Features of children's skin
Children's skin is different from adult skin.
Babies are born with very thin skin - the dermis of newborns is approximately two times thinner than the middle skin layer of adults. The outer layer, the epidermis, thickens gradually as the baby grows older. In the first month of life, the skin may be red or purple. This is due to the fact that the blood vessels in babies are located close to the surface, and there is not enough subcutaneous tissue, which is why the skin may look “transparent”. This is especially noticeable when the newborn is cold - a marbled vascular network appears on the skin.
The skin of babies loses moisture faster, it is more vulnerable to bacteria, viruses, fungi and mechanical stress. It begins to thicken only at 2-3 years and this process lasts up to 7 years. The skin of younger schoolchildren is already beginning to resemble the skin of adults in its characteristics and functionality. But after 10 years, children's skin faces a new test - this time, puberty.
It is not surprising that thin children’s skin reacts to any external influence or internal processes with rashes of various sizes, colors and structures. And not every childhood rash can be considered harmless.
Atopic dermatitis
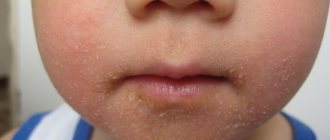
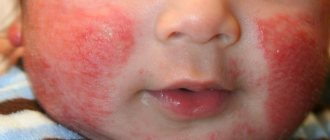
Chronic inflammatory skin disease appears 2–3 months after birth, but there are cases of atopic dermatitis occurring at 3–4 years. This is the most common type of eczema. The disease is often accompanied by asthma or allergic rhinitis.
Characteristics:
- Where observed : cheeks, arms, legs, knee and elbow bends.
- How it appears : Itchy, red, swollen, very dry and cracked skin. Ich leaks from damaged areas.
- Reasons : unknown exactly. There is an assumption that genetic predisposition, “sterile” living conditions, and immediate allergic reactions to a large number of irritants (food, dust, animal hair) are to blame.
- Treatment : atopic dermatitis goes away on its own over time. The disease is made easier by lifestyle adjustments. Children need to regularly moisturize their skin, take salt baths, avoid woolen clothing and choose an appropriate diet. The doctor prescribes corticosteroids, systemic immunosuppressants, and refers him to ultraviolet irradiation.
Causes of rash in the sternum area
The main cause of chest rashes is improper skin care.
Improper skin care is one of the main factors of rashes. A scattering of acne on the chest appears due to the fact that the pores become clogged with sweat and subcutaneous sebum if you neglect to shower. This is a comfortable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which causes inflammatory processes.
Pimples on the sternum often appear due to a lack of valuable elements. Vitamin deficiency is more likely to affect teenagers, expectant and nursing mothers, and people with heavy physical and mental labor.
If the rash appears together with severe itching and irritation, this may indicate the presence of skin diseases, such as eczema, shingles or one of the types of dermatitis, as well as an infectious process or allergy.
Allergens include pet hair, pollen, household dust, household chemicals, food, alcohol, and medications. For example, it can sprinkle on a person after taking antibiotics or iron supplements. A similar reaction to ultraviolet rays is possible after visiting the beach or solarium.
For the above reasons, a rash in the sternum area occurs in representatives of any gender and age. But there are certain factors that affect men, women or children specifically.
Among women
When pregnancy occurs, a rash may appear on the chest
Changes in estrogen synthesis in the body lead to excess subcutaneous fat, which usually manifests itself as rashes. For hormonal reasons, rashes occur in a woman if she:
- pregnant;
- breastfeed;
- waits from day to day for menstruation;
- had an abortion or lost a fetus;
- entered menopause.
Pimples on the sternum appear due to excess hormone synthesis in adolescents of both sexes.
A rash on the chest in women in the form of scarlet pimples that tend to itch and itch may be a reaction to a poor-quality or tight bra, popularly called urticaria.
In men
A rash on the chest in men indicates internal diseases
A rash on the chest in men can indicate internal diseases, in particular, pathologies of the stomach and intestines, kidneys, liver, and prostate. But most often the problem is neglect of personal hygiene rules.
If the rash on the male chest does not disappear within a couple of days even with regular bathing, and the itching and burning only intensify, you should immediately see a therapist or dermatologist.
In children
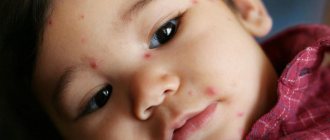
External manifestation of measles
In newborn babies, rashes can occur in the first days of life as a reaction of the skin to adapt to the new environment. Usually such manifestations pass quickly. In infants, rashes are often associated with the quality of the mother's diet and, accordingly, milk. A formula-fed baby may react with a rash to inappropriate formula.
Common childhood illnesses that cause rashes include:
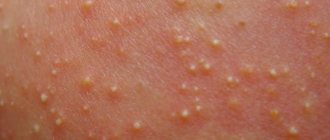
- Miliaria is a rash of small itchy blisters that occurs due to blockage of the sweat glands due to excessive sweating. Usually concentrates on the abdomen, chest, buttocks.
- Exanthema is a skin rash that looks like spots, papules, vesicles, formed under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Chickenpox is a viral disease in which blisters grow and burst on the chest, face, arms, and legs.
Rules for preventing the appearance of a rash on the back of a child
Most often, a rash on the back in children is the result of an allergy or poor hygiene. In such cases, parents usually know what an allergy may occur to and can cope with this phenomenon themselves.
Hygiene requirements:
- Teach your child to shower every day before bed. The skin should be cleaned with a well-soaped washcloth, then the remaining soap should be completely washed off the body.
- Review your diet. Exclude foods that cause allergies, sweets, fatty, spicy foods. Replenish your diet with neutral dishes that do not cause health problems.
- Review the child’s clothes, check that all of them, especially underwear, are made from natural fabrics.
- Wash children's clothes separately from adults with special hypoallergenic children's powders, set the washing machine to the highest rinse setting.
- Change and wash baby bedding regularly. If a rash appears, the bed is changed daily.
- Wash and bathe children only with products purchased at the pharmacy, intended for use on problem skin.
For any recurrence of a rash on the back, it is necessary to visit a dermatologist, get a new consultation, a new prescription.
A rash on the back should not be left unattended; it causes serious discomfort to the child, and most importantly, it can be a sign of a dangerous internal disease.
Causes
The reasons that cause the development of skin rashes can be varied. A lot depends on the age and general condition of the child.
In newborns and babies in the first year of life, the rash is quite often physiological, which should not cause any particular concern on the part of adults. The baby’s skin adapts to its new habitat – waterless, and this process is often difficult for the baby. Therefore, any adverse effect can cause rashes all over the body.
The most common rash at this age is hormonal acne, in which white or yellow pimples may appear on the face and neck. This phenomenon is caused by the maternal hormones estrogen, which the child received in the last months of the mother’s pregnancy. Gradually, their influence on the body decreases, hormones leave the child’s body. By six months, not a trace of such pimples remains.
Babies very often react with an allergic rash to inappropriate food products, substances, medicines and even household chemicals that the mother uses to wash linen and bedding and wash floors and dishes.
Another common cause of rashes in infancy is diaper rash and prickly heat. A rash on the body, head, arms and legs at an early age appears due to infectious diseases, as well as due to violations of hygiene rules.
Slight dryness of the skin in the first 3-4 weeks after birth is a variant of the physiological norm.
From birth, a baby’s skin is covered with a lipid “mantle,” the so-called fatty protective layer. The “mantle” is gradually washed off and washed away. With proper care, this temporary natural dryness is easily compensated by the child's body - the sebaceous glands gradually begin to produce the required amount of protective lubricant.
There are not many physiological reasons for the appearance of a rash after a year. In rare cases, hormonal imbalances caused by exposure to maternal sex hormones persist. All other cases mostly have pathological causes. In preschool age, the incidence of viral infections, which are characterized by a rash, increases in children. These are chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever and other childhood diseases.
A one-year-old child who has not yet started attending kindergarten and organized children's groups has a lower risk of contracting herpes or other viral infections than children aged 3 to 7 years. Local immunity at this age begins to work better than in infants, for this reason many bacterial skin ailments can be successfully avoided.
Preschoolers are more susceptible than other children to parasitic diseases, in which a rash appears as a result of the influence of internal parasites (helminths) or external parasites - lice, scabies, skin mites - on the body.
Up to 3 years of age, the impact of allergens on the child’s body is still strong, and therefore the appearance of a rash on different parts of the body - on the face, head, stomach, elbows and even on the eyelids and ears - is a fairly common occurrence after eating a product containing an allergen, one or another drug, contact with pollen, animal hair, household chemicals.
But acne in preschool age is rare. And even if it does occur, then we are most likely talking about metabolic disorders, lack of vitamins, minerals, and diseases of the internal secretion organs.
For children over 10 years old
After 10 years, children have only one type of physiological rash - teenage acne. Under the influence of sex hormones, which begin to be produced in the bodies of girls and boys, the sebaceous glands are activated.
So, pimples and pimples of varying sizes and intensity “bloom” on the forehead, nose, cheeks, and sometimes on the forearms, back and even buttocks.
The immunity of children is already sufficiently developed, preventive vaccinations have not left their mark on the body, and therefore the risk of contracting “childhood diseases” in adolescence is much lower. Many children have already had them before.
Bacterial and fungal infections and parasitic skin diseases, such as scabies, take first place among infections accompanied by rashes. This is due to lack of hygiene and the inattentive attitude of most teenagers to the requirements to wash their hands after going outside or use bactericidal soap.
A rash in 15-16 year old teenagers can also be a symptom of a sexually transmitted disease, since quite a lot of boys and girls at this age begin to be sexually active. Rashes on the skin of the face and upper body can also be a consequence of taking steroids, with the help of which boys, and sometimes girls, try to create a “beautiful, sculpted” body during fitness classes.
Allergic rashes in adolescence are not as common as in younger children. Usually, if a teenager is allergic, the parents know about it and the appearance of rashes will not surprise or frighten them at all, since they already have a good idea of how to deal with it.
At any age, the cause of a rash can be metabolic disorders, lack of vitamins A, E, C, PP, as well as dysbacteriosis, disruption of the stomach, intestines, and kidneys.
Symptoms
Considering the reason that triggered the development of the rash on the arms, cheeks, face, buttocks, palms, back, feet or butt, you can determine the main symptoms of the rash.
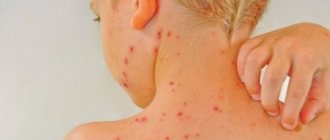
Measles
The measles viral infection appears a couple of days after the body temperature rises and redness in the throat appears along with a cough and runny nose. The rash initially covers the face and head, spreading to the arms and legs. Thus, the entire body becomes covered with a rash within a few days. The spots are large and raised above the skin.
Chicken pox
With chickenpox, spots appear on the face and subsequently spread to the entire body. At the beginning, the rash, reaching a size of 4 mm, has a red tint, and then bubbles filled with cloudy liquid appear. Next, the bubbles dry out, and a dark red crust forms on them, which itches. In addition, your temperature may rise.
Types of rashes with characteristic symptoms
It is worth highlighting acne as the most common skin disease. Factors that provoke black spots on the chest and face, which turn into purulent inflammation, include:
- work in enterprises that are harmful to health;
- stressful conditions;
- hormonal imbalances;
- unbalanced diet;
- careless attitude towards taking oral contraceptives;
- selection of cheap, low-quality cosmetics;
- wearing clothes made from artificial materials.
Acne appears after the end of breastfeeding for the same reasons as during pregnancy. A hormonal imbalance affects the functioning of the sweat glands, which causes the skin pores to become clogged with excess sebaceous secretions and become inflamed. In this case, black dots turn into red spots, then into ulcers. Swelling and itching are likely to occur. In addition, scratching and cracking of the skin are possible.
A rash on the chest can be caused by the penetration of a subcutaneous mite
A red rash on the sternum in men and women can be caused by the penetration of a subcutaneous mite into the epidermis. With scabies, pimples begin to itch and hurt if moisture gets on them. Young people are more likely to catch this infectious disease. Also, red spots on the body may appear due to intestinal helminths.
A small rash on the sternum in adults in the form of white pimples may indicate a metabolic disorder. In this case, whitish blisters will appear on the back, chest, neck and skin under the breasts. They are observed in 50 percent of people with diseases such as gastritis, duodenitis and other intestinal pathologies.
Reddish rashes on the mammary glands along with swelling may indicate inflammatory breast cancer. Lung cancer is characterized by spots on the chest that are encircling in nature, but at the same time resemble harmless pigment spots.
Methods for diagnosing and getting rid of rashes
A pediatrician, allergist, gastroenterologist and infectious disease specialist can understand the causes of the rash.
For diagnosis, standard methods are used - blood, urine, and stool tests. Quite often, skin scrapings and samples of the contents of vesicles and pustules are taken for analysis. This makes it possible to establish not only an accurate diagnosis, but also the type and type of pathogen, if we are talking about an infection, as well as what drugs the pathogens are sensitive to.
Parents should undress the child, examine the skin, note the nature of the rash (vesicles, pustules, papules, etc.) and its extent. After which you should measure the child’s body temperature, examine the throat and tonsils, note other symptoms, if any, and decide to call a doctor.
Small red
This is one of the most common types of rash, and parents of children of any age can encounter it, but most often of early, preschool and primary school children.
To identify the etymology of rashes on the skin of the chest, contact a therapist or immediately a dermatologist. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will direct the patient to undergo tests. The following laboratory tests will be required:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood test for hormones;
- coprogram.
The doctor may prescribe an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, mammary glands, testing for demodicosis and allergic dermatosis. If there are suspicions that the rash is caused by an allergy, an autoimmune disease, problems in the field of gynecology, gastroenterology, consultation with specialists will be needed.
Allergic reactions on the skin are eliminated with the help of antiallergic drugs
Skin rashes can be initiated by infectious and non-infectious causes. An experienced doctor will determine the disease by the nature of the rash and the corresponding symptoms.
In case of allergic reactions, the rash is removed using antiallergic medications and eliminating contact with the allergen. An infectious rash is treated by eliminating the underlying cause of the disease.
In any case, treatment for rashes on the chest should be comprehensive, including local and general medications. Prerequisite: a course of vitamin therapy and compliance with hygiene rules. The complex effect will make it possible to get rid of the rash and identify the cause of the disease and eliminate it. As a preventive measure, special attention should also be paid to hygiene and proper nutrition.
What should parents do?
A sudden exanthema or rash in a child that appears on the butt and itches always causes confusion among parents, since not everyone knows what to do.
First of all, you should carefully inspect the child’s clothes. Often, a rash appears on a child’s hands after changing washing powder or buying new clothes. In this case, you should avoid contact with the irritant and, perhaps, the problem will go away on its own.
If a child suddenly develops rashes on the buttocks, but they do not itch or cause discomfort, the cause should be sought in improper care. Often it is enough to change the brand of diapers and treat the baby's skin with antiseptic cream or powder.
A rash on the legs and butt of a child without fever can be either an allergic reaction or a manifestation of dermatitis. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause.
What is the best treatment and what to do so that an infant stops experiencing discomfort - it depends on the cause of the skin reaction. It will be possible to get rid of the problem only after eliminating the factor that provokes the appearance of redness and blisters.
A rash on a child’s bottom appears as a result of exposure to various factors. Untimely treatment of rashes can lead to complications.
Table of diseases by type and location of rash
This is not a complete list of diseases that occur with the formation of a rash.
Most ailments, as can be seen from the table, require mandatory medical consultation; some, for example, meningococcal infection and scarlet fever, require emergency medical care.
It is important to remember that many infections that appear on the skin can be very contagious. Therefore, you should not take your child to the clinic at your place of residence, so as not to infect others in the general queue. It is best to call a pediatrician at home .
If possible, you can take the child to a specialized infectious diseases hospital, where it is possible to quickly undergo the necessary examination and confirm or refute the infection.
Precautionary measures
If you notice the appearance of a rash in your baby, do not panic. You must act wisely. You should not tell your child about this and show your excitement, as this can cause panic and depression in the baby. You shouldn’t focus her attention on this.
Observe the following precautions:
- Never try to hide the rash using cosmetics. Foundation and powder can make you feel worse;
- Do not squeeze out the tumors, this will increase the area of the rash;
- Do not use the remedy for treatment until it has been agreed with your doctor, even if it has helped someone you know;
- Provide an individual towel for your baby;
- If you decide to combine drug treatment with traditional medicine, be careful about the components you are going to use.
These simple recommendations will help you avoid serious mistakes that could worsen the situation.
Treatment
Treatment of a rash does not always require only local action; most often it is a whole range of measures aimed at changing the child’s living conditions, revising his diet, and taking medications.
The rash should be treated only after the true cause of its occurrence is known, because incorrect treatment can only worsen the child’s condition. Depending on the true nature of the skin rash, different treatments will be prescribed.
The rash that accompanies most “childhood” diseases (chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever, etc.) does not require treatment. No medications or folk remedies can affect its duration.
Depending on the severity of the disease itself, the doctor prescribes immunomodulatory drugs, antiviral drugs, vitamins, and antipyretic drugs.
A child with a viral infection is advised to drink plenty of warm fluids.
For the most part, antiviral drugs sold in pharmacies have no effect; they have no proven effectiveness. Many popular homeopathic remedies are also essentially a “dummy” placebo effect.
But nothing else is required from these medications, because viral infections go away on their own, with or without pills. The drugs are prescribed so that parents have something to do while on sick leave and so that the doctor is not accused of inattention.
Typically, treatment of a viral infection takes from 5 to 10 days, after the rash disappears there are no traces left. An exception is chickenpox, in which damaged vesicles can leave quite deep, life-long pits in the skin.
A pustular rash caused by pathogenic bacteria is treated with antibiotics and antiseptics. Moreover, antibiotics are selected after a culture test, when the doctor has clear information about which bacteria caused the suppuration and to which antibacterial agents they demonstrate sensitivity.
Children are usually prescribed penicillins, less often cephalosporins. For mild infections, local treatment with ointments that have an antimicrobial effect is sufficient - Levomekol, Baneocin, erythromycin ointment, gentamicin ointment, tetracycline ointment.
In some cases, with an extensive and severe infection or an infection that risks spreading to internal organs, antibiotics are prescribed orally - for children in the form of a suspension, for preschoolers and adolescents - in tablets or injections.
Preference is given to broad-spectrum drugs, usually of the penicillin group - Amoxiclav, Amosin, Amoxicillin, Flemoxin Solutab. If drugs in this group are ineffective, cephalosporin antibiotics or macrolides may be prescribed.
Well-known aniline dyes are often used as antiseptics - a solution of brilliant green (brilliant green) for staphylococcal infections or “Fukortsin” for streptococci. Damaged skin is treated with salicylic alcohol.
Along with antibiotics, if they are prescribed orally, the child is recommended to take drugs that will help avoid the occurrence of dysbacteriosis - “Bifiborm”, “Bifidumbacterin”. It is also useful to start taking vitamin complexes appropriate for the child’s age.
Some purulent rashes, such as boils and carbuncles, may require surgical intervention, during which the formation is incised crosswise under local anesthesia, the cavity is cleaned out and treated with antiseptics and antibiotics. There is no need to be afraid of such a mini-operation.
Heat rash and diaper rash
If a baby develops prickly heat, this is a signal for parents to change the conditions in which the child lives. The temperature should be at 20-21 degrees Celsius. The heat only makes the prickly heat worse. Irritation from sweat, although it gives the child a lot of excruciating sensations and pain, can be treated fairly quickly.
The main cure for this is cleanliness and fresh air. The child should be washed with warm water without soap or other detergents. Several times a day you need to give your baby naked air baths. You should not wrap your child up, but if he does get sweaty, for example, while walking outside in a warm overall in winter, then immediately upon returning home, bathe the child in the shower and change into clean and dry clothes.
For severe diaper rash, damaged skin is treated 2-3 times a day. Most carefully and thoroughly - after daily evening bathing. After it, Bepanten, Desitin, and Sudocrem are applied to still damp skin with signs of prickly heat. Use the powder with great care, since talc dries out the skin very much.
Baby cream or any other greasy creams or ointments should not be applied to the skin of a child with heat rash, as they moisturize and do not dry out. You should also avoid getting massage oil on diaper rash during evening restorative procedures.
Allergic
If the rash is allergic, treatment will involve finding and eliminating the child's exposure to the allergenic substance that caused the rash. To do this, the allegologist performs a series of special tests using test strips with allergens. If it is possible to find the protein that caused the rash, the doctor gives recommendations on eliminating everything that contains such a substance.
If the antigen protein cannot be found (and this happens often), then parents will have to try and exclude from the child’s life everything that poses a potential threat - pollen, food (nuts, whole milk, chicken eggs, red berries and fruits, some types of fresh herbs and even some types of fish, plenty of sweets).
Usually, eliminating the allergen is more than enough for the allergy to stop and the rash to disappear without a trace. If this does not happen, or in case of severe allergies, the doctor prescribes antihistamines (Tavegil, Cetrin, Suprastin, Loratadine and others).
At the same time, it is advisable to take calcium supplements and vitamins. Locally, if necessary, the child is given hormonal ointments - Advantan, for example. Severe forms of allergies, in which, in addition to a skin rash, there are pronounced respiratory manifestations, as well as internal pathologies, the child is treated as an inpatient.
Fungal infections
Fungal infections are very contagious, so the child must be isolated. The children are treated as inpatients. Older children will be admitted to the infectious diseases hospital in case of moderate to severe illness. Antifungal ointments are prescribed as local treatment - Lamisil, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole and others.
In case of extensive damage, when colonies of fungi have “settled” not only on the limbs, on the wrist, on the legs or on the neck, but also on the back of the head in the scalp, in addition to ointments, the child is prescribed antifungal agents in tablets or injections.
At the same time, doctors recommend taking immunomodulators, as well as antihistamines, since waste products of fungal colonies quite often cause an allergic reaction. Treatment for fungi is the longest, after the first course, which lasts from 10 to 14 days, a second, “control” course is required, which must be carried out after a short break.
Treatment of a parasitic infection will require parents to take extensive hygiene measures, since all such ailments are contagious. The child is isolated from other children, and the discovery of scabies or pediculosis is reported to the kindergarten or school so that these institutions can declare quarantine and possibly identify new infected people.
At home, all clothes and bedding of a sick child must be thoroughly washed and ironed. He himself cannot be bathed during treatment.
The time has passed when the treatment of such diseases was quite painful. There is no need to sprinkle lice dust on your head or smear your skin with kerosene.
Modern products in the form of shampoos and solutions for head lice and ointments for scabies and a number of other parasites have a pleasant smell.
It is important to follow safety precautions during treatment. Almost all products are toxic; they should not be allowed to get into the baby’s eyes and ears, mouth or mucous membranes.
Worm infestations
After determining the type of parasite, it is recommended to first cleanse the child’s body of waste products of worms. To do this, you should take enterosorbents, for example, Enterosgel, for 2-3 days. Only after this are anthelmintic drugs prescribed.
At the same time, children are prescribed antihistamines so that their body can more easily overcome not only intoxication due to worms, but also the consequences of taking drugs against parasites.
The doctor decides what exactly to treat for giardiasis, roundworms or pinworms. Not all drugs that are effective in adolescence are suitable for treating children and primary schoolchildren. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Pyrantel, Albendazole, Levamisole and Piperazine.
It is not recommended to treat parasites with traditional medicine, because even if there is an effect from eating lemon and garlic, it will not happen soon, and after taking the drug, most helminthic infestations die within a few hours. During treatment, the child should follow a diet.