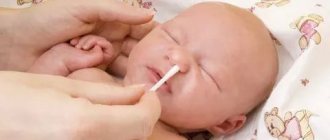
Treatment of a purulent wound in a child
Children are constantly on the move. They do not know fear and do not think about the consequences of their games, so wounds and scratches are a common occurrence for an active child. Sometimes babies do not show their injuries to their parents, and over time an abscess forms on the damaged area. What to do with purulent wounds on a child?
Any wound should be treated before visiting a doctor, but if a purulent focus appears over time, it is recommended to consult a specialist
Symptoms of an abscess in a child
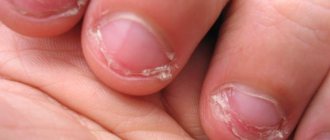
Abscesses can appear on any part of the baby's body. Both deep cuts and small scratches suppurate. Wounds on the finger near the nail are very unpleasant. Symptoms of an abscess:
- redness of the skin around the wound;
- the place of suppuration is hot to the touch;
- throbbing pain;
- swelling of adjacent tissues;
- headache, weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of a vesicle with pus.
Causes of purulent wounds
Suppuration occurs when an infection enters the wound. This often happens in children with weakened immune systems. Predisposing factors include high humidity, poor personal hygiene and improper treatment of cuts.
Hangnails and the habit of biting nails can provoke the development of suppuration on the fingers
The main reasons for the appearance of purulent wounds on the fingers in children include:
- burrs;
- ingrown toenails (how to treat an ingrown toenail in a baby?);
- fungus;
- splinters;
- habit of biting nails and putting fingers in mouth;
- cuts from sharp edges of paper or toys;
- getting dirt or sand into the wound while playing.
In newborns, suppuration is rare. The main cause is ingrowth or injury due to improper trimming of the nail. For this reason, it is recommended to remove overgrown areas of the nail plate in a straight line, preserving the corners.
Treatment using medications and folk remedies
If an abscess forms in a child, it is necessary to seek medical help. The specialist will prescribe treatment depending on the patient’s age. You cannot open purulent lesions yourself, as this can lead to the spread of infection.
Therapy is aimed at cleansing the wound of pus, getting rid of inflammation and restoring damaged tissue.
In infants
Treatment of infants is approached with caution. When choosing drugs, it is necessary to take into account possible side effects and not exceed the recommended doses. To cleanse the wound of pus, use hydrogen peroxide or a manganese solution. Antiseptics are used to treat the surface around the affected area.
After cleansing, apply a sterile bandage with ointment previously applied to the wound. All manipulations must be carried out with gloves. The dressing is changed at least once a day. The following ointments are used to eliminate the infection:
- Levomekol;
- 1% Salicylic;
- Baneocin (instructions for use for Baneocin powder for newborns).
After pus stops accumulating in the wound and a crust forms, wound-healing drugs are used. For infants, Bepanten, Methyluracil, Solcoseryl, Actovegin ointments are used (see also: why is Actovegin ointment prescribed to children?). The drugs are applied directly to the wound. You don't have to wear a bandage.
When choosing folk remedies for treating abscesses, it is necessary to take into account the baby’s individual reactions to herbal components. Traditional methods promote rapid healing and facilitate the release of pus. The following traditional medicines are considered the safest for treating children:
- Soda solution. You need to mix 2 parts of soda with 10 parts of water, soak a bandage in the solution and apply it to the site of inflammation for 15 minutes.
- Boiled potato compresses.
- Treat the affected skin with sea buckthorn oil 2-3 times a day.
In children older than one year
Treatment of children older than one year follows the same scheme as for babies. However, the list of drugs used in therapy is much wider.
To eliminate the infection, Vishnevsky, Streptocide, Ichthyol, Levomekol, Dioxidin ointments are used. After eliminating the pus - Dolobene and Troxevasin.
If the spread of infection is suspected, children over 3 years of age can be given antibiotic tablets - the drug is prescribed by the attending physician.
To heal wounds, traditional medicine recipes based on honey or aloe are used. A popular remedy is an ointment made from 1 raw egg yolk, a teaspoon of honey and 1 tbsp. spoons of flour. Often a cut aloe leaf or gauze soaked in its juice is applied to the inflammation.
What to do to prevent the wound from festering?
Proper first aid will prevent the open wound from festering. First of all, you need to wash the wound with an antiseptic (hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine) or soap solution. Next, treat the edges of the wound with brilliant green or Fukortsin, and apply a sterile bandage over the deep wound. In case of severe injuries, after providing first aid, you need to take the child to the emergency room.
Pediatrician of the 2nd category, allergist-immunologist, graduated from the Belarusian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development.
Read more »
Purulent wounds. What it is?
A purulent wound is characterized by the development of an infectious process or, more simply, the formation of pus, swelling and necrosis of tissue, and the proliferation of harmful microbes.
The peculiarity of a purulent wound is that, unlike other types of wounds, it takes longer and is more difficult to heal. It's no secret that children are more active and inquisitive than adults.
They spend a lot of time playing outside, often fall and get hurt, so children have a higher risk of getting hurt.
Parents should remember that absolutely any wound, regardless of its size, can be infected with bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Proteus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Klebsiella spp. After all, a child, if the wound does not hurt, can calmly continue playing in the ground or in the sand. And this is dangerous due to infection and subsequent suppuration!
Treatment of a purulent wound is selected depending on the phase of the wound process.
PERIODS AND PHASES OF HEALING OF PURULENT WOUNDS
| Healing periods | Features of treatment | |
| Early healing period | The first 12 hours after injury. Characterized by the presence of a blood clot and a primary inflammatory process | In the early period, the main task is to prevent complications and possible wound suppuration. If the wound is not treated, then the matter may end not only in a visit to the surgeon at the clinic, but also in the hospital. A visit to the surgeon can be avoided if you use Sulfargin ointment in a timely manner - this is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. It is active against staphylococcus, clesibella, E. coli and other opportunistic bacteria that penetrate the wound and cause suppuration. The main active ingredient of the drug is silver ions, which have a powerful antimicrobial effect. |
| Degenerative-inflammatory period | Approximately 5-8 days. Necrotic changes, formation of purulent exudate, and tissue edema are noted. During this period, the patient complains of pain in the wound area, body temperature may rise, and there is general weakness and hyperemia. | The main task at this stage is the fight against microorganisms in the wound. If the wound is extensive, then a course of oral antibiotics is prescribed and a bandage with silver-based ointment is applied over the wound. |
| Regenerative period of wound healing | On average it lasts 30 days and is divided into three phases: Phase I: The amount of purulent discharge from the wound decreases; the wound is filled with granulations (the tissue becomes bright pink or red). Phase II: The wound begins to fill with connective tissue; The swelling gradually goes away. Phase III: A scar is formed. | Antimicrobial ointments are widely used, including Sulfargin, which contains 2 antimicrobial components: 1) Silver ions 2) Sulfadiazine Silver-based ointment maintains the wound in a moderately moist state, thereby accelerating healing; a crust on the wound in this case does not interfere with healing. The goal of therapy at this stage: accelerate the process of granulation and formation of new tissue at the wound site. To speed up the epithelization process, physiotherapeutic treatment is used (electro- and phonophoresis, UHF) |
Parents' attentive attitude to the child's health, up to a daily examination after a walk or a day spent in kindergarten, will help prevent a large number of problems. A small scrape or pimple left untreated from a knee injury caused by falling off a bicycle can develop into a more serious and dangerous problem.
It is difficult to stop small children - they are very mobile and, if they play too much, they can hit or scratch themselves. If the wound is not treated, an abscess appears on the damaged area due to poor hygiene. Should I treat it myself or contact a specialist? Is it worth eliminating abscesses in infants yourself? Which treatment methods are better to use - traditional or medicinal?
Causes and symptoms of abscesses in children
Causes of suppuration near the nail:
- habit of biting nails;
- cuts and abrasions received during play or falling;
- scratches caused by animals;
- splinters;
- ingrown nail;
- careless cutting of nails;
- hangnails left after cutting nails.
Suppuration not only looks unsightly (redness appears, the tissue around the abscess thickens and swells), but also causes pain to the child.
Twitching spasms are felt, pus accumulates, and the ichor comes out. The finger becomes inactive, every movement brings pain.
During the formation of an abscess capsule, the child’s body temperature may rise, he quickly gets tired and becomes nervous.
First aid for a child
You can ease the pain of a purulent wound by dipping your finger in a warm bath (water with salt, potassium permanganate, alcoholic infusion of calendula or soap, chamomile decoction). This procedure needs to be done several times a day. However, this is one of the methods of first aid, and not a means of treatment, so in any case, the help of a specialist will be required.
It is impossible to puncture a bladder with pus - the liquid will not flow out completely, and the puncture will not bring any benefit. The pus will continue to accumulate, and the child will again experience discomfort.
Treatment of purulent wounds on the finger in infants and older children
If you notice an abscess on your finger near the nail, start treating it immediately. If the affected area is small, the abscess can be cured on your own. Traditional methods will help in a few weeks, medications will help faster. First of all, treat the reddened area with an antiseptic - it can be iodine or brilliant green. Then use medications or traditional recipes.
If the abscess is noticed late, when pus has already begun to accumulate, under no circumstances should you open it yourself, because a secondary infection can easily be introduced into an open wound. Without the help of a specialist, you can only speed up the process of abscess maturation; for this, salt baths are used.
Medications
To treat a purulent wound, ointments are used: Vishnevsky, ichthyol or Levomekol. They have antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. However, these remedies have many contraindications, and you should not use them without consulting a specialist.
Dimexide solution has a powerful antiseptic effect. Lotions with this drug are used in cases where warm compresses or baths are contraindicated.
Folk remedies
There are much more folk remedies for treating abscesses than medicinal ones. The most common and effective:
- bath with salt and soda (300 ml of water, salt and soda 1 tablespoon each, hold the sore finger for up to 20 minutes);
- honey cake (mix 1 tsp each of flour and honey, apply to the sore finger for 8-12 hours);
- puree of fresh carrots, onions, beets (mix with a small amount of aloe juice, apply to the abscess);
- fresh aloe leaves (cut lengthwise, cut off the thorns, apply to the injured finger, change every 3 hours);
- tincture of Sophora japonica (sold in a pharmacy; lotions are made from it on a sore spot);
- St. John's wort (1 tablespoon of dried herb, pour 300 ml of boiling water, cover, leave for 20 minutes, cool to a comfortable temperature, then make lotions or baths);
- resin-resin (apply to gauze or cloth, apply to the abscess for 3-4 hours).
To make the pus ripen faster, you can prepare a paste of baked onions and laundry soap in a 2:1 ratio. Apply the resulting product onto a bactericidal patch and apply it to the sore finger. The dressing needs to be changed every 4 hours.
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist, graduated from Samara State Medical University with a degree in Pediatrics.
Read more »
Possible causes of an abscess
- A purulent abscess on the finger often occurs due to the habit of biting nails. A child’s teeth damage the skin, allowing pathogenic bacteria to enter the body.
- The finger is festering due to hangnails. Since children's skin is very delicate, even a small defect in the skin near the nail allows dirt to penetrate the body.
- The inflamed area breaks out due to the pliability of the nail plate in infants. If you trim your nails incorrectly or carelessly, you can deform the nail, which can lead to it growing into the skin. This, in turn, leads to tissue inflammation.
READ ALSO: Red spots on the skin in adults and children - types of rashes and their photos, allergies with and without itching
How to wash a purulent wound and how to treat it: an algorithm for treating and dressing festered wounds
A purulent wound is characterized by the development of a local inflammatory process with purulent discharge. Any clean wound can fester when various microorganisms or dirt particles enter it. In this situation, it is necessary to properly treat the purulent wound, otherwise the condition will worsen and numerous and quite serious complications will arise.
In this article you will learn how to treat purulent wounds, how to properly wash the wound, and you will also find an algorithm for treating and dressing a suppurating injury.
Washing a festering wound
To improve the regenerative properties (healing) of the soft tissues of a purulent wound, it is necessary to ensure its complete cleansing. For this purpose, the wound cavity is washed. Moreover, this procedure is carried out both during the initial and subsequent treatments.
It should be remembered that in the presence of an extensive wound with a large amount of discharge, it is necessary to remove the main volume of pus first. It can be pulled out using a rubber bulb or an aspirator. After this, they proceed to washing.
The sequence of washing a festering injury:
- Prepare medications for rinsing and the necessary equipment. Wear sterile gloves;
- Purulent wounds should be washed with antiseptics such as:
- An antiseptic is poured into the wound cavity. The stream of solution should be strong enough to wash away the discharge. As a rule, hydrogen peroxide comes in bottles with a convenient narrow tip, which ensures sufficient dosing of the product. If there is no such device, then use a disposable syringe (volume 10 or 20 milliliters) without a needle;
- After rinsing, the cavity must be blotted with a dry, sterile gauze cloth. The edges of the injured area should be treated with alcohol, iodine or brilliant green (the more common name is “green”).
Treatment of purulent wounds
Wound treatment is carried out daily, with each dressing. For this purpose, various antiseptics are used, as well as ointments and solutions with antibiotics and enzymes.
Processing in a hospital is carried out under sterile conditions. If this manipulation is carried out at home (the wound is not large and the discharge is light), then it is necessary to thoroughly wash your hands, use sterile bandages and napkins, and disinfect the scissors (treat with an alcohol solution or medical alcohol).
Algorithm for treating a purulent wound:
- Remove the bandage, if any;
- Clean the wound with hydrogen peroxide;
- Dry the cavity with a sterile cloth;
- Spray the surface with an antiseptic solution;
- The edges of the injury also need to be treated with alcohol solutions (iodine, brilliant green);
- An antibacterial agent is placed in the cavity . In the first phase (inflammation), solutions are widely used, and in the second - ointments;
- Dressing is in progress.
Solutions used in treatment:
- Antiseptics help clean the wound and prevent the development of the decomposition process. These drugs are used in the inflammation phase, when intense discharge of pus is observed. Chlorhexidine and Hydrogen Peroxide are most often used in hospitals. They prevent the development of infection and have a detrimental effect on some microbes (especially anaerobic) and fungi. Modern drugs of this group are Iodpirone and Miramistin;
- Hypertonic solutions are used to improve the outflow of purulent secretions and remove bacteria from the wound. They improve the effect of passive drainage. In surgery, a 10% sodium chloride solution is preferably used. Boric acid also cleanses the wound site well;
- Antibacterial solutions are used to destroy microbes and relieve inflammation. The drug Dioxidin is widely used, which has a bactericidal effect, that is, it kills bacteria.
- Dimexide solution has a complex effect. It works as an antiseptic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antihistamine. This solution prepares soft tissues for the absorption of other dosage forms.
Ointments used in treatment:
- Antibiotic ointments : Tetracycline, Methyluracil, Levomekol, Baneocin, Levosin and others. Currently, surgeons prefer water-soluble ointments such as Baneocin, Levosin and Levomekol. They are well absorbed and do not interfere with the outflow of pus;
- Vishnevsky ointment still does not lose its popularity and is used in the treatment of open injuries;
- Ointments with enzymes , for example, Iruksol. Preparations containing enzymes such as trypsin and chymotrypsin improve the regeneration of damaged tissues.
Dressing rules
Dressing of a purulent wound is carried out daily. If the discharge is abundant, then the bandage is changed 2 times a day.
Extraordinary dressing may be carried out in the following cases:
- Significant contamination of the dressing over a short period of time;
- Increasing pain or its sudden onset;
- The appearance of bleeding.
This procedure is carried out under sterile conditions in a special room - a dressing room. Extensive wounds require treatment in the operating room under anesthesia.
Algorithm for performing dressing:
- The procedure is carried out by a doctor and a nurse. They should thoroughly clean their hands and wear sterile gloves;
- The patient lies down or sits on the couch;
- If necessary, local anesthesia is performed;
- If there is a bandage, it must be carefully removed without causing pain to the patient . It is cut using scissors. If it sticks to the wound site, then it is soaked with hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin solution. After this manipulation, gloves should be changed;
- The wound is washed with antiseptic solutions, after which the cavity is dried with a sterile gauze pad;
- If there is drainage, the materials are removed and the cavity is washed again;
- Treating the edges of the injury;
- If there are areas of necrosis (death of soft tissue), the doctor removes them. The purulent pockets are also opened and subsequently washed;
- If necessary, a new drainage is installed;
- Ointment or napkins moistened with medicine are placed in the injured area;
- The wound must be covered . To do this, a bandage is applied, or the bandage is secured with an adhesive plaster.
All instruments must be processed and disinfected, and used dressings must be immersed in a disinfectant solution and then disposed of.
Folk remedies for treating purulent injuries
There are many traditional medicine recipes that help heal festering wounds. However, it should be remembered that before starting treatment with these drugs, you must consult with your doctor.
Folk remedies must be approved by a specialist, since otherwise they may worsen the pathological process. You should also consider the presence of allergic reactions to natural ingredients.
How to treat a purulent wound at home? The indoor plant Aloe has long been used to treat this kind of pathology. Aloe pulp and juice have a bactericidal, wound-healing and draining (pulling out pus) effect.
Treatment with Aloe leaves:
- It is necessary to squeeze the juice from this plant. Soak a sterile gauze pad with this juice and apply it to the damaged surface. Change the dressing every 3 hours;
- The plant leaf must be washed well and then cut lengthwise. It is applied with pulp to the wound and securely fastened. Duration of exposure is 2 hours, after which the sheet must be changed;
- You can make a paste from the pulp of the plant and apply it to the damage.
You can wash a purulent wound at home using a decoction of chamomile flowers . To prepare it, you need to take 2 tablespoons of dry chamomile and 200 milliliters of boiling water. The decoction is prepared in a water bath. After which it is cooled and filtered.
Onion gruel helps remove pus and promote healing. It is applied to the injury itself and left for 5 hours.
Solutions of salt and soda are used to rinse the cavity, they help clean it:
- Preparation of soda solution: 2 parts soda and 10 parts water;
- Preparation of saline solution: 1 part salt and 10 parts water.
Before using all of the above remedies in the form of compresses, it is necessary to treat the wound.
Victor Systemov - expert of the 1Travmpunkt site
This article is often read with... Purulent wounds Algorithm for dressing a purulent wound Treatment of wounds Algorithm for performing PST of a wound (primary surgical treatment) Treatment of wounds Algorithm for dressing a clean wound Treatment of wounds Use of Chlorhexidine for treating wounds and cuts
Classification of bleeding First aid for cuts and abrasions
Features of treatment in children
If you notice an abscess on your child's finger, be careful. The fact is that not all remedies and treatment methods that are suitable for adults can have a positive effect in children. If the condition worsens, you should immediately contact a specialist.
If a wound appears on the side of the finger, you need to treat the damaged area with antiseptics to prevent the development of the disease. To eliminate swelling, steaming the affected finger in a solution of soda, potassium permanganate or salt is suitable.
If a child has ingrown nails into the skin, tamponade is performed. This procedure takes place in several stages. First, your hands are steamed in a warm soda solution. Next, the ingrown toenail is pulled back using a sterile instrument, and a piece of gauze soaked in any antiseptic is placed under the retracted area of the nail plate (we recommend reading: a baby has an ingrown toenail - what to do?). After which the finger is bandaged.
Drug therapy
The choice of treatment method and medications depends on the degree of neglect of the disease and the time that has passed since the onset of felon development. In the early stages, further development of the pathology can be prevented at home using the folk remedies discussed below.
If the child suffers from severe throbbing pain and the swelling does not subside, you should seek help from a surgeon. The specialist will examine the baby, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Abscesses are treated using the following means:
- Levomekol is an antibiotic-based ointment. It draws out pus well. After disinfection, apply to the inflamed area.
- Ichthyol ointment. It is applied to the pathological area. It has the ability to penetrate deep into the skin, where it kills pathogenic bacteria, soothes and reduces inflammatory processes, relieving swelling and reducing pain.
- Antifungal ointments. Used when the fungus penetrates the affected tissues. The following drugs are suitable for children: Mikozan, Batrafen, Demikten, Belvedere. Before applying the product to the nail, the damaged areas are filed off with a nail file.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are best used in the early stages of the disease, as they will not help cure complications. Such drugs are loyal to the immune system and usually do not cause side effects.
For a small cut, improvised means such as ice or any item in the freezer will help. Using it, a cold compress is applied to the problem area. Cold slows down metabolism, thereby stopping the inflammatory process. This compress will also reduce pain and swelling.
You can neutralize germs, relieve swelling and draw out pus using a bath with saline solution (1 tbsp per glass of warm water).
Other effective folk remedies include:
- Baths with furatsilin solution. Place the baby's sore finger in the bath for 10-15 minutes, then rinse and bandage with a loose, not very tight bandage.
- Applications with blue clay, which has the property of drawing pus from the wound, while simultaneously disinfecting the affected area. It also has a bactericidal effect, so it can be applied to an open wound. The clay is applied to a bandage, which is applied to the disturbing area. This compress should be kept for 3-4 hours, after which the area of skin that was under the bandage is washed and sealed with a sterile bandage.
Baked onions are a very effective remedy for purulent abscesses.
- Baked onion compress. You should bake the onion in the oven or microwave, cut out the core so that your finger can fit there. The problematic finger is placed in the bow and fixed in this position with a bandage. The bandage should be kept on for 3 hours, after which you need to wash your hands and bandage your finger.
- Beetroot compress. Before the procedure, the damaged nail must be disinfected (you can keep it in the saline solution discussed above). Apply finely chopped beets to the wound and bandage tightly. This bandage should be kept for 4-5 hours.
- Treatment of abscess with herbal decoctions. Our ancestors also engaged in gathering and treated diseases with medicinal plants. To prepare a decoction, you need herbs with antiseptic properties that help remove inflammation (chamomile, St. John's wort, plantain leaves, sage, lilac inflorescences). To a decoction of 2 tbsp. herbs and 400 ml of boiling water, add a large pinch of soda. Keep your finger in the warm solution for 10-15 minutes.
If pus appears under the nail during or after the procedures, it is better to squeeze it out. This will contribute to the baby’s speedy recovery.
In what cases is surgery required?
What to do if the patient does not recover, and the damaged area festers even more? A surgeon comes to the rescue. He examines the small patient and then operates on the problem area. The pus is cut out from the wound, then it is washed with an antiseptic solution. After the operation, the finger is bandaged, the sterile bandage is changed 3-4 times a day.
Algorithm for treating a purulent wound
A purulent wound is characterized by the development of a local inflammatory process with purulent discharge. Any clean wound can fester when various microorganisms or dirt particles enter it. In this situation, it is necessary to properly treat the purulent wound, otherwise the condition will worsen and numerous and quite serious complications will arise.
In this article you will learn how to treat purulent wounds, how to properly wash the wound, and you will also find an algorithm for treating and dressing a suppurating injury.
What to do if the wound does not heal and festeres: treatment methods
Wounds
Treatment of purulent wounds depends on the location, severity, clinical picture, and stage of inflammation. It is aimed at removing exudate and dead cells. Traditional methods of therapy are used in combination with medications as prescribed by a doctor.
What to do if the wound festers and does not heal
People do not pay attention to minor abrasions and scratches that occur on the lip, cheek, leg, arm, chin, knee. Redness is a sign of an inflammatory process, provoked by the presence of purulent discharge.
The condition is accompanied by an increase in local temperature and fever. If personal hygiene rules are not followed, the risk of developing an abscess increases. Exudate is a yellow discharge that occurs in places of damage due to the inflammatory process.
Failure to comply with the rules of asepsis and treatment can lead to the growth of bacteria.
You can treat a purulent wound with antiseptics - Chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide. There are different methods of performing the procedure using medications. The purpose of the manipulation is to dry the affected area and prevent the inflammatory process.
Features of wound treatment
Treatment of scratches, abrasions, abscesses, and cuts is carried out in a hospital or at home. The pathological cavity with pus should be washed with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Laundry soap has antibacterial properties. The first procedures can be carried out using the product, then the purulent wound should be treated with antiseptics:
- furatsilin;
- peroxide;
- Chlorhexidine is used to treat a purulent cavity.
In case of severe tissue damage in combination with inflammation, the edges of the wound are lubricated with ointments containing an antibiotic.
Drugs used for treatment are used to prevent the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into tissues. The exposed surface is fixed with an antiseptic bandage.
Postoperative sutures, diabetic ulcers, post-burn injuries, bedsores with serous discharge must be treated under the supervision of specialists in a hospital setting. The doctor, using a medical set of instruments, dressings, and antiseptics, can extract purulent exudate. Necrotic flaps of tissue are removed surgically.
Treatment methods
To speed up the recovery process, purulent wounds need to be treated comprehensively. The therapy is aimed at:
- elimination of pain;
- cleansing the surface of purulent contents;
- suppression of inflammation;
- increasing the protective functions of the body;
- acceleration of cell regeneration.
A conservative method of treating a purulent wound involves the use of traditional medicine recipes. As an independent therapy, the method is considered unacceptable. Native drugs are used to stimulate healing. If drug treatment does not produce results, surgery is performed to excise the necrotic tissue.
Hypertonic solution
The action of the product is based on the generally accepted laws of physics - osmotic pressure. Moistened gauze draws moisture from organic tissues, allowing serous contents to be removed.
The salt concentration in human blood plasma is 0.9%. This fact explains the use of an isotonic solution for diluting drugs. Hypertonic fluid is characterized by a concentration of 1 to 10 percent. For external use, use a 2% concentrate. The 10% product can be purchased at a pharmacy or prepared at home.
To prepare you need to add 3 tbsp. l. salt in 1 liter of hot water. After the crystals are completely dissolved, they should be cooled.
Treatment of purulent non-healing wounds with a hypertonic solution is carried out in 4 stages:
- Moisten gauze, folded in 8 layers, with salty liquid.
- Apply to the wound, securing the compress with a bandage. It is impossible to cover the pathological area with film.
- Leave the compress on for 10-12 hours.
- To achieve the effect, the course of treatment should be 7-10 days.
Local preparations
To treat purulent lesions, the doctor prescribes a local medication. In severe forms of the pathology, antibiotics are additionally taken. Drugs used:
- Small affected areas are treated with liquid antiseptics with a drying effect - iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate solution, Miramistin. Powdered products are used - Furacilin, Baneocin, Xeroform.
- Sintomycin ointment, Tetracycline are used in treatment if a purulent boil occurs on the mucous membrane or near the eye.
- Enzyme-based products – Chymotrypsin, Streptokinase. The doctor prescribes it in the form of solutions for compresses. The components suppress the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- At the first stage of wound treatment, ointments containing a water-soluble antibiotic - Levomekol, Levosin - are prescribed. The ointment is applied to the cavity using a cotton swab or used as a compress. Medicines draw out serous contents from the purulent cavity. Vishnevsky ointment and other outdated options are not used in the modern treatment of infectious and inflammatory lesions. The situation is due to the lack of water-soluble ability.
- Fatty gels based on petroleum jelly - Methyluracil, Tetracycline ointment. Used at the final stage of treatment - the period of scarring.
What are the specifics of dressing ordinary and purulent wounds?
To prevent secondary infection of damaged tissues, you must follow the instructions for performing the procedure:
- Remove the old bandage.
- Toilet the wound.
- Perform treatment - manipulations to remove exudate, application of medications. When dressing, you need to take into account the possibility of serous contents getting on healthy tissue.
- Apply a sterile bandage.
To achieve a treatment effect, the specifics of disinfection of clean and purulent lesions should be taken into account.
| Clean wounds | Purulent wounds |
| Dressing tools | |
|
|
| Sequence of actions after removing the previous bandage | |
|
|
| Manipulation algorithm | |
|
|
When treating a purulent wound, you need to pay attention to the condition of the tissue:
- hemolysis;
- tetanus is accompanied by twitching of the affected fibers;
- anaerobic infection is characterized by dryness and necrosis.