A cyst in a newborn’s head can be diagnosed in the tissues of the left or right hemisphere quite often. The appearance of such abnormal formations in babies is due to the fact that during their embryonic growth or during childbirth, temporary tissue deformation may occur in the brain tissue due to metabolic disorders and poor blood circulation.
Types of disease
Traditionally, doctors classify brain cysts according to the following criteria:
- appearance time
- localization
- cavity properties
Based on these data, such formations are divided into the following types:
- Choroid plexus cysts usually appear in the fetus in the womb. The sooner it appears, the greater the chances of eliminating it on your own. As a rule, if it develops at the very beginning of pregnancy, the completely harmless cyst resolves by the time the baby is born or during infancy. The cavity is preserved in case of complications both during pregnancy and during obstetric activities. The disease often occurs due to infections suffered by the mother.
- The subependymal form in infants is the result of poor blood supply to the cells and tissues of the brain. This form is also called cerebral, and it occurs, as a rule, as a result of hypoxia and subsequent tissue death. The presence of such a disease makes it necessary to keep the baby under the supervision of doctors at all times.
- An arachnoid cyst, also called a cerebrospinal fluid cyst, forms on the superficial areas of the brain. The causes of its occurrence are also insufficient blood circulation, previous inflammatory processes, and injuries during childbirth. This form is dangerous because it develops quite quickly and can compress certain areas of the brain, leading to serious complications. But such a manifestation of a cyst is diagnosed only in 3% of all cases of such a diagnosis.
Diagnostic features
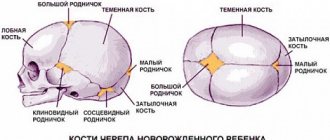
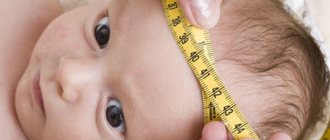
The disease can be diagnosed after the birth of a child using neurosonography. This ultrasound examination is carried out through the fontanel and provides reliable information without ionizing load on the body. Such a diagnosis can only be carried out on newborns and children up to the twelfth month of life, until the sutures of the skull finally fuse together.
Neurosonography is indicated for the following pathological conditions:
- Infant suffocation.
- Fetal hypoxia.
- C-section.
- Infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
- Genetic abnormalities.
- Recession or bulging of the fontanel.
- Birth injuries.
- Lack of weight.
- Detection of pathology during intrauterine development.
- Profound prematurity.
- Prolonged labor.
Subsequently, MRI or CT is used for examination, which makes it possible to accurately determine the location of the cystic cavity, its size and shape. During these diagnostic measures, children under 6 years of age are in medicated sleep. Based on the results obtained, the doctor draws conclusions and determines further treatment tactics.
If a cyst detected on a child’s head grows slowly, then drug therapy is used aimed at eliminating the cause of its occurrence. Drugs are prescribed to improve blood circulation in the damaged area of the brain. The most commonly used medications are:
- Cerebrolysin.
- Cortexin.
- Actovegin.
- Instenon.
If the doctor reveals that the cause of the anomaly is an inflammatory process, then antibiotics and antiviral drugs are prescribed. To strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators and vitamin complexes are used. The course of treatment, drug names and dosage are determined individually.
Surgical intervention
When the results of the examination show that the cystic tumor has a tendency to grow rapidly, specialists resort to surgical intervention. It is divided into 2 types:
- Palliative, including bypass surgery and endoscopy.
- Radical, involving craniotomy.
Bypass surgery has both positive and negative aspects. This method is less traumatic, but does not eliminate the risk of infection. The patient is fitted with a system of shunt tubes to remove fluid from the cyst. Parents are warned of the adverse effects that the cystic cavity may refill once the shunt is removed.
Endoscopy is a progressive and relatively safe method of removing the contents of a cystic tumor. There is no need to install or change a shunt system here.
Radical methods are resorted to in extreme cases. Trepanation of the cranium involves excision of the cyst with all its contents. This is an extremely difficult, traumatic and dangerous procedure that almost never occurs without consequences. These include:
- Deterioration of hearing and vision.
- Speech impairment.
- Frequent headaches.
- Attacks of dizziness.
- Deformation of the excised area of the skull.
Causes
Obviously, a brain cyst in a newborn does not just appear. The reasons for its occurrence are quite serious and often cause different consequences:
- congenital pathologies of the central nervous system
- injuries
- cerebral hemorrhages
- past infections, especially meningitis and encephalitis
- herpes virus infection
- impaired blood circulation in the brain tissue and, accordingly, hypoxia
All this leads to the death of brain tissue, and cavities filled with fluid form in such areas. In most cases, the formation remains in place, it does not grow, and does not pose any particular risk. But in some cases, their growth is still possible, and then there is a danger of developing brain pathologies.
Cyst growth occurs for reasons such as:
- Increased pressure in the cavity itself.
- Infection with infectious diseases.
- A concussion already in the presence of a cavity formation.
- Bruises, injuries to the toddler.
Classification
There are several types of tumors in infants. They differ in location and period of formation. A cyst in the brain of a newborn poses a great danger to some parts of the organ, so a specialist needs to accurately determine the type of formation.
Arachnoid
Arachnoid cysts are common in boys due to trauma during childbirth.
The tumor is presented in the form of a membranous cavity. Tissue joints vary in shape and size. In a newborn, spinal substance accumulates inside the membrane. Arachnoid cysts are common in boys due to trauma during childbirth. The tumor grows quickly and compresses the nerve tissue.
Subependymal
A shallow cavity containing cerebrospinal fluid is located just below the cerebral cortex due to vascular damage.
A shallow cavity containing cerebrospinal fluid is located just below the cerebral cortex due to vascular damage. Hemorrhage can be extensive. The consequences of a subependymal cyst of the brain in newborns appear as the walls increase in size and spread to other areas of the brain.
Choroid plexus cysts
Choroid plexus cysts disappear on their own as the fetus develops.
Choroid plexus cysts are a physiological disorder. During the intrauterine formation of the brain, cavities with fluid or pseudocysts are formed. As the fetus develops, they disappear on their own. In rare cases, such tumors are diagnosed late in pregnancy or after birth, which is always associated with a difficult pregnancy or infection.
Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns and fetuses does not cause neurological disorders, brain function remains at the desired level. A benign formation is determined already at 14 weeks of pregnancy. False cysts are among the safest consequences of childbirth, which are formed as a result of microscopic hemorrhages of embryonic tissue. According to geneticists, a pseudocyst appears in the head of a newborn due to certain genetic mutations.
Colloidal
A colloid cyst poses a serious danger if it grows or changes position slightly.
A cyst in the ventricle of the brain is a congenital colloid formation. It is of hereditary origin. During the process of conception, a gene of a specific type is transferred to the newborn. The tumor has thin walls and gelatinous contents. Sometimes poses a serious danger in case of growth or slight change in position.
Porencephaly
A porencephalic cyst of the brain in newborns is a tumor that forms between the lateral ventricle and the subarachnoid region. Sometimes it can reach enormous sizes and affect the entire hemisphere of the head.
Sometimes porencephaly can reach enormous proportions and affect the entire hemisphere of the head.
Porencephaly is dangerous due to its complication, which in medicine is called cystic brain. Symptoms and progression of the cyst significantly impair the quality of life of the newborn.
Symptoms
Typically, the fluid-filled brain cavity itself does not cause any symptoms in newborns. But if it compresses areas of the brain, grows and causes additional complications, the following signs may appear:
- excessive regurgitation, which in older children leads to vomiting
- pulsation in the swollen fontanel
- slowing down the child’s development – both psychomotor and physical
When the formation grows noticeably, additional symptoms appear:
- Headache.
- Increased pressure inside the skull.
- Noise in ears.
- Increased drowsiness or, conversely, sleep disturbance.
- Slow movements and other complications of motor activity.
- Hypertonicity, like hypotonicity, of muscles.
- Cramps.
- Fainting.
- Tremor.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Mental disorders leading to hallucinations.
Many of these signs are simply impossible to track in newborns, since they still move little and cannot talk about their sensations and pains. Therefore, if there is any anxiety, unusual behavior, or weakness, you should immediately show the child to a pediatrician and neurologist.
Symptoms also depend on the location of the cyst. For example, if located in the back of the head, it can cause blurred vision. The cavity in the cerebellum leads to deterioration in coordination of movements. When it is located near the pituitary gland, complications arise in the functioning of the endocrine system.
What are the types of tumors in a newborn?
Among the large number of cystic formations in human brain tissue, only some of them are capable of affecting the tissue of the cerebral cortex of a newborn. Based on the results of research and many years of studying the problem of small cysts in a newborn’s head, doctors today identify several main types of tumors that appear due to birth injuries or viral infections in the baby’s brain. Let's list them.
Arachnoid cyst
According to doctors, an arachnoid cyst in a baby’s head is the most common. Such cystic formation can appear both during embryonic development and after childbirth due to mechanical damage to the cortex tissue. What is a cyst in the head of a newborn? The tumor is characterized by the fact that it does not resolve on its own and can provoke the development of dysfunction in various parts of the child’s brain.
The cause of the appearance of such a cyst can be either inflammatory or bacterial diseases, or damage to the tissue of the arachnoid membrane during childbirth. When does a cyst in the head in newborns go away? Treatment for such a tumor can begin already in the first days after the birth of the child. It is worth saying that a cyst of this type, if it is not exposed to external influences of bacteria or chronic inflammation, quickly decreases in size and disappears.
Cerebral tumor
A cerebral cyst in a newborn’s head is extremely rare. As for the causes, in the case of a cyst in the head of a newborn child, the reasons for its development are associated with injury to brain tissue. The tumor appears due to severe intracranial violations of the integrity of the tissues of the gray matter of the brain.
Such tumors in newborns, as a rule, lead to the development of many pathologies and developmental abnormalities. They can also cause paralysis or congenital heart failure. Depending on its location, a cyst of this type often provokes visual or hearing impairment in the baby, malfunction of the musculoskeletal or speech apparatus, which entails the need for long-term treatment and recovery.
Collodial cyst
A collodial cyst in the head of a newborn child appears in the early stages of development in the womb due to genetically determined developmental pathologies or the presence of congenital chronic diseases in the woman’s body. The consequences of collodial cysts in the head of a newborn child can also result in the most dangerous problems.
Dermoid tumor
Dermoid brain tumors in newborns are a rare but dangerous disease. The causes of a cyst in the head of a newborn of this type are associated mainly with the closure and deformation of stem cells, which are intended to form the child’s face, in the body of the brain. The consequences of a cyst in the head in newborns are also dangerous. Due to the characteristics of growth and formation, such a tumor is considered extremely pathogenic and toxic. As a rule, a child with a dermoid cyst does not survive to the due date or is born with damage to brain tissue that is incompatible with life.
Pineal tumor
This type of cyst in a newborn’s head appears in the child’s brain due to a malfunction of the pineal gland. Primary forms of cysts in the penial region of the brain are not dangerous or pathogenic for life and brain tissue. Treatment of a cyst in a newborn baby’s head is also quite simple. In the first months after birth, children with such tumors quickly recover and return to normal.
In rare cases, a pineal cyst in a newborn’s head cannot be diagnosed even in the first stages of growth. In the future, a pineal type cyst can provoke the appearance of inflammation, headaches or sleep disturbances. To avoid a negative development of the scenario, a cyst in a newborn’s head should be regularly monitored by CT or MRI.
WE RECOMMEND YOU TO WATCH:
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT:
Diagnostics
Considering the seriousness of possible complications, you should not ignore the appointment of tests for your baby. Moreover, it is possible to diagnose a cyst without any complex operations: to determine the presence of one, it is enough to undergo neurosonography (NSG) - ultrasound of the brain. It does not cause discomfort, so babies tolerate the procedure calmly and often just sleep.
NSG is performed through an open fontanel. If there is a suspicion of such formations and complications after childbirth, NSG is prescribed immediately after the birth of the baby. When symptoms appear later or there are no symptoms at all, it is recommended to do an ultrasound of the brain every month, and then as prescribed by a neurologist.
A similar procedure must be carried out for premature babies and babies born with injuries. It is recommended that those who experienced oxygen deprivation during pregnancy be examined by a neurologist. But doctors insist on conducting NSG both monthly and at 3, 6, 12, even in the absence of a diagnosis.
If a subependymal cyst is identified, the baby is prescribed an MRI - magnetic resonance imaging. They also undergo it regularly - several times a year.
Treatment
Treatment of cavity formation of the brain depends mainly on its type, location, presence of complications and other factors. As a rule, for a choroid plexus cavity that appears during fetal development, neurologists do not prescribe treatment, since it goes away on its own.
Other forms of the disease require at least monitoring: doctors say that the cyst should disappear within the first twelve months of life. If this does not happen or, on the contrary, it begins to grow and causes new complications, medical intervention is required.
The only critical situation is an arachnoid cyst, which never resolves on its own. It is treated promptly. It could be:
- radical surgery - craniotomy to completely remove the cavity formation
- palliative procedure - shunting removes fluid, endoscopy can be used to remove the entire contents of the cavity
The first option is considered dangerous due to its traumatic nature. Shunting is considered a safer method, but it only removes fluid. In this case, the presence of a shunt in the head can lead to infection of the brain.
Endoscopy also involves minimal intervention, but requires a highly qualified neurosurgeon.
Children whose parents contacted a neurologist in a timely manner and received adequate and competent treatment have a chance for a full recovery.
Possible complications
As has been said many times, the risk of complications depends on the localization and progression of the band formation. Despite the absence of symptoms in infancy, you should not refuse to follow up with doctors in the future: not all cysts disappear. Such asymptomatic cavities can manifest themselves during adolescence, when children are injured, lead a more active lifestyle, and try smoking and drinking. If even the most harmless cyst begins to progress due to various factors, the following consequences can be noted:
- Development of blindness.
- Hearing impairment.
- Divergence of head bones.
- Development of hydrocephalus.
- Brain hemorrhages.
- Death.
As a rule, in most cases, doctors give a favorable prognosis. Timely diagnosis, medical supervision, supportive therapy or radical methods used on time - all this allows us to talk about a complete recovery.
Having a cyst is not a reason to panic. It is only important to observe the child and monitor the condition of the cavity formation. Medical supervision will allow you to avoid complications and take timely measures in case of disease progression.