Low blood pressure in a child
Low blood pressure is not a rare occurrence, especially in school-age children. Most often, children aged 10 to 14 years are susceptible to hypotension, and most of them are girls.
With low pressure, blood circulation slows down and, as a result, insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues of all organs occurs - hypoxia. For children, this condition is especially dangerous, because hypoxia can negatively affect the development of the entire organism and lead to various pathologies.
In order not to lose attention to the development of hypotension in a child, it is important to know the normal level of pressure. Blood pressure standards for each age are different and depend on the level of physical activity, the child’s weight and genetic predisposition.
During the process of active growth of the body, the volume of blood pumped by the heart increases, and the level of pressure in children increases every year. The heart rate, on the contrary, decreases, because cardiac cycles increase.
Acute hypotension
An acute decrease in pressure can occur with acute circulatory disorders, severe intoxication during infections or poisoning, with sepsis, dehydration or acute blood loss. In these cases, hypotension is considered as a complication of the disease and is eliminated when providing first and emergency care to children.
Secondary acute hypotension is also called a decrease in pressure during shock or collapse, accompanied by acute oxygen starvation of the brain and disruption of the functioning of vital organs - kidneys, liver, heart. The assessment of the severity of such a condition is usually determined not by how much the pressure has decreased, but by how quickly and how expressed this happened, and whether the baby’s body has had time to adapt to the disturbances.
Primary arterial hypotension is pathological hypotension that occurs as an independent disease. The main reasons for its development are heredity, especially if the baby’s mother has hypotension, an unfavorable course of pregnancy in the mother, lack of movement and physical activity of the baby, the presence of foci of chronic infections in the child - tonsillitis, adenoiditis, emotional stress or psychological characteristics of the baby.
The mechanism of development of hypotension is formed due to hormonal and nervous influences; inhibition processes predominate in the child’s body, and hormones enter the circulatory system, sharply reducing blood pressure. As a result, the nutrition of all organs and tissues, especially brain tissue, is disrupted.
Among the manifestations of hypotension in a child, complaints of headaches of various localizations predominate - in the forehead, back of the head or around the circumference of the head. There is dizziness, weakness, lethargy, spots or darkening in the eyes when moving from a horizontal to a vertical position, decreased memory and learning ability, abnormal temperature of the extremities - cold hands and feet, a feeling of numbness. Such children do not tolerate travel in transport, stuffy rooms and stress. During crises, with paroxysmal hypotension, a periodic decrease in pressure below 90 by 50 mmHg may be observed, but there may also be a persistent decrease in pressure - permanent hypotension.
The most striking symptom of chronic hypotension is orthostatic hypotension or even collapse (impaired consciousness). In these conditions, there is a sharp decrease in systolic blood pressure by 10-20 mmHg or lower, and diastolic pressure decreases by 5-10 mmHg. and below. In case of collapse, the pressure when getting out of bed decreases sharply, and the baby may faint. These pressure disturbances can be observed for up to 1-3 minutes, and then gradually recover. Most often, problems with blood pressure are observed in the morning, all of which is accompanied by cerebrovascular accidents. The child may experience dizziness, tinnitus, and fainting, and most often they occur in school-aged children and adolescents.
Norms of blood pressure and heart rate in children
- newborns - from 60/40 to 96/50, pulse - from 110 to 170;
- children under one year old - from 90/50 to 112/74, pulse - from 102 to 162;
- children from 2 to 3 years old - from 100/60 to 112/74, pulse - from 90 to 140;
- children from 3 to 5 years old - from 100/60 to 116/76, pulse - from 86 to 126;
- children from 6 to 9 years old - from 100/60 to 122/78, pulse - from 78 to 118;
- children from 10 to 12 years old - from 110/70 to 126/82, pulse - from 60 to 100;
- teenagers from 13 to 17 years old - from 110/70 to 136/86, pulse - from 60 to 80.
How to correctly independently calculate the norm of blood pressure in a child and measure it using a tonometer, watch the video:
It is necessary to monitor the child's blood pressure level, especially during periods when the child complains of being unwell. Frequent low blood pressure in children is a serious problem.
This condition negatively affects well-being, reduces the child’s physical activity and concentration during school. In addition, hypotension may indicate the presence of serious malfunctions in the body and signal the development of diseases.
Age characteristics
Parents should understand that blood pressure may change throughout the day.
- Up to one year. Immediately after birth, the baby’s blood pressure can still fluctuate from 96/50 to 60/40. Within a month it will change - from 112/74 to 80/40.
- From one year to three years, the baby no longer develops so quickly. Blood pressure can range from 112 over 74 to 110 over 60.
- From three to nine years of age, a reading from 116/70 to 110/60 is considered normal. Schoolchildren may have hypotension due to stress.
- Teenage years. The normal range is from 136/86 to 110/70. At this time, a decrease in pressure is a normal phenomenon associated with hormonal changes.
Causes of low blood pressure
A one-time decrease in pressure can be caused by the influence of external factors. Persistent hypotension - arterial hypotension can be primary - an independent disease and secondary - occur against the background of other diseases.
The cause of the development of primary hypotension in children can be vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypotonic type.
This is a disruption of the functioning of various parts of the autonomic nervous system. It can develop due to severe pregnancy or childbirth, due to traumatic situations in childhood and adolescence, or be hereditary.
Secondary hypotension develops against the background of the following conditions:
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- concussion and traumatic brain injury;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- viral diseases;
- allergic reactions;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- metabolic disease.
Sometimes the development of hypotension in children is caused by the following physiological factors:
- Genetic predisposition. Sometimes persistent low blood pressure in children is a physiological feature of the body. This is especially observed in adolescents who are tall and have a slender build.
- Sports loads. Low resting blood pressure is often observed in child athletes due to the high frequency of physical training.
- Hormonal changes in adolescents. Hormones produced by the pituitary gland and adrenal glands affect vascular tone. During adolescence, hormonal fluctuations can cause low blood pressure.
- The child's living environment. In children living in high mountain areas with low atmospheric pressure, blood pressure levels are lower than generally accepted.
These reasons are not considered pathological, and usually low blood pressure does not cause physical discomfort and does not have a negative impact on the development of the child.
In girls, blood pressure may decrease during the menstrual period. With heavy blood loss, the level of hemoglobin decreases, organ tissues do not receive enough oxygen, and vascular tone decreases.
If during the menstrual cycle you experience severe malaise and a decrease in blood pressure, you should consult a pediatric gynecologist.
Low blood pressure in adolescents can also be caused by drinking alcohol, smoking cigarettes or hookahs, vaping (electronic cigarettes), or taking drugs. It is important to notice in time a child’s addiction to bad habits and protect him from it.
Prevention of hypotension in children:
To prevent hypotension in children, proper nutrition is important. You need to eat 4 to 6 times a day, small portions. Not only children with hypotension should not eat before bed, but also people of any age and with any diagnoses (unless otherwise prescribed by your doctor). Late in the evening it is better to give your child light food - for example, vegetable salads without mayonnaise.
It is better for hypotensive patients to include as much protein as possible in their diet. For breakfast it is better to eat cottage cheese or cheese. A large amount of proteins is found in peas, legumes, and lentils. This is worth considering when you are planning a diet for your child. A large amount of sweets is not recommended for children with hypotension, although you can sometimes hear a different opinion from inexperienced parents. If you give your child sweets, let it be dark chocolate, marshmallows or marshmallows. You can also include dried fruits and orange fruits in the diet of a child with hypotension.
Teenagers with hypotension can drink coffee: ground or instant. Caffeine tones the body. Among drinks, black tea also increases blood pressure. It is worth noting that ginseng preparations are given to children to prevent hypotension. It is better to carry out prevention in the autumn-winter period. Among the herbal remedies, Eleutherococcus and Zamaniha are effective. You should not think that these are harmless drugs. You should consult your doctor regarding their use.
It is necessary to eliminate stress from the child’s life. Provide him with positive emotions. It is useful for a child to have a hobby and play sports.
Symptoms of the disease
The following symptoms may appear against the background of low blood pressure:
- frequent fatigue and drowsiness, most often occurring after school or physical activity;
- a sharp decrease in concentration and level of mental abilities;
- dizziness and clouding of consciousness, short-term loss of consciousness;
- headaches and migraines, with strong pulsation in the temporal region or at the back of the head;
- feeling of nausea, frequent vomiting for no reason;
- intestinal cramps, diarrhea, abdominal pain;
- muscle weakness, muscle aches and pain, tremors of the limbs or the whole body;
- violation of the body's temperature regulation - chills at normal air temperatures, cold and wet extremities;
- feeling of lack of oxygen, frequent involuntary deep sighs;
- increased body sweating;
- pale skin.
Do not ignore the symptoms described above and consult a doctor immediately.
Symptoms
Knowledge of the clinical picture will help to better understand the pathogenesis of hypotension. A similar sign in newborns is often accompanied by:
- severe muscle weakness;
- lethargy;
- pale skin;
- coldness of the extremities.
Such children lack natural activity. Unnatural calm should alert parents.
In cases where low blood pressure is detected in a teenager or a child of primary school age, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Headache. They usually appear in the morning immediately after the child wakes up. They have a pulsating and pressing character. They become stronger during school classes, when the weather changes, or when there is an excess of emotions. In particularly difficult situations, headache does not allow the child to lead a normal lifestyle, play and have fun. He becomes lethargic and tends to rest more.
- Low performance. With hypotension, the child quickly gets tired of physical or mental activity, and the desire to do anything disappears. No matter how much he sleeps, the feeling of weakness and fatigue does not go away.
- Another sign of hypotension is problems with memory and concentration.
- Frequent mood swings, irritability and tearfulness. Hypotonic children are too cautious and touchy. They are less active and mobile than their peers. Sometimes there are difficulties with communication.
- Dizziness. Most often it appears at the moment when the child changes body position, for example, gets out of bed. Also, your head may feel dizzy in a too stuffy room.
- Fainting. This is a characteristic sign of chronic hypotension or a disease in the acute stage.
- Crisis. The child suddenly becomes ill. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, lethargy, increased salivation, abdominal discomfort and rapid heartbeat. The skin is usually covered in cold sweat.
- Heartache.
- Lack of appetite.
- Bloating and bowel problems.
- Bleeding from the nose.
If one or more of these symptoms appear, you should contact your doctor immediately. Knowing the signs and etiology of the disease will help you notice a deterioration in time.
to the point ↑
Diagnosis of hypotension
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a detailed examination to exclude pathologies of internal organs. At the initial visit to the pediatrician, the child may be referred for additional examination to specialized doctors. The type and procedure of the examination depends on the specialist to whom the patient will be referred.
To diagnose hypotension, the following medical tests will be required:
- measuring blood pressure at rest, after physical activity, monitoring pressure over a certain period of time (day, two weeks);
- electrocardiogram and echocardiogram of the heart and blood vessels;
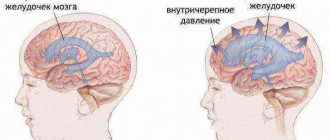
- consultation with a neurologist and examination of cerebral vessels;
- general and biochemical blood and urine tests;
- examination of the fundus by an ophthalmologist;
- examination of the tonsils and sinuses by an otolaryngologist;
- consultation with a gynecologist for girls;
- blood test for hormone levels and diagnostics of the endocrine system.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, first of all, blood pressure measurements are needed. This is usually done in a sitting position for the first half. The measurement occurs three times, the interval between these is three minutes. Also, it is not done immediately after mental or physical stress, but after an hour has passed. In addition, the following diagnostic methods are used: ECG, ECHO-kg, ABPM, study of autonomic homeostasis, EEG registration, psychological testing, clinical and biochemical blood tests, consultation of the necessary specialists in order to exclude secondary arterial hypotension. To confirm the diagnosis of arterial hypertension, daily monitoring and tests with different types of stress are used. During the study, it is important to identify the cause of the increase in pressure if hypertension is secondary. This is what helps the doctor prescribe effective treatment. If the cause of hypertension is not eliminated, treatment measures will not give the desired effect, the result will be temporary.
Treatment of hypotension
Depending on the cause of hypotension in a child, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. If low blood pressure is due to a hereditary predisposition or living environment and does not cause discomfort in life and study, then treatment is not required.
If hypotension develops against the background of VSD, then in addition to drug therapy and outpatient monitoring, preventive measures are prescribed to correct blood pressure:
- adherence to daily routine and sleep patterns;
- balanced nutrition, additional intake of a complex of vitamins and minerals;
- moderate physical activity: swimming, cycling, walking in the fresh air;
- taking herbal medicines;
- reduction of academic and extracurricular workload;
- therapeutic herbal baths and massage.
You may need appropriate treatment from a psychologist or psychotherapist if the cause of the development of VSD in a child was due to individual psycho-emotional personality characteristics or the influence of negative social factors at school or family.
If secondary hypotension is diagnosed, the underlying disease is treated first. In addition, symptomatic treatment of low blood pressure in a child is prescribed with drugs that stimulate the central nervous system.
Treatment tactics
Therapy for hypotension is prescribed taking into account the age of the child.
Folk remedies
If there are no contraindications, you can try alternative medicine recipes. They have no side effects and are safe. But despite this, their use requires consultation with a doctor.
Among the folk remedies, herbal infusions and decoctions can increase blood pressure. According to the recommendations of experts, they can be drunk instead of tea and other drinks. These include:
- Eleutherococcus;
- ginseng;
- currant;
- celery;
- lemongrass;
- lure;
- raspberry and parsley leaves.
Separately, it is worth mentioning about eleutherococcus and ginseng. Most often they are used in the form of ready-made tinctures, which have a large number of useful properties:
- tone the body;
- strengthen blood vessels;
- increase immunity;
- normalizes blood pressure.
Another remedy that helps cope with hypotension and reduce its severity is chopped radish with honey. The ingredients should be mixed in equal proportions and given to the child as a separate dish or with other foods.
to the point ↑
Correct mode
Equally important for low blood pressure is your daily routine. Experts give some advice regarding this:
- The child's rest should take at least 9 hours a day.
- The baby should spend at least 2 hours outside. At the same time, he should not be under the sun.
- It is important to properly distribute mental loads, alternating them with entertainment and games.
to the point ↑
Balanced diet
You can normalize your child’s blood pressure with proper nutrition. The menu should include the following products:
- Spices and herbs, such as bay leaves, pepper or cinnamon.
- Fatty fish and meat.
- Fermented milk products with high fat content.
- Bakery.
- Green and black tea.
- Honey.
- Potatoes, semolina, buckwheat and other products that contain starch.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits that will help replenish vitamin deficiencies. Particular attention should be paid to cabbage, carrots, pomegranates, etc.
- Any types of nuts.
Also, the diet of a child with low blood pressure should include foods that will help compensate for the lack of protein in the body:
- hard cheese;
- eggs;
- soy milk;
- legumes (fresh and canned);
- smoothie made from fruits and berries.
Children suffering from hypotension should eat more often than healthy children. Food should be varied. You need to add snacks to your main meals.
to the point ↑
Walking in the fresh air and therapeutic exercises
First of all, regularity is important. It is advisable to allocate at least 2 hours a day for this. The child must be dressed according to the weather and not spend a lot of time in the open sun.
Physical exercise requires no less regularity. They should be selected by the attending physician.
Gymnastics for hypotension has several goals:
- general improvement of the body;
- mood lifting;
- improving blood circulation;
- training of organs and organ systems;
- increased muscle tone.
There are several useful exercises for low blood pressure:
- Walking comes first. There are no special instructions regarding breathing. Each part takes half a minute to complete. First you walk normally, and after that you need to swing your arms, raising your knees. Next, you should put your hands on your belt and walk on your toes. At the end - again half a minute of normal walking.
- To perform the next exercise you will need a gymnastic stick. Stand straight, place your feet shoulder-width apart. The stick should be located behind the body near the shoulder blades. It is necessary to perform four turns alternately in each direction. At the same time, you need to turn both your head and body.
- Standing straight, raise your arms up. As you inhale, stretch, and as you exhale, lower your arms down and relax your body. The exercise should be performed slowly. Repeat 3-5 times.
to the point ↑
Hardening
Of all the hardening procedures when treating hypotension in a child, special attention should be paid to the contrast shower. It has an extremely beneficial effect on the body:
- gives vigor;
- strengthens the immune system;
- tones blood vessels;
- improves blood circulation.
In order for a contrast shower to benefit a child’s body, it is necessary to adhere to several rules:
- At the very beginning (first 15 seconds) the water should be warm or hot.
- Next for 15 sec. change the water to cold.
- Then it's hot again. Repeat this three times.
- At the end of the procedure, rub the child’s body with a towel.
- Every 2-3 days you should lower the water temperature.
- It is recommended to start training in the summer.
You should not take a contrast shower if there are problems with the heart, problems with blood vessels, or if the disease has worsened.
to the point ↑
Massage
Massage is an effective treatment for hypotension. It has the following effects on the body:
- Normalizes the functioning of the nervous system.
- Improves resistance to negative external influences.
- Accelerates the recovery process and recovery from diseases that cause blood pressure to decrease.
- Helps cope with unpleasant symptoms.
In some cases, massage is strictly prohibited. This includes the child’s poor health, too low blood pressure, and a period of exacerbation of hypotension.
During the procedure, special attention is paid to the collar area, spine, abdomen and legs.
Important! Only a specialist can perform massage of the spinal column in children!
to the point ↑
Phytotherapy
To increase blood pressure, you can give your baby one of the herbal teas. They have a complex effect on the body:
- normalize sleep;
- help cope with neuroses;
- relieve pain in the heart and tachycardia;
- return to functionality;
- give vigor;
- relieve fatigue.
Herbal mixtures for low blood pressure include herbs such as chamomile, nettle, motherwort, sage, St. John's wort, heather, sweet clover, and lemon balm. Baths with herbal decoctions, such as valerian, help.
Separately, it is worth mentioning hypotension in infants. Often, pressure can drop during an anhydrous period, that is, when the ambient temperature becomes higher and the amount of moisture in the body is reduced. Therefore, you should monitor your child’s drinking regime.
to the point ↑
What you need to remember (video)
- Low blood pressure in a child may indicate the presence of serious illnesses.
- Prolonged oxygen deprivation of body tissues against the background of hypotension can negatively affect the development of the child.
- It is important to independently monitor your child’s blood pressure and not ignore symptoms of hypotension.
- Only a doctor can diagnose the disease and prescribe proper treatment. Be sure to consult a doctor if your child has symptoms of hypotension.
Prevention measures
Proper nutrition is considered one of the most effective.
The diet should include honey, royal jelly, nuts, herbal infusions (ginseng, lemongrass, Rhodiola rosea), celery, apples, as well as other components with properties to increase the vitality of the body.
A healthy lifestyle also plays an important role in normalizing the blood circulation process.
Preventive measures against hypotension include:
- the diet should contain foods that have a tonic effect on the body (food should be enriched with vitamins, beneficial elements and fatty acids);
- Dark chocolate, buckwheat, pomegranates, apples, liver, egg yolks, carrots, green parts of plants, etc. are good indicators for increasing blood pressure (the introduction of such products into the diet will not only increase blood pressure if necessary, but will also be a means of preventing hypotension );
- the use of herbal biostimulants for the periodic occurrence of symptoms of hypotension (tinctures of aralia, rosea rhodiola, lemongrass, ginseng);
- avoiding dehydration (each person is recommended to drink at least two liters of water per day);
- daily exercise (it is enough to do a few exercises, and not spend hours in the gym);
- healthy and complete sleep;
- playing sports (swimming, regular jogging, at least minimal visits to the gym);
- exclusion of stressful situations or;
- hardening and contrast shower (invigorates and tones the body);
- daily breakfast (you can limit yourself to portions of light dishes, but the body must receive food in the morning);
- if symptoms of hypotension appear suddenly (if you are in good health), then you must consult a doctor in a timely manner to find out the cause of this condition (internal bleeding can cause a decrease in blood pressure, creating a threat to life).
If the recommendations are followed, the risk of hypotension will be reduced. An exception is congenital forms of low blood pressure, but even in this case, the correct daily routine will help alleviate the body’s condition.
Watch the TV show “Live Healthy” with Elena Malysheva about hypotension:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=8I6FHDO2u4k
How are such children treated?
Usually, a whole range of measures for the treatment and rehabilitation of such children is developed; as a rule, they are observed by a pediatrician and a cardiologist (and sometimes a neurologist) simultaneously.
Therapeutic measures begin with general strengthening measures - the child is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air, engage in more and more active sports and physical education, get enough sleep, follow a daily routine - work and rest should be reasonably alternated. However, the loads for such children must be dosed - participation in strength sports and competitions is not for them; water procedures are indicated. The baby is advised to eat a rational and balanced diet; morning tea (black or green) or coffee is acceptable.
The prescription of vitamins and procedures that have a tonic effect on the nervous system is indicated - caffeine, tincture of Schisandra chinensis, ginseng, glutamivit.
Drug therapy is indicated only in cases of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure or a serious condition of the child, when complaints are made - this is the prerogative of the doctor.
By adulthood, and sometimes even earlier, in 85% of children, hypotension goes away without a trace. This is due to the peculiarities of modern growth and development of children, with acceleration. The child’s blood vessels simply cannot keep up with the active growth of the skeleton, due to which the vascular tone does not make it possible to maintain the pressure at certain normal values. With age, the muscular framework of blood vessels is fully formed and the pressure normalizes.
Causes and predisposing factors
Usually, each baby has a combination of several factors that can be causative or predisposing or provoking.
One of the main reasons for the development of VSD is the hereditary and constitutional features of the activity of the VNS. The parents' tendency to have disorders in the autonomic nervous system is often inherited by their children.
An important role in the development of VDS is played by the course of pregnancy and childbirth, and according to statistics, up to 80-90% of children with this diagnosis are born as a result of rapid or prolonged labor, with the use of various obstetric aids. Upon detailed questioning - when the child cried, was he restless in the first month of life, was there regurgitation, unmotivated increases in temperature to high numbers or prolonged low-grade fever, hemorrhages in the retina - many note characteristic changes.
An important role is played by traumatic lesions of the nervous system - traumatic brain injuries, closed and open, tumors and infections of the brain and spinal cord, poisoning with effects on the nervous system.
An important role is played by the mental and emotional state of the child, an unfavorable environment at home, psychological incompatibility of family members, alcohol abuse by parents, improper upbringing - cruelty, hypo- or overprotection, conflicts at school, mental fatigue.
Provoking factors for the development of VSD are infections, chronic diseases of organs and systems, tonsillitis, caries and sinusitis as sources of chronic infection. Important factors are hormonal disruption in the body during puberty and acquired problems with the endocrine system.
Important for development are the influences of physical inactivity, excessive physical exertion, surgical interventions and anesthesia, unfavorable or sharply changing meteorological conditions, allergies, etc.
The basis for the development of the disease is a failure of the system of adaptation to stress; due to excessive mental and emotional stress, an imbalance of metabolism and hormonal balance occurs. The coordinating activity of the hypothalamus and nervous system suffers. As a result, the formation of unpleasant symptoms in the cardiovascular, digestive and other systems.