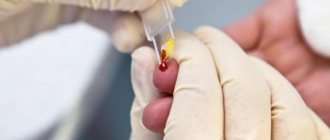
Diagnostics
For differential diagnosis, the following types of studies are used:
- Examination with a dermatoscope, which allows you to see any pathology on the skin with multiple magnification.
- Study of pigment formations with a Wood's lamp, which uses weak ultraviolet radiation. Melanin absorbs ultraviolet light well, so areas with a high pigment content appear darker, while areas with less pigment appear lighter.
- In doubtful cases, computer diagnostics of moles is carried out using a videodermoscope.
- Tissue biopsy with histological examination. Finding cells with signs of proliferative growth is an indication for consultation with an oncologist.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Antifungal agents for toenails and fingernails. Effective and inexpensive, prices, reviews
Reasons for education
Have your child noticed pigment spots? The reasons for their appearance may be different. In the medical literature, two large groups of factors are distinguished that can provoke the formation of pigmentation on the skin:
So, the first category includes genetic predisposition. If immediate relatives are susceptible to the formation of pigment spots, then there is a high probability of their occurrence in the child.
Congenital factors also include skin tumors that appear as a result of complications that arise during labor.
Non-infectious causes of white spots
Spots in a child can be either congenital or appear over time. Not all of them require treatment, some remain for life, some disappear on their own.
Hypomelanosis and pityriasis rosea
With this disease, white spots on the body appear in newborns during the first month of life. In this case, a birth defect caused by a lack of melanin is diagnosed. Dyschromia provokes serious problems in the functioning of the nervous system, possibly retarded growth and development.
Frequent viral diseases are also considered a possible cause of hypomelnosis. The baby has general weakness and decreased immunity.
In this case, serious specialized treatment is necessary to avoid harmful consequences for the entire body as a whole. Such a diagnosis can only be made by a specialist and self-medication is dangerous.
There is no need to be scared by the name; this is not the kind of lichen that is contagious and transmitted by contact. The mechanism of its occurrence has not been sufficiently studied, but doctors know one thing for sure - it occurs in children who often suffer from viral and colds against the background of reduced immunity.
Characteristics of formations:
- spots are clearly visible on the skin;
- do not have a specific location;
- the patient does not experience discomfort or pain when pressed;
- The surface of the skin is flaky and may itch slightly.
The disease goes away spontaneously. But pediatricians recommend wiping the affected areas of the skin with salicylic acid to speed up healing.
Vitiligo
A white spot on the skin of a child of this nature is caused by discoloration of a certain area. Melanin is completely absent in the epidermis, which causes the presence of white or milky spots on the body.
The “favorite” place for localization in children is the face, hands and knees. These spots do not cause discomfort, only in fairly rare cases there is slight itching a couple of days before they appear.
Modern medicine has not invented an effective cure for vitiligo, nor has it fully established the mechanism of development of the disease.
Possible and proven reasons include the following:
- genetic predisposition;
- autoimmune diseases;
- decreased immunity due to severe viral pathologies;
- constant or prolonged contact with pesticides. Children may be intolerant to washing powders or personal hygiene products;
- hormonal disorders;
- infection with parasites (protozoa and worms);
- stress, psychological discomfort.
Traditional methods of treating white spots are offered (a decoction of St. John's wort for wiping areas of the skin). But they can only have some cosmetic effect, and not affect the very cause or mechanism of development of the disease.
In this case, specific drug treatment is not prescribed. The patient is advised to spend less time in the sun, wear closed clothes, strengthen the immune system and not be nervous.
If the cause is an autoimmune disease, then the underlying pathology is treated.
Pityriasis alba and tumorous sclerosis
A distinctive feature of this disease is oval plaques on the face (this is where they appear first), then they can appear on the arms and neck. The disease affects children from 3 to 16 years old, but does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child.
It is rather a cosmetic defect that spoils the aesthetic appearance, especially of teenage girls. To speed up the disappearance process, you need to moisturize the discolored area as often as possible, do not sunbathe or visit a solarium.
The pathology is quite serious, characterized by the initial appearance of white spots on the face, and then on the neck, arms and torso.
Along with this it is also noted:
- underdevelopment of the nervous system;
- damage to internal organs;
- mental retardation.
Specific treatment is prescribed only after a thorough examination and confirmation of the diagnosis.
Causes of appearance in older children
Pigmentation is spots on the epidermis, darker or lighter than the skin, with a distinct contour and scale larger than a mole. Such spots are formed due to the uneven distribution of melanin. There are two types of such skin imperfections:
- Hypermelanosis is excess melanin in the upper layer of tissue.
- Hypomelanosis is a lack of melanin.
The reason for changes in the volume of melanin in the skin can be infection, disease and genetic factors.
Hyperpigmentation appears as small or large spots on the body. They can be darker than the base skin tone, and sometimes have a very dark shade.
We recommend reading
- How to get rid of age spots on the face
- Beneficial properties of castor oil in the fight against age spots
- Composition and effect of Oriflame anti-pigmentation cream
Often the cause of the blemish is prolonged exposure to the sun. Spots appear where the skin has been damaged. This manifestation does not require special treatment. Sun tanning should be avoided for a long time.
Sometimes the cause of hyperpigmentation is:
- chronic kidney and adrenal diseases;
- liver diseases;
- gastrointestinal disease;
- lack of proper nutrition;
- lack of vitamins B6, B12, A;
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- visual defects;
- allergic reaction to medications.
In most cases, hyperpigmentation is not dangerous for the child, but requires constant investigation.
Hypopigmentation can be a congenital defect, but more often develops in preschool and school age. The disease manifests itself as light pink spots. Gradually they become colorless (vitiligo).
Lack of melanin is inherited, but sometimes accompanies diseases of the endocrine, nervous system and metabolic disorders. Lighter areas of the skin are highlighted by color and drier skin.
Before you see a doctor, you need to make sure that it is a pigment spot and not another disease. To do this, it is necessary to observe the neoplasm for some time.
It can be diagnosed using the following criteria:
- scale up to 6 mm;
- even color;
- uniform edges;
- the stain does not grow and does not change its structure.
Types of hypopigmentation in newborns
The cause of the development of hypomelanosis is a disorder of melanin synthesis due to the absence of melanocytes in the skin. May manifest as the following pathologies:
Albinism is the disappearance of color pigment in the skin. Disturbances in pigmentation also occur in the hair and irises of the eyes. The disease is considered genetic, but has not yet been studied. Interestingly, the largest percentage of the disease is in the Negroid race.
Albinism is a congenital pathology (lack of pigment on the skin, hair, eyes)
Vitiligo is white spots that appear at birth or appear in the further development of the baby. Discolored areas are no different from the surrounding skin - they do not stand out, do not peel, and cannot be felt. At first the spots are small, but with age they merge into a larger area. In the sun they do not darken or tan. Vitiligo is classified as a cosmetic defect; it does not affect the child’s health in any way.
Vitiligo - white patches on the skin without pigment
Hypomelanosis Ito. The disease begins in utero and is most often influenced by a hereditary factor. White stripes or waves can be seen already in the first days of the newborn. During adolescence, they become more noticeable or, on the contrary, disappear completely.
Features of newborn pigmentation
In infants or children up to one year from birth, the appearance of pigment spots is often related to congenital pathologies that are caused by:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Difficult labor and complications;
- But there is also an acquired disease associated with pigmentation.
In any case, if such skin defects are detected, a comprehensive diagnosis should be carried out to identify the causes of the spots and how to eliminate them. Some tumors require urgent removal. Others are completely safe and do not require treatment.
When moles are dangerous
When moles appear in a newborn, it is necessary to pay attention and regularly visit a dermatologist. The doctor will use a dermatoscope to examine the formation, determine its nature and the presence of cancer cells.
When bathing or changing your baby, you should carefully examine new spots or changes in existing ones. Birthmarks in a baby are not dangerous if there are no alarming symptoms. These signs include: intense increase in size and change in color, localized on the face, clear boundaries have disappeared, blood or clear liquid is released. It is necessary to visit the office of a pediatric dermatologist if the nevus in the area that is swollen and irritated is covered with hair. A cause for concern is the appearance of a bumpy surface or compaction that begins to peel off.
After the examination, the dermatologist will determine the period during which parents need to monitor the spot. If the situation worsens, the doctor will prescribe surgery to remove the nevus to avoid degeneration into a malignant formation. It is allowed to remove the growth after two years if there is no need to get rid of the stain.
Finding out the main reasons
The main places where dark areas of the skin are located:
- Along the spine, on the shoulder blades;
- In the décolleté area;
- On the face, behind the ears;
- On the legs, arms.
Some brown spots on the arms and back have a clear localization if they are caused by age-related changes.
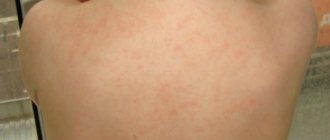
Spots on a child's back are not always a sign of a specific disease. In some situations, a rash appears due to negative environmental factors. The body's response to the action of allergens and failure to comply with hygiene measures are common situations for children from one year to 7-9 years. If red spots on the child’s back do not go away, cause discomfort and accompanying symptoms are observed (fever, general weakness), contact your pediatrician immediately.
The list of possible reasons:
- Chickenpox;
- Measles;
- Bacterial sepsis;
- Meningitis;
- Lichen.
One of the most common factors that provoke the appearance of rashes is prickly heat. This is a harmless small rash on a child’s back, which is caused by overheating of the body, high levels of humidity, and insufficient hygiene. The mechanism of appearance is associated with blockage of the sweat glands.
Differences between spots on a child's back
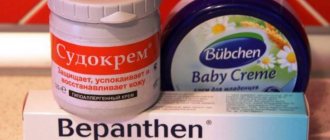
After returning from a walk, did you notice that your child’s back is red? This is a sign that you are not dressed for the weather, your skin is sweaty and prickly heat appears. You can get rid of it by washing and thoroughly drying the rash areas (it is also recommended to lubricate them with a drying cream - Sudocrem). Prevention – absence of overheating and profuse sweating. When going outside, dress your baby in clothes that are easy to take off. Miliaria is not dangerous to health and is not contagious to others.
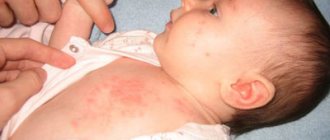
The majority of all back lesions are caused by various types of allergic dermatosis. In children aged 1 to 4 years, the rash is most often caused by the following reasons.
- Atopic dermatitis (diathesis or infantile eczema). The pathology affects the face, buttocks and limbs.
- Strophulus - urticaria with the development of papules on the skin.
- Exudative diathesis. The acute severity of the exacerbation period persists for up to 2 years.
- Dermatitis, which is transmitted by contact.
dermatitis in children Atopic dermatitis in children exudative diathesis in children
The allergic form develops through direct contact of the body and the allergen (with a single repetition or with regular exposure). A pathological reaction develops due to sensitization of the body to the composition of a certain substance. Sensitizers most often are components in plants, animal antigens, chemical compounds, infections, and some products. Contaminated water and the environment also have an impact.
The contact form is manifested by the appearance of rashes on the area of the skin that comes into contact with the allergen. For example, on the back due to rough clothing or an unsuitable bathing sponge. Characteristic symptoms: itching, redness, swelling of the spots. If left untreated, the skin on the back becomes rough, crusty, and loses sensitivity.
Chicken pox (the causative agent belongs to the group of herpes viruses) is another reason why red spots appeared on the child’s back. Small blisters filled with clear exudate form on the skin. They quickly burst and a crust remains in their place.
Lubricating with brilliant green or a dark solution of potassium permanganate is a prerequisite for stopping the infectious focus. Processing should be continued until the crust is completely separated. You need to lubricate the stains at least 12 times a day. Don't forget that the disease is contagious. The peculiarity is that it can be repeated once (you don’t get sick twice).
Acute preceding symptoms are typical for the disease. Before the rash appears, the child may have a fever, a feeling of nausea and subsequent vomiting. There is also redness and sharp pain in the tonsils, and a headache. The skin turns red, becomes dry and rough.
Measles disease, symptoms, treatment and photos Signs of scarlet fever on the tongue Scarlet fever in children on the body
The ways of transmitting scarlet fever are direct communication with the patient or the use of one object. The disease appears 6-10 days after infection. This is a bacterial pathology, which is expressed by the following symptoms:
- A small scarlet rash on the child’s back;
- The tongue is raspberry-colored;
- General weakness of the body.
The causative agent is hemolytic streptococcus. The rash is first localized in the armpits and neck, then moves to the back. When you touch the skin, it feels like fine sandpaper.
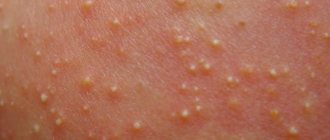
When the disease occurs, small pimples containing pus appear on the baby’s back. These spots are on the child’s back, worsening after a shower - so bathing the baby during this period is prohibited. The rash can also affect the arms, legs and even the head. When the blisters burst, they damage adjacent healthy skin and the infection spreads throughout the body. To prevent infection, pustules should be treated with a swab soaked in alcohol. Then cauterize them with a solution of brilliant green or manganese.
Vesiculopustulosis in children2 Vesiculopustulosis in children1 Vesiculopustulosis in children
Signs of rubella
If there is a pathogen in the body, the rash is detected immediately. Locations: back, legs, neck, head. How does the pathology manifest itself? A small pink rash forms on the skin, which frightens parents due to the area it occupies. Among the accompanying symptoms is an increase in body temperature, as with acute respiratory infections. The disease is typical for children of different ages: from several months or more.
Signs of rubella in a child
Why is roseola dangerous?
Another name for the disease is sudden exanthema. Children aged 1 year and older are at risk of infection. Among the typical manifestations:
- The temperature rises, but the child remains alert (does not show signs of illness);
- Small pink rash after 2-3 days after infection;
- Extensive areas of rash - back and other surfaces of the body
Roseola in children: symptoms
Pink spots quickly disappear on their own. The pathology does not pose a health hazard. But it is better to consult a doctor.
Hives
The pathological spots are colored bright pink, and the blisters resemble a nettle burn. The skin itches, the rashes are symmetrical, and after the blister disappears there are no traces left on the dermis. If there is a fever, aching joints, rapid spread of blisters and difficulty breathing, the child should be taken to the hospital immediately. Only a doctor can select suitable treatment measures.
Urticaria in children photo
In terms of external characteristics, brown areas vary greatly. The classification of different rashes is briefly described below.
| View | Description |
| Lentigo | Flat spots on the skin of brown color. The shape of the rash can be round or elongated. They can be single or numerous. |
| Freckles | Small rashes. The formations can completely disappear in winter. |
| Chloasma | Characterized by hyperpigmentation. New growths are light brown. Usually such rashes are localized near the face. |
| Nevi | In simple words, these are birthmarks. They have smooth outlines. Light brown spots on the body can degenerate and take on a malignant form. Symptoms such as an increase in size and change in the shape of a mole are dangerous. |
You will not be able to recognize on your own what kind of tumor is present and how to get rid of it.
Causes of rebirth
Scientists have found that birthmarks are an accumulation of special cells called melanocytes on an area of the skin. They may have excessive pigment or not contain it at all.
In the first case, the mark will be dark in color, in the second it will have a shade lighter than the color of the surrounding tissue. There are also varieties of deep burgundy, wine-colored spots formed by a concentration of blood vessels - hemangiomas.
Scientists call all such formations on the body nevi.
A birthmark is a general name for many neoplasms that affect the human body. They can be different in shape and size. Some rise above the skin, while some, on the contrary, are hidden under its layer.
Above in the photo is an acquired dysplastic nevus. It can be caused by skin diseases, taking hormonal medications, ultraviolet radiation, or skin trauma.
The main causes of malignancy of moles:
- Hereditary factor.
- Excessive solar exposure. In this case, sunburn received in childhood plays an important role. The greater the dose of solar radiation received in childhood, the more likely the appearance of dysplastic nevi in an adult. Such formations have a very high risk of degeneration.
- Tanning obtained in solariums has been a leading factor in the increase in the incidence of melanoma in recent years.
- Decreased immunity (chronic diseases, stress, pregnancy).
- Aging.
When the tumor size is less than 1 mm in diameter, about 90% of patients live more than 5 years. When the melanoma diameter is more than 1 mm, there are already metastases. In the presence of such malignant nevi, the survival prognosis is extremely low.
A mole sometimes undergoes a number of malignant changes.
But what are the causes that a person can prevent?
How you can cause transformation:
- trauma to the nevus - squeezing, tearing, scratching or rubbing - both with violation of integrity and with its preservation;
- excess sunlight or artificial ultraviolet radiation. This can be either careless neglect of protection against UV radiation while relaxing on the beach, or abuse of a solarium.
The reasons for the transformation of a mole into melanoma are as follows:
- mechanical damage - friction with clothing, straps, skin trauma;
- hormonal changes in the body - most often occur during adolescence and pregnancy. Another cause may be thyroid disease.
- damage by ultraviolet rays - sunlight activates the division of melanin cells and causes pathological changes in skin cells.
Light-skinned, fair-haired people with light eye colors, those with red hair and freckles are most susceptible to the effects of ultraviolet radiation.
At risk are pregnant women and those who have a family history of melanoma.
Risk factors include:
- large congenital nevi;
- the appearance of new moles, the growth of old ones;
- nevi that cover the entirety of a specific part of the body.
It is difficult to reliably find out why the tumor became malignant, since any impact on it is undesirable.
- This could be a biopsy, traumatic cosmetic treatment, any damage, as well as an excess of ultraviolet radiation.
- An important factor is a genetic deviation, as well as a feature of the skin - light skin prone to burns from ultraviolet radiation is much more common in patients with melanoma.
List of other reasons
Spots similar to lichen (they do not itch and do not cause noticeable discomfort) are a possible manifestation of a special form of pathology. This is Zhiber's pink lichen, which is characterized by the primary formation of a maternal plaque. A bright red spot (3-5 cm in size) appears on the back and rises slightly above the skin.
Another cause of such spots is seborrheic dermatitis. The reason for the development is the increased production of sebum and the active development of microflora against this background. Yellow and pink spots and plaques of various shapes (round, elongated, with clear boundaries) appear on the back. At the site of pathological foci, redness, swelling, crusts and cracks on the skin become wet. A possible complication is a purulent inflammatory process.
Seborrheic dermatitis: causes Symptoms of pityriasis rosea in children
What else causes lichen-like spots?
- Deprive yourself. It is characterized by a small rash and the formation of ulcers. These symptoms indicate that there is a fungus in the body. Antibacterial agents for treatment are prescribed by the doctor. The disease is contagious to others.
- Meningitis. This is a dangerous pathology, the list of serious consequences of which even includes death. The reaction to the formation of a small rash, which is a consequence of subcutaneous hemorrhages, should be immediate.
- Measles. Symptoms are rash and high fever. The child’s eyes also become red, the mucous membranes become inflamed, and he suffers from a runny nose and cough. The rash is bright red. Measles is a dangerous disease in which an ambulance should be called immediately. The list of complications includes chronic diseases (bronchitis, pneumonia).
Diagnosis and treatment
For differential diagnosis, the following types of studies are used:
- Examination with a dermatoscope, which allows you to see any pathology on the skin with multiple magnification.
- Study of pigment formations with a Wood's lamp, which uses weak ultraviolet radiation. Melanin absorbs ultraviolet light well, so areas with a high pigment content appear darker, while areas with less pigment appear lighter.
- In doubtful cases, computer diagnostics of moles is carried out using a videodermoscope.
- Tissue biopsy with histological examination. Finding cells with signs of proliferative growth is a good time to consult an oncologist.
- The treatment tactics for pigmented formations, if they do not cause any physical or aesthetic discomfort, consist of dynamic observation. Lightening and whitening external agents for removing areas of pigmentation in children are practically not used.
- Most medications contain hormones or chemicals that are harmful to the baby. After the doctor's permission, spots on a child over 6-7 years old can be treated with parsley, cucumber or lemon juice.
- If a decision is made to eliminate the pathological formation, the method of destruction is selected individually.
- Surgical removal involves excision of the affected area with a scalpel. The tissues are sent for histological examination. After the operation, scars and cicatrices remain. If malignant degeneration of a pigmented formation is suspected, it can only be removed surgically
- Cryotherapy, when destruction is carried out by ultra-low temperatures. Liquid nitrogen causes instant freezing and necrosis of pathological tissues. Used to remove small vascular tumors in children - hemangiomas. After cryodestruction, an inconspicuous spot remains. Damaged tissues are completely regenerated after six months.
- Electrocoagulation is a method of eliminating a skin defect using high-frequency currents. The manipulation is painful and requires the use of anesthesia. Rarely used in children.
- Laser therapy. Small moles and spots are removed instantly using a laser beam. This method allows you to accurately calculate the depth of action and the diameter of the beam, so as not to injure healthy skin. Use only for benign neoplasms.
- Radio wave method. The device is equipped with a tungsten filament that produces high-frequency waves. Pathologically altered tissues are cut away to healthy skin. Epithelization occurs quickly, sometimes leaving a cosmetic scar.
"Mongoloid spot"
This type of pigmentation is a type of nevus. Externally, it is a large pigmented spot in a child, similar to a hematoma, which is most often found on the buttocks, lower back or leg. In 90% of cases it occurs in children of the Mongoloid race. In our country, babies from mixed marriages are most often born with this skin defect. The reasons for the appearance of the “Mongoloid spot” are the genetic characteristics of melanin production in representatives of certain nationalities: Chinese, Japanese, Africans, Indians, Pakistanis and some others.
Such a pigment spot does not pose any danger to the baby’s health and in most cases disappears or significantly brightens on its own by the age of 5.
Age pigmentation
The manifestation of age-related pigmentation on the face is characterized by brown spots of various shapes and diameters that appear under excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun, the location of which is determined by the places of melanin accumulation, regardless of skin type. They do not change their shade regardless of any factors, including at certain times of the year, like freckles.
Age-related pigmentation on the face (after 45 years) is caused by changes in hormonal levels due to the onset of menopause and has the appearance of benign neoplasms. Baking malfunctions are also a common cause of blemishes on the face.
There are several varieties of such pigmentation:
- lentigo;
- keratoma (senile wart) is a round plaque with scales, yellow-gray in color, which can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm, so doctors recommend removing it;
- age-related spotty pigmentation (senile hyperpigmentation, senile freckles) is observed on the forearms, the backs of the hands;
- flat xanthoma of the eyelids (xanthelasma) - orange (yellow-orange) oval, ribbon-shaped plaques; These pigment spots are located under the eyes, on their inner corners.
Treatment of pigmentation
Treatment is selected taking into account the established diagnosis.
Important! Self-medication is highly undesirable. Any methods of combating the disease must be agreed with the attending physician.
Local treatment
First of all, local treatment is recommended to patients. These are various ointments and creams. The medicinal composition is applied directly to the affected area.
For brown formations, you need to apply creams based on glycolic, lactic, and citric acids. When using them, you must follow the instructions for use.
Creams and ointments are used only as prescribed by a doctor. This is due to the presence of mercury compounds in their composition.
Medicines
Requires the use of lightening agents. The group of antifungal drugs includes zinc ointment. Salicylic ointment is used as an antibacterial drug.
Salicylic ointment Zinc ointment
If pigmentation is a secondary symptom, then complex treatment aimed at the underlying disease is required. Sometimes there is a need to use hormonal medications.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies is popular. Lemon juice has whitening properties. It is mixed with water in a ratio of 1 to 8. The resulting liquid should be wiped over the skin.
Important! Folk remedies are effective only with traditional treatment. Before using natural medicines, you must consult a doctor.
Onion juice helps relieve pigmented areas. Dairy products have whitening properties. They wipe the skin or use them to make masks.
Cosmetic procedures are highly effective. They will help return the skin to its original color in a short time. The main thing is to approach the selection of a specialist responsibly.
When a woman carrying a child notices the presence of brown spots on her stomach and breasts, a surge in hormones is to blame. Pigmented areas in pregnant women form on the face, nipples, and shoulders.
The following recommendations will help prevent pigment spots on the abdomen, under the breasts and the development of complications:
- Reduce the number of walks in the sun;
- Drink vitamins, eat fresh vegetables, berries, fruits;
- Control hormonal levels;
- Take a thyroid function test.
Types of birthmarks
Many babies are born with skin without defects. But this does not mean that there are no spots on the body. It happens that they are faintly colored and difficult to detect when examining the skin.
Moles in newborns are clearly visible in only one baby out of a hundred. In the rest, the formations are not detected; only by the age of 2–5 years do they acquire their color and become noticeable. There are two types of nevi in newborns:
- pigmented moles of brown or black with blue color;
- red spots (angiomas, hemangiomas) of bright pink, red color.
The color of spots is influenced by the cells that form them. If the mark is formed from actively producing melanocytes, the color of the moles is brown or black. And the nevus from the vascular cells will have a red color.
Most often, pigmented formations occur in infants. A factor influencing the formation of such marks is a large amount of melanin in a small area of skin. Melanin is a pigment produced by pigment cells - melanocytes. It is what affects the color of a person’s eyes, hair and skin tone. The degree of melanin production in the body directly depends on the functioning of the endocrine system. There are several types of formations, the structure of which contains pigment cells:
- Mongolian spot. Occurs in babies with Mongoloid genes. A formation appears in the sacrum area. Outwardly it looks like a large bruise, which then spontaneously disappears by the age of five. It does not have a negative effect on the baby's health.
- Dysplastic marks. They have irregular outlines, different sizes and degrees of color. It happens that formations look like single elements.
- Moles. The formations look like dots of different colors and appear on all parts of the body: stomach, back, limbs, head.
- There is another type of birthmark - this is a congenital nevus, formed from pigment cells. In this case, the lesions are characterized by their extensive size.
Bottom line
Pigment spots in children have a different nature of occurrence and often do not require any medical intervention, but if it is still needed, then it must be treated strictly in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
You shouldn’t buy your baby an expensive, fashionable cream for freckles, because these formations can go away on their own. Moreover, they do not interfere with a small child in any way.
Any medications, even harmless folk methods, require consultation with a doctor. Take care of your children's health. And monitor the external condition of their skin more often; if even the most microscopic spot appears, consult a doctor. What if it's a hemangioma? Which requires treatment and can cause serious irreversible consequences.
What's happened
A nevus is a benign neoplasm that is formed from pigment cells. The localization site is any area of the skin or mucous membrane. In most cases, such formations are not dangerous to the child’s health and do not cause him any inconvenience.
The formation of nevus cells begins in the womb. When exposed to a number of factors, cells begin to actively produce pigment, which subsequently appears on the surface of the skin in the form of a mole or birthmark.
Depending on their origin, all moles are divided into two large groups:
- congenital nevus in children - a child is born with a certain number of pigment spots;
- acquired – moles appear during life.
In addition, moles are divided into the following types.
Simple
The spots are orange-pinkish in color. The most common location is the thighs and buttocks of the baby.
Until a child reaches two years of age, simple neoplasms are practically invisible to the human eye. They can only appear when the newborn is crying or tense.
Intraepidermal
Refers to the most common type. The neoplasm has a round shape and a flat surface, with clear boundaries. Color can vary from light to dark brown.
Such nevi form during the first 20 years of life.
Strawberry
Can be presented in various sizes. They have a reddish color and a soft structure.
They are located in different parts of the body immediately after the baby is born. They can also form in the first month of a child’s life. Up to 12 months, such a neoplasm can increase in diameter, but by the age of 10 it goes away on its own.
Cavernous
It is a rarer type that occurs in newborns. It differs from the previous type in its structure. The neoplasm has large elements, and its base is formed deep in the layers of the skin.
In the first 6 months, rapid growth of the spot is observed, then the rate decreases slightly. This formation may finally disappear before the child reaches 5 years of age. As a rule, a scar may appear at the site of such a growth.
Dark spots
In most cases they are presented in small sizes. Can be painted brown. In rare cases they are black. In case of large volumes of tumors, they must be removed.
Brown birthmark
Such neoplasms have a flat surface, which can be brown in varying degrees of intensity. Localized anywhere in the body.
They can appear immediately after birth or after a certain period of time. If there are more than five birthmarks, the baby should be shown to a specialist.
Hanging
This is a benign neoplasm, the formation of which occurs from epithelial cells. May be dark in color or skin tone. The location in most cases is the groin area, armpits, external genitalia or neck.
According to doctors, such moles should be regularly monitored as they may pose a threat to the child's health.
Blue flat
This is one of the types of pigmented nevus. Such formations are most often large in size, difficult to remove and can be dangerous for the baby’s body.
Mongolian spots
They are detected in most cases on the buttocks, thigh or sacral region. In 90 percent of cases, infants with Asian roots are diagnosed with this type of neoplasm.
Fiery
Such spots have a bright red color because their structure consists of dilated capillaries. Most often presented in convex shapes.
If a child has such a formation on his body, this may indicate abnormalities in the growth and development of soft and bone tissue. If the fiery nevus is localized on the face, the child should be shown to a specialist. This condition may indicate problems in the brain.
Causes of brown spots
Pigment formations are classified according to location and nature of manifestation:
- Features of lentigo pigment spots. Dark spots on a person’s stomach are dense to the touch and are called Lentigo. They can be located singly or in small groups. Brown spots along the spine, on the back due to age-related changes. Lentigo does not threaten the development of oncological complications. They are formed due to the accumulation of a large number of melanocytes in which melanin accumulates.
- Nevi or moles. Spots on the body with clear edges and light brown color are called moles. They are innate and do not threaten human health, but they cannot be injured or torn off. They can be located in any area of the body.
- Becker's nevus. A distinctive feature of this type of moles is a yellow tint and uneven, asymmetrical edges of the spots. Often, such pigmentation occurs in adolescent males, caused by dysfunction of hormones in the body.
- Nevus of Ota has a dark blue, black tint and is localized mainly on one side of the face. It can also be located on mucous membranes, only the cosmetic side of the issue is of concern.
- Nevus Ita. The difference between nevus ita is in localization - the areas of the face, neck, shoulders, area of the shoulder blades, have uneven outlines and color. From a medical point of view, it does not require treatment, because does not develop into melanoma, it is only a concern as a cosmetic defect.
- Freckles (ephelites) are harmless pigmented areas that do not threaten health. They most often occur in fair-haired and red-haired people. Hyperpigmentation is more common in women. Their number increases during the period of greatest solar activity (spring, summer).
- Brown pigmentation due to fungus. When fungal infections develop, a person's skin becomes covered with a painful and uncomfortable rash. The peculiarity of these spots is that they can crack, peel and hurt.
- Toxic type melanosis. The formation of toxic melanosis spots is caused by substances such as oil, oil, coal and other fuels and lubricants. Such pigmentation is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in health.
- Melanosis of the arsenic form. Factors that provoke the formation of this type of pigmentation are the use of medications with arsenic. Brown spots on the body can occur in those people who encounter arsenic in the process of work.
- Melanosis named after Dubreuil. This problem is a sign of the development of cancer. Over time, the small rash increases significantly in size and changes color from light yellow to dark brown. Nodules and papules itch, the area around begins to turn red and peel. If a dark spot between the shoulder blades or the back itches, you should not do this, as infection may occur.
- Acanthosis nigricans. A problem in which black pigments are observed on the skin. Localization occurs most often in the area of those parts of the body where there are more folds, for example, buttocks, armpits, neck, groin. The reasons for the development of acanthosis nigricans are excessive intake of hormonal drugs during pregnancy and the appearance of malignant tumors.
- Urticaria pigment type. Purple and red spots form on the human body, followed by rashes and blisters. In childhood, such skin diseases go away on their own, but in adulthood they lead to dangerous complications.
- Leopard cider. Pathology, which is characterized by the formation of a large number of pigmented areas. This problem is accompanied by damage to the heart, impaired respiratory function, brain function and is caused by gene mutations.
- Poikiloderma. The pathology is accompanied by swelling and atrophy of the skin with a protruding rash. Most often the disease is observed in women and is hereditary.
- Flat warts. Benign flat neoplasms of a pale pink and brown hue. The growths look like small nodules that rise above the skin and can form on the hands, face and other parts of the body.
- Pityriasis versicolor. Infectious damage of a fungal nature that affects the skin, with pigment formations of different shades (yellow, pink, brown) observed. Damaged areas are characterized by peeling, inflammation is not observed.
- Mongolian spot. A congenital cosmetic defect that appears as a gray-blue pigment with uneven rounded edges. Often the pigment is localized in the groin area, on the buttocks. No treatment required.
Brown pigments in the facial area (cheeks, eyelids, forehead) are safe for health. Apart from aesthetic discomfort, they do not cause any inconvenience, so many do not treat them.
Darkening and pigmentation of the breasts can be caused by excessive consumption of contraceptives (hormone-based).
To do this, use the following folk remedies against pigmentation:
- Protein mass. You will need to combine 2 tsp. chicken protein, 1 tsp. hydrogen peroxide, 1 tsp. low-fat cottage cheese. Treat skin pigments daily.
- An ancient effective mask. take hydrogen peroxide, ammonia, and cottage cheese in equal parts. Use the resulting mixture 2 times a day on problem areas.
Pigmentation has been studied many times by dermatologists. Brown spots on the body are the result of the presence of special cells in the human body - melanocytes. The components are responsible for the formation of melanin. It is also called brown pigment.
Important! Skin pigmentation is the result of malfunctioning melanocytes. The true causes can be both physiological and pathological.
It is interesting to know that with congenital cell activity, a child can be born completely dark-skinned. Conventionally, the root causes of the formation of brownish formations can be divided into three categories. They may be the result of environmental influences, mechanical stress, or pathological processes.
Various cosmetic procedures can provoke cell activation, the effects of which are described below.
| Procedure | Influence |
| Peelings | Peels of all types have an effect. These procedures renew the skin. The stratum corneum is removed. The skin becomes more sensitive to ultraviolet rays. Aggressive influence also has a negative effect. Small particles injure the body. Lack of care after peeling leads to the appearance of brown areas. Hyperpigmentation begins |
| Botox, injection of hyaluronic acid | These procedures are traumatic. Afterwards, careful skin care will be required. |
| Depilation, mechanical cleaning | The procedures damage the top layer of skin. Promotes increased production of melanin. |
These are the main procedures that lead to increased pigmentation. The skin suffers when using low-quality cosmetics. It is important to choose gentle cosmetics.
The appearance of brown formations is caused by ultraviolet radiation. The changes are especially noticeable in people with fair skin. The most harmless result of environmental influences is the appearance of freckles.
One of the common causes of brown spots on the human body is old age. As you age, the performance of internal organs deteriorates. Metabolic processes slow down. For this reason, regenerative processes stop. Sooner or later, round brown spots appear on the skin.
Hormonal imbalances within the body lead to the appearance of pigmented areas. They can even be the result of stressful situations or lifestyle changes.
Diseases
Round brown spots on the skin are the first symptom of dangerous diseases. It is the skin that is one of the first to react to negative health changes.
If a spot appears on the skin, you need to seek help from a doctor. This symptom is the result of precisely diseases that need diagnosis.
Types of nevi
The moles in the photo are just a few examples of the manifestations of nevi. There are five groups of pigment spots alone, and in each of them there are also varieties of nevi.
Melanocytic nevi of epidermal and dermal origin, respectively, dermal melanosis, Clark's nevus, congenital melanocytic nevi - these groups of nevi are the main ones. The photo above shows a papillomatous nevus belonging to the first group.
According to the nature of their manifestations, birthmarks in the photo may look small (1-2 mm), large (up to 10 cm), red, black, brown, may protrude above the surface of the skin or be flat. Some nevi resemble warts.
The types of moles are many and varied. Moles can be located on absolutely any part of the body and even on the mucous membranes. Depending on the morphological characteristics (color, size, shape, surface), the following types are distinguished:
- By color:
- Red (vascular tumors - hemangiomas).
- Brown and black (birthmarks, common moles and dysplastic nevi).
- Purple (warty, raised moles).
- Blue and blue nevi.
- White (fibro-epithelial growths).
- To size:
- Small (no more than 5 mm).
- Medium (up to 15 mm).
- Large (up to 10 cm).
- Giant (over 10 cm).
- Form:
- Flat (smooth surface).
- Convex (rough surface).
- Warty growths (can grow on a stalk).
There are:
- Melanoma-dangerous nevi are formations that are highly likely to degenerate into a malignant tumor. Such nevi are also called dysplastic, they include:
- Giant birthmarks, colored brown and any shades of this color.
- Elements of blue and cyan color – such formations have the highest risk of degeneration into skin cancer.
- Intermediate - nevus cells are located at the border of the epidermis and dermis. The rate of transformation into skin cancer is very high. The localization of such nevi is the palms and soles.
- Precancerous Dubreuil melanosis is a nevus on the face, the appearance of which resembles a pigment spot. This formation is irregular in shape, like a geographical map. Its size is more than 2 cm, the degree of coloring is different and heterogeneous.
- A melanoma-dangerous nevus, the cells of which are localized in the upper part of the epidermis, found in the vast majority of people:
- Fibrous-epithelial moles (convex, white).
- Verrucous (warty growths of various colors).
- Papillomatous.
- Lentigo - most often, these multiple spots appear on the face and are red or light brown in color, sometimes they are dark. The shape is wrong. Their sizes are small.
- Coffee stains - in some cases, these nevi are related to neurofibromatosis. If several coffee stains appear on the body, you should contact a neurologist.
- Mongolian spots are grey-blue in color, irregular in shape, vary in size and are found in children. They do not pose any danger and go away on their own by puberty.
Moles come in different sizes: from a barely noticeable dot to a large spot located on the skin and in its inner layers.
Nevi are classified into vascular (hemangiomas) and pigmented.
- The first type develops due to the enlargement and fusion of capillaries.
- Pigmented - formed by groups of pathological melanin cells.
By size, moles are divided into:
- small (up to 2 mm);
- medium (up to 6-10 mm);
- large (from 10 mm).
Based on the type of localization, nevi are:
- epidermal (located on the top layer of skin);
- borderline (occupying both the surface and deep layers of the skin);
- intradermal (located in the thickness of the middle skin layer);
Let's consider the types of moles and their meaning in order to understand the possible risks of formations on your body or their significance in your own destiny.
The main difference between nevi is the nature of their formation.
What types of moles are there on the body?
This could be a vascular cluster or a pigmented area of skin with excess melanin.
The form of neoplasms can be different:
- convex;
- flat;
- smooth;
- warty;
- hanging;
- hair.
Vascular moles are divided into capillary (flat) and cavernous (lumpy, in the form of nodules).
- In color, depending on the blood vessels, they can range from bright crimson to purple or blue.
- They occur both on the skin and on mucous membranes, or on the lip.
Causes of occurrence in infants
The pigmented form of neoplasms on any part of the baby’s body can be caused by the following reasons:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Injuries during fetal development;
- Birth injuries;
- Pathologies during pregnancy;
- Taking medications by the mother during pregnancy.
To understand what to do with the pigmentation of a newborn, you need to undergo an examination. Depending on the cause of the appearance and nature of the development of the tumor, the doctor will decide on further actions.
If, for example, a baby has a pigment spot on his lip. Only laboratory and clinical studies will help to understand what type it is - either it is a coffee stain that does not require treatment, or a nevus that needs to be examined to avoid unnecessary complications.
Ways to get rid of moles and birthmarks
If you decide to get rid of a birthmark or mole, you should listen to the doctor’s recommendations. There are several safe and quite simple ways to remove such tumors:
- Injections of medications directly into the spot, which stimulate the death of overgrown vessels or other tissues.
- Cryotherapy is the freezing of warts or moles using nitrogen. After a few days, the area where liquid nitrogen was applied heals and becomes covered with a crust, after which the crust disappears along with the new growth. With the help of cryotherapy, you can only get rid of small warts or moles (see also: warts on a child’s hands).
- Laser. Using a powerful beam of light, you can remove unwanted formations on the body painlessly and quickly. After the procedure, the healing process takes very little time, especially when compared with cryotherapy.
- Radio waves. Sometimes the doctor recommends getting rid of the tumor using a device that affects the mole with radio waves. First, the doctor will give an anesthetic injection, then remove the nevus. Healing after the procedure is quick and there are usually no scars left.
- Removal with a scalpel. This method is quite traumatic; it is used in cases where the birthmark is large. Despite the fact that today there are more advanced treatment methods, surgical excision remains a fairly popular procedure.
Finally, I would like to advise parents not to panic if their child has spots or moles on his body. You should definitely consult a doctor, or better yet, see another specialist. In this case, it will be easier for parents to make the right decision and protect the child from possible problems in the future.
What is hemangioma?
A hemangioma is a pink or red spot on the skin. Its difference from other types of age spots is that it is not an accumulation of melanin, but a benign tumor that forms as a result of damage to blood vessels. According to medical statistics, such age spots are common in children in the first six months. In addition, it is noted that such neoplasms are more common among girls.
The reasons for the development of such a tumor are intrauterine disorders in the formation of the fetal circulatory system, as well as complications during childbirth. In 70% of cases, the neoplasm disappears on its own by the age of 7. Of the remaining 30%, 10% of children experience involution of hemangioma during adolescence. This happens due to changes in hormonal levels.
This type of pigment spots can form not only on the skin, but also on internal organs, disrupting their functioning. Therefore, hemangioma can be dangerous to the health and life of the child. If pink or red pigment spots appear on a child’s arm, face, occipital region, or abdomen, then there is a need for a full medical examination of the little patient and further specialized monitoring of neoplasms.
Skin pigmentation in normal and pathological conditions
Parents often have doubts about changes in the pigmentation of their baby’s skin as they grow older. Particularly concerning is the presence of pigment spots, voluminous moles, and complete discoloration of areas of the skin. To understand what should cause concern, let’s first determine the normal pigmentation and coloration of children’s skin.
The skin of Caucasian children in childhood is colored from soft pink to flesh-colored, and this is due to a certain content of melanin pigment inside the cells, as well as translucent small vessels - capillaries passing under the skin. In addition, the skin has different colors depending on the thickness of the stratum corneum and subcutaneous tissue. The main skin pigment is melanin, it is contained inside pigment cells, forming the color of the hair, irises of the eyes and the main shade of the child’s skin. The more melanin the skin contains, the darker it is. Children inherit the characteristics of pigment deposition from their parents, but there are situations when there is no pigment at all - this condition is called albinism.
Causes of skin pigmentation
Large and small spots on a child’s skin appear due to the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. Pigment spots are inherited from parents to children. There are frequent cases when pigmentation in a child and mother (father) is located in the same place on the body.
- Infantile hemangioma. This is a benign tumor that appears in the first days (weeks) of a child’s life. It is a brown pigment spot that appears as a result of a congenital defect of the circulatory system. Often, hemangiomas do not harm the child.
Other reasons why age spots appear in children:
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! An effective and affordable remedy for condylomas. find out what this product is>>
- malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- decreased immunity, lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- impact of negative external factors;
- a sign of the development of a hereditary disease - neurofibromatosis.
What causes age spots to appear in children from birth?
Some age spots appear in children from the first days of life. They are localized on the neck, arms and legs, face, back and stomach. Some children are more susceptible to skin pigmentation, and from the moment they are born, birthmarks appear on their body. The following children have a chance of developing such “marks”:
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! Right now you can find out a cheap way to get rid of all warts. FIND OUT >>
- owners of snow-white skin;
- those born before their due date;
- girls, unlike boys, are several times more likely to be born with age spots.
According to medical statistics, in 30% of toddlers before the age of three, hemangiomas disappear on their own without surgical or other types of intervention. For the majority of children (about 60%), disappearance occurs before the age of seven. The remaining 10% are children under 9 years of age. The disappearance of the characteristic “mark” occurs later than for other children.
What should parents know about the reasons?
If we talk about the reasons for changes in skin color in children, then parents should understand what they may be associated with. Often these are mechanical, physical or infectious skin lesions. In this case, excessive irritation of melanocytes is formed, which is why they begin to accumulate pigment. An example of this could be post-infectious pigmentation - after measles, streptococcal infection and some others. This phenomenon is unstable, and parents notice a gradual evening out of skin color.
Pigmentation can occur in areas where the skin rubs against clothing, as well as in areas exposed to various chemicals or medications (for example, this condition is sometimes caused by antibiotics). Sometimes a change in skin color is a sign of a fungal infection (pityriasis versicolor). There may be problems with pigmentation due to hormonal metabolism disorders - for example, Addison's disease, problems in the metabolism of adrenal hormones.
Often, parents may notice pigmentation if their children have suffered sunburn. This usually manifests itself in adolescence, against the background of hormonal changes, and is typical for the face and back, less often the shoulders and chest.
Skin care
Pigment spots on a child’s face and nevi on the body do not require special care, you just need to carefully monitor them. Parents are obliged to prevent the toddler from damaging the formation on the skin. Often, due to injury to the nevus, infection occurs and an inflammatory process occurs. In the best case, everything will work out, in the worst case, a benign formation will develop into a malignant one. If there is the slightest damage to the birthmark or modification of the nevus, there is no need to postpone a visit to the doctor.
PAY ATTENTION! Find out how to quickly and reliably remove condylomas and papillomas. find out >>
Freckles
Freckles, or “sun-kissed” freckles, appear in children older than one year if there is a genetic predisposition. They are one tone darker than the base color of the skin. In addition, in the summer, under the influence of sunlight, the spots become brighter, but in the winter, on the contrary, they fade. Orange-brown “hemp” covers the cheeks, forehead, and chin. Freckles are also found on the shoulders, back, and legs.
Such pigmented skin was previously considered a characteristic feature of lower-class people. Today, freckles are a reflection of the individuality of their owner. In addition, it is noted that such spots gradually fade starting from the age of 25.
Nevertheless, quite often those with sun spots turn to specialists to remove such pigmentation. There are a variety of methods for eliminating freckles:
- cosmetic whitening products and folk recipes;
- cryotherapy;
- chemical peeling;
- laser therapy;
- dermabrasion;
- removal by light waves.
But before deciding to use the above methods, it is worth considering that removing age spots always leads to trauma to the skin, and irreversible complications often occur.
Thus, any neoplasms on a child’s skin require examination and observation. If in some cases pigment spots in children turn out to be absolutely harmless, then in others they are dangerous for the baby. Therefore, timely detection of the problem and provision of necessary medical care can preserve the health of the baby.
Skin pigmentation is a change in the color of the dermis. Not only adults, but also children face this phenomenon. Pigment spots in a child appear under the influence of various reasons, both external and internal. They often cause concern among parents. In some cases it is in vain, in others it is completely justified. What you need to know about birthmarks, and which of them are dangerous for the child?
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Even “advanced” papillomas and warts can be removed at home, without surgeries or hospitals. Just read what Yuri Savin advises to read the recommendation.
Treatment of spots
As a rule, age spots on the skin do not require special treatment. If parents are concerned about the presence of suspicious formations on the baby’s body, they need to see a pediatrician who, after an examination, will decide whether to deal with the problem. In any case, any seals and pigmentation on the skin must be monitored so as not to miss the first signs of a possible disease.
Adults treat age spots using various methods. This includes laser removal, cryodestruction, and surgical operations. It is not advisable to carry out these procedures in children. If nevi and spots do not cause harm or discomfort to the child, but spoil the aesthetic appearance, you need to consult a doctor about medications to remove skin pigmentation. Today, pharmaceutical companies offer a wide variety of ointments and creams that can get rid of blemishes on the skin. Among these funds are:
- Aknestop cream and Curiosin gel. Under 12 years of age there are no specific contraindications for the use of the products.
- Gel "Skinoren". Indicated for the treatment of children from 12 years of age.
- First aid cosmetic product “Amanita against.” Used to treat children from the 3rd year of life.
Return to contents
Folk remedies
Recipes from traditional healers are considered no less effective than medications. They act gently and are gentle on children's skin. The only disadvantage of use is the long course of treatment. To remove nevi, plant components are used that are always at hand.
Parsley root
Parsley roots will not harm the child; they are successfully used in the fight against pigmentation. Recipe for preparing the solution:
- take 10 g of parsley roots;
- pour 250 ml of boiling water;
- leave the infusion for an hour;
- moisten a cotton swab and apply to problem areas 3 times a day;
- course of treatment - 1 month.
Return to contents
Cucumber juice
Cucumber is used to get rid of birthmarks on the skin. The therapy will be long but successful. Folk remedy recipe:
- take a cucumber and chop it;
- mix the cucumber mass with Vaseline or baby cream (1:1);
- apply the solution to the problem area;
- leave for 20 minutes and rinse with water;
- treatment is carried out daily for 1-1.5 months.
A pigment spot in a child does not require special treatment, but increased attention should be paid to it constantly. If new nevi appear on the baby’s body that do not cause discomfort and do not change their color or shape, then there is no need to worry. At the slightest suspicion of malignancy, a visit to a doctor and diagnostic testing is required. Early detection of the disease will help maintain the child’s health and prevent complications.
Pigmentation disorders in children
Skin pigmentation in children is observed quite often, but parents cannot always distinguish pathological elements from completely harmless moles and age spots on their own. Therefore, if you have any doubts or a sudden change in skin color, you should contact a dermatologist - the doctor will accurately determine the causes of this condition.
Generally speaking, pigmentation in children can change in two fundamentally opposite directions:
- state of hypermelanosis (increased pigmentation)
- state of hypomelanosis (sharp weakening of pigmentation up to complete disappearance of pigment).
These conditions can be total in their manifestations, that is, children dramatically change the pigmentation of all skin integuments as a whole; this happens infrequently, but usually problems with pigmentation have a local or limited-area manifestation, affecting one or several parts of the body. Most often, pigmentation problems occur in the back, face and limbs. Typically, children do not experience physical discomfort from changes in skin color, but there is a pronounced cosmetic defect and psychological discomfort.