feeling of a lump in the throat. Pain when swallowing and hoarseness of voice are noted. Next, you gradually feel aching in the muscles. Possible runny nose. The child gets very tired, becomes capricious, and complains of tearing pain. A pronounced clinical picture of asthenovegetative syndrome. |
| Second | The second and third days are considered the peak stage. The fever still persists. The cervical, submandibular and lymph nodes increase to two centimeters. The tearing sensations in the oropharynx become more unbearable, and either small pustules or a whitish-yellow film form (depending on the shape). |
| Third | Symptoms from the previous day may persist. Deterioration in well-being is also possible. It is very difficult for the child to open his jaw; he still refuses to eat. There may be an unpleasant taste in the mouth due to pus. |
| Fourth | The fever may persist, but the reading on the thermometer becomes lower. |
| Fifth | In moderate forms, hyperthermia may persist on the fifth day. However, the dynamics of recovery are becoming positive. |
| After the fifth day | Gradually the fever decreases, general health returns to normal. Appetite appears, the child will be able to open his mouth and make sounds. The swelling of the tonsils subsides, they cleanse themselves. Purulent follicles or film dissolve and subsequently completely disappear. |
Characteristic manifestations of the follicular form
The follicular form is characterized by the presence of purulent formations. The cause of the disease is harmful bacteria.
It is characterized by an acute onset and more pronounced intoxication. It can last for four days.
The purulent follicular form is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Increased intoxication;
- Heat;
- The occurrence of headache;
- The presence of purulent formations;
- The appearance of a white coating;
- After the follicles are resolved, the patient's condition improves.
The duration of the disease can be ten days. Delayed initiation of treatment can lead to dangerous complications.
How to distinguish a sore throat in a child
The difference between a sore throat and ARVI is huge. The first case has its own characteristics: as a rule, pustules form on the tonsils, the child is unable to open his mouth, eat or talk, and asthenovegetative syndrome is observed. The mark on the thermometer stays at high levels for several days. With ARVI, the temperature quickly passes, leaving only a runny nose and cough. In general, ARVI is easier.
It is difficult to recognize and determine a sore throat without fever, which is why it is often confused with a common cold. If a child complains of discomfort and soreness in the throat, be sure to send him to the hospital. By assessing the condition of the mucous surface of the oropharynx, the doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis and treat the child.
Clinical picture
The incubation period from the moment the pathogen enters the body until the initial symptoms of the disease appear can be either 2 days or 10-14 days. It all depends on the state of the child’s immunity and the type of virus. Among the primary manifestations of the disease, doctors call:
- general weakness, aches throughout the body;
- temperature rise to 38 degrees;
- profuse drooling;
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- itching sensation in the throat;
- decreased appetite.
These are the first symptoms to occur. Literally after a few hours or days, the clinical picture changes. Children develop cough and nasal congestion. Upon visual examination, swelling of the tonsils becomes clearly visible, and upon palpation, hardening of the lymph nodes. It is possible that small papules may appear on the palate, which after some time transform into vesicles with serous secretions and soon burst.
Depending on the type of virus that provoked the development of sore throat, its manifestations may vary. Let us consider the main differences in the clinical picture using the example of common pathologies.
Which doctor treats sore throat in children?
A pediatrician monitors and prescribes medications for the child, as it is necessary to constantly monitor the functioning of the heart and kidneys and prevent complications. If a sore throat occurs once and does not recur in the future, observation by a pediatrician will be sufficient.
If a child’s sore throat recurs frequently, you should consult an otolaryngologist. He will conduct an endoscopic examination, assess the condition of the palatine tonsils for the presence of purulent contents in their lacunae, and conduct a streptotest, which can show whether streptococcus bacteria are the cause of the infection.
Surgery
In most cases, it is possible to treat sore throat in children 4 years of age without surgery. Tonsils should only be removed in extreme cases. Typically, surgery is prescribed for recurrent sore throat, which occurs at least 7 times a year or five times every year for two years. Surgery is also necessary if the sore throat recurs for three years in a row, developing at least once a year.
In the chronic form, removal of tonsils is the only method by which this disease can be overcome. Excessively enlarged tonsils are also a reason for their surgical removal. Surgery is required for purulent complications.
How to effectively treat a sore throat in a child
The time of initiation of therapy plays a big role. In order for treatment to proceed quickly and as effectively as possible, it is necessary to correctly and promptly begin to treat a sore throat that is just beginning.
If a child has a sore throat with purulent ulcers, first aid should be provided as soon as possible, because such forms are more severe and take longer.
An integrated approach includes certain medications prescribed by a pediatrician or otolaryngologist, means for local treatment of the oral cavity, procedures according to traditional medicine prescriptions, diet and bed rest.
Drugs
Naturally, you cannot prescribe and give medications to your baby on your own. The necessary medications and their dosage are prescribed exclusively by the attending doctor, taking into account allergic reactions.
Below we consider the list of medications that pediatricians most often prescribe for sore throat:
- Antipyretic medications (indication for use - temperature above 38.5 degrees): Paracetamol, Panadol, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Efferalgan, Calpol. Use in the form of suspensions and suppositories is acceptable. Aspirin and Analgin are prohibited.
- Antibiotics (use for at least ten days), penicillin series: Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Ecoclave; macrolides: Sumamed, Azitrox; cephalosporins: Cephalexin, Zinnat, Suprax, Pancef.
- Antihistamines: Cetrin, Suprastin, Zyrtec, Zodak.
- Vitamins: group B and C, Multi-tabs complex, Centrum, Pikovit, Alphabet.
- Probiotics: Linex, Acipol, Bifiform, Bifidumbacterin Forte and so on.
- Herbal remedies: Tonsilgon.
- Immunomodulators: Kipferon, Viferon.
Please note that any sprays (“Hexoral”, “Inhalipt” and others) can only be prescribed to three-year-olds and older children.
It is a big mistake to stop taking antibiotics after all symptoms disappear. The causative agent of the disease may still be in the child’s body, and then the acute form will become chronic. You must complete a full course.
After recovery, you need to refuse any vaccinations and Mantoux.
Treatment of the throat for sore throat
At home, to alleviate symptoms, it is permissible to treat the child’s mouth to relieve acute, bothersome pain. It is not recommended to lubricate your baby's tonsils with antiseptics. This damages the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and worsens the course of the purulent form. Lugol or Iodinol are strong and mucosal irritants. There is no need to use them for infants; it is permissible for an older child to treat the throat with a sore throat no more than once a day, but only after a face-to-face consultation with a doctor.
Such local treatment of the oral cavity should be carried out after eating food. To achieve the effect of the procedure, you need to clean your mouth every three hours. After the child’s oropharynx has been treated, he should not eat or drink for half an hour, otherwise the effectiveness of the procedure is reduced to zero.
If you need to treat your baby’s throat, then you need to choose only one (maximum two) remedy to avoid overloading the body with medications.
ethnoscience
A variety of herbal infusions will perfectly ease severe sore throats and gently relieve soreness and inflammation in the red throat. But you must remember that folk recipes will pay off only with an integrated approach to recovery. So, what can you drink if you have an acute sore throat?
- If a sore throat has just begun, you need to give your child a slice of lemon to chew (this is natural vitamin C) or propolis. Propolis is a natural antibiotic. Or you need to prepare this drink (suitable only for children over five years old!): put a small slice of butter and one to one and a half spoons of honey in a glass of hot milk.
- Tea with raspberries or rose hips. It has a powerful diaphoretic effect and helps remove inflammation.
- Not all children will like the following drink, but its effectiveness is not inferior to the others: onion juice. You can take a teaspoon of it three to four times a day.
Of course, the most effective procedure in such a situation is rinsing. But due to the fact that it is very difficult for a child under five years old to do this, the method is suitable for older children. Let's look at the most popular folk recipes:
- Water and table salt. Suitable only for the manifestation of catarrhal form without pustular ulcers. Add one or one and a half teaspoons of salt to a glass of warm water. The child should rinse the oropharynx with the resulting solution four to five times a day.
- Infusions from different berries, leaves and flowers of plants to choose from: viburnum, chamomile, calendula, sage or thyme. They will have an analgesic and antiseptic effect.
- You can prepare a mixture of water either with Miramistin solution (0.01%), or with hydrogen peroxide (one and a half to two tablespoons per glass) or with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Diet
During such a period, it is very important and necessary to eat nutritious, but not high-calorie foods. Among them are boiled or steamed chicken, white fish and beef (can be made in the form of cutlets or meatballs). In the first days, it is best to prepare your child broths and soups with pieces of vegetables (for example, cauliflower or potatoes). The soft consistency of the dish does not irritate the mucous membrane and when swallowing the product there is a minimum of painful sensations.
It is also necessary to ensure that the food prepared for the child is not hot or cold. No need to add seasonings and spices. It is necessary to lighten the diet, remove all sweet and fatty foods from it.
The best drinks for a child are berry fruit drinks and freshly squeezed juices, rosehip infusions and tea with lemon. It is advisable to take at least one liter of liquid per day.
Daily regime
For sore throat, children are always prescribed strict bed rest. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, the child will be haunted by a constant need to sleep due to hyperthermia. This phenomenon is normal, as the body recovers faster. Sleep helps build up strength to fight infection. At night, sleep should last at least eight hours, during the day - from four or more hours.
No active games or activities or walks in the fresh air should be carried out, especially during prolonged temperatures. Bathing should also be postponed. If a week after the onset of a sore throat, the temperature has subsided, you can wash the child in the shower, but without sitting in the bath for a long time.
In what cases is hospitalization indicated?
Pediatricians insist that a child under one year of age, when diagnosed with tonsillitis, must be immediately admitted to an inpatient department. This will allow you to provide urgent assistance in a timely manner and prevent complications. Indications for immediate hospitalization of a child include:
- fever not controlled by medications, intoxication, confusion and convulsions;
- complications that have arisen (abscess, phlegmon and others);
- presence of diabetes mellitus or renal failure.
Carrying out diagnostics
Diagnostic measures should be carried out by an infectious disease specialist.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of bacteriological studies, which make it possible to determine the type of specific causative agent of the disease.
Treatment of the disease will depend on the characteristics of tonsillitis.
This material may also be of interest to you:
Primary tonsillitis is characterized by the presence of signs of an inflammatory process. The number of leukocytes in the blood increases.
To make a diagnosis of secondary tonsillitis, serological blood tests are necessary.
Based on the data obtained, a final diagnosis is established.
Possible complications in children after tonsillitis
If you do not go to the clinic in a timely manner or self-medicate, serious complications very often arise. And as a result, a sore throat will have to be treated for a very long time, and the occurrence of complications will increase the period of complete recovery. Possible complications of the catarrhal form in a child are laryngitis, tonsillar abscesses, secondary infection and hemodynamic disorders. In the follicular and lacunar forms, in addition to the complications already listed, bronchial inflammation, otitis media, meningitis, brain abscess, sepsis, infectious arthritis of the joints, thrombocytopenic purpura, and, less commonly, nephritis may be added.
How to proceed?
Sore throat can appear 12 hours after illness. The disease develops quickly and acutely. The child loses appetite and desire to drink liquids (due to a constricting pain in the throat), weakness, moodiness appears, and the voice becomes hoarse.
Due to a number of possible complications of angina, mandatory observation by a doctor and compliance with treatment are required. If the sore throat drags on or treatment begins too late, you should insist on the child staying in the hospital. Children's sore throat can affect other body systems.
Disease prevention
To prevent your child from getting a sore throat, it is enough to follow simple recommendations, because ordinary prevention is the key to good health.
- Give your child spicy, hot and too salty food as little as possible, as it irritates the mucous membrane of the oropharynx;
- The child should not be overcooled or drink cold drinks, especially on the street;
- Your child and you must be systematically examined by an otolaryngologist and dentist to promptly detect the development of an infection;
- limit contact with sick people, avoid large crowds of people;
- do not ignore the baby’s complaints about the slightest discomfort;
- exercise regularly or do light exercise;
- You should always treat your and your child’s hands with an antiseptic and wash them with soap after visiting public places;
- maintain a sleep schedule. With a lack of sleep, any person's immunity decreases and the likelihood of catching colds and more serious infections increases.
If early symptoms similar to a sore throat appear, the best and correct decision would be to consult a doctor at the initial stage of a sore throat.
Treating the child correctly
Sore throat is a serious and dangerous disease for a child. You cannot self-medicate and rely only on folk recipes and vitamins. Treating the oral cavity and making herbal infusions is not enough. The task of parents is to take their child to an appointment with a pediatrician on time. After all, even an unreasonable delay of several days can seriously affect the baby’s health. If a one-year-old child falls ill, a doctor’s examination is necessary in any case, because the baby himself will not be able to say what exactly is bothering him. There is no need to neglect prevention; you must follow all the recommendations of doctors.
Previous post Paracetamol for children - children's dosage and instructions for use for fever
Next entry When does a baby start to crawl - at how many months do babies crawl on their own?