What is colostrum?
Colostrum is the baby's first food after birth. This substance helps the child’s body adapt to the new world. It is odorless and has a semi-liquid consistency of white-transparent color. The calorie content of colostrum is almost twice that of milk. The value is 150 kcal per 100 ml. The density of the secretion is 1.05-1.06. About 85% of the substance consists of water, which is a solvent for other components, such as fats, carbohydrates, proteins, lactobacilli, vitamins, enzymes, and hormones.
Cow's colostrum: benefits and indications for use
Cow's colostrum is unique in that it is recommended for use both in human immunodeficiency conditions and in autoimmune conditions, i.e. it is universal, it can correct immunity: strengthen it or weaken it, depending on the situation. Cow's colostrum helps very well with the following diseases: - heart and vascular diseases; - asthma; — allergies (all types); — depression and stress; - Alzheimer's disease; — chronic fatigue syndrome; - sinusitis; - pharyngitis; - headache; - pneumonia and bronchitis; - multiple sclerosis; - diarrhea; — diabetes mellitus and diseases of the endocrine system; - hypoglycemia; - rheumatoid arthritis; — osteoporosis; - otitis media; — dysbacteriosis; - Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis; - candidiasis... It’s simply impossible to list all the diseases in which cow’s colostrum can help a person; we limited ourselves to only the main ones.
When does the secret appear?
Each woman’s body is individual, so expectant mothers may see colostrum at different times. In fact, the substance is produced already in the first weeks of pregnancy, but its amount is insignificant. This process continues throughout the gestation period. It is easier to recognize the appearance of discharge in the 2nd and 3rd trimester, as its volume increases. After childbirth, colostrum is released in maximum quantities and serves as the first source of nutrition for the baby. A few days after the baby is born, the secretion replaces breast milk, which the child consumes as the main food during breastfeeding.
How does colostrum appear? Physiological process!
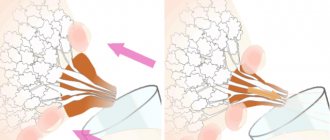
After conception, changes begin in the female body, and they do not bypass the breasts. It swells and increases in size. The longer the pregnancy, the more active all sections of the mammary glands are: the tubules become wider, the lobules of the glands become larger. Such changes occur due to the intense production of fluid in the breast, which is commonly called colostrum. And all this happens under the influence of the hormonal background of a pregnant woman. The hormones directly “responsible” for this process are prolactin and oxytocin.
When a mother feeds her newborn, oxytocin causes the myoepithelium that surrounds the alveoli to contract. Thanks to such contractions, the first milk appears under the influence of the hormone prolactin and comes out of the nipple. During breastfeeding, oxytocin enters the gland, thereby helping fluid move through the subareolar ducts to the nipple.
With stable production of these hormones throughout pregnancy, the breasts will steadily increase in size, increased sensuality will appear, the nipples will swell, and the woman will be able to easily feed the newborn after childbirth.
Composition and properties
Colostrum contains many components that create the value of the secretion.
- Antioxidants and immune bodies form the protective function of the body.
- Immunoglobulin proteins eliminate toxins.
- Transfer factors are immune memory devices that help the child's body recognize infectious attacks.
- Enzymes help normalize the functioning of the digestive system.
- Amino acids promote muscle development, brain and heart function.
- B-casein. The benefit of colostrum lies in the intellectual development of the baby.
- White blood cells help destroy bacteria and viruses.
- Immunoglobulin A has a protective function for the mucous membranes of the body.
- Endorphins help build physical resilience and resist stress.
- Prebiotics normalize intestinal flora.
The composition of colostrum is in many ways better than breast milk. Although the daily amount of secretion is much less. But do not worry that the child does not get enough to eat; such concentrated colostrum with a high calorie content in the first day is enough for the baby to fully develop.
Foremilk and hindmilk: when does it come and what is the difference?
Mother's milk, even from the same breast, varies in composition. For this reason, it is classified into anterior and posterior. Foremilk is formed in the anterior lobes of the gland and, accordingly, enters the baby in the first 20 minutes of feeding. It is lighter and less fatty than the so-called posterior one, which begins to flow to the nipple in the second half of the process or even closer to the end of feeding. It is important to understand that these are not different types of product for feeding, the difference is only in the composition.
Why is this happening? As the baby sucks milk from the front of the breast, secretions from the back begin to flow into the nipple through the ducts. Along the way, it absorbs particles of fat deposited on the walls of the ducts. At the same time, the fat content of breast milk changes gradually, imperceptibly for the mother and imperceptibly for the baby. Therefore, there is no point in thinking about how much fore and how much hind milk the baby received during feeding.
But if, after finishing the meal, a woman has milk left and she decides to express it, it should be understood that it is the back fluid that will end up in the container. Thus, when expressing breast milk, you get a product with a maximum fat content, which means that you will need less to feed it than if you just gave your baby the breast.
In addition, knowing the specifics of changes in the composition of milk is important for those who are in a hurry to feed the baby as soon as possible and change breasts during the same feeding. It turns out that the child eats “light” milk from two glands, and the most nutritious, but also the most inaccessible, remains in the breast. After such a meal, the baby will most likely become hungry ahead of time, and he will not receive the necessary macronutrients.
Effect on the baby's body
In the first hours after birth, the baby is placed on the mother’s breast so that drops of secretion into the baby’s body allow particles of useful substances to form the correct microflora and the baby’s immunity. For several days, the baby's main nutrition consists of absorbing a small volume of these secretions from the mammary gland. Despite the fact that very little colostrum enters the baby’s body, it performs an important function for his life:
- Forms the baby’s immune system, saturating it with useful compounds.
- Supplies lacto and bifidobacteria, promoting the formation of proper intestinal flora. This secretion helps remove meconium, the original feces.
- Normalizes the functioning of the digestive system. The child gradually begins to absorb milk on his own due to the introduction of enzymes.
- Helps remove excess bilirubin, which can lead to physiological jaundice. Which in turn is fraught with damage to the brain and nervous system.
How to improve lactation
After a mother and baby leave the maternity hospital, she should know how to speed up milk production. Getting adequate nutrition for the child depends on this.
One of the main rules for developing breast milk is to put the baby to the breast frequently. As soon as the child shows concern, you need to react immediately. At first, feeding can even be every 15 minutes.
It is important to give your newborn as much food as he asks for. Do not forcefully remove your baby from the breast. Good feeding in the morning is especially important. The baby should eat until he releases the breast on his own.
The first time may not be easy. But it is a timely response to the child’s requests that makes it possible to establish full contact between mother and baby. Over time, both organisms begin to work synchronously, which has a positive effect on both the development of the child and the condition of the young mother.
Sometimes women begin to worry about cracks appearing on their nipples, but this is fixable and can be solved with the help of special medications or traditional medicine methods. In addition, the mother may worry that the baby demands the breast too often, but after a minute or two abandons it. In such a situation, you need to remember that the child receives not only nutrients from milk, but also water. If the baby is just thirsty, then he will ask for the breast, but quickly give it up, and there is nothing wrong with that.
One of the main conditions for normal lactation is a good emotional state and the absence of nervous tension. During the period when the child is in infancy, the young mother often experiences a lot of difficult psychological moments. You need to learn to endure them steadfastly and without worry. To strengthen the nervous system and increase strength, you should use vitamin complexes and adhere to proper nutrition.
Norm and deviations
Colostrum in pregnant women looks like a translucent white liquid with a yellowish tint and sticky to the touch. The thickness of the secretion, as well as the intensity of the color, depends on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body. In the last trimester, colostrum with blood can be considered normal if the inclusions are insignificant. But such a situation needs to be discussed with a gynecologist.
The amount of secretion can vary from a few drops to multiple fluid secretions. The absence of discharge during the prenatal period is not a pathology. But if there is no lactation after childbirth, then the woman needs to consult a gynecologist. The discharge may stop for a while and resume again, which is also normal and does not require treatment. A significant deviation is considered when colostrum is secreted mixed with pus or if the secretion has an unpleasant odor. A pregnant woman should be alerted to a rise in temperature, pain and the presence of lumps in the mammary gland.
Discharge during pregnancy
Colostrum is the secretion produced by the mammary glands during pregnancy and some time after childbirth.
While expecting a baby, a woman's breasts change: glandular tissue grows, ducts expand, nipples and areolas darken and become more sensitive. An increase in hormone production stimulates the onset of secretion. Under the influence of prolactin and oxytocin, preparation for the upcoming lactation begins in the second trimester. Drops of thick sticky liquid are periodically released from the nipples. This is colostrum.
There is no clear concept at what stage of pregnancy its production should be considered normal. In some women, it can flow quite profusely from the breasts already from 14–15 weeks, while others do not feel any changes until labor approaches.
“Training” the glands does not affect the quality and quantity of future milk in any way - it is just a hormonal change. But such an important sign, if it appears, cannot be ignored.
When a little fluid is released, it does not have an unpleasant odor, impurities of pus or blood, there is nothing to worry about. Early excessive discharge from the nipples can be caused by nervous shock, stress, overheating, hypothermia, rough stimulation, uncomfortable, tight underwear, massage, which is prohibited for the glands to be subjected to even in the absence of pregnancy.
If the discharge is accompanied by nagging pain in the uterus and bloody clots, you need to consult a doctor - increased tone and the risk of miscarriage are likely.
Trying to squeeze out or express premature colostrum during pregnancy is prohibited; this can provoke an increased release of oxytocin and subsequent miscarriage. When caring for the mammary glands, you just need to take care of careful hygiene: wash your breasts daily with warm water, blotting your nipples with a soft cloth, wear cotton underwear without pits, use special inserts that prevent getting wet, and change them on time.
This will avoid the development of infection; colostrum is a favorable environment for pathogens. It is necessary to use shower gels and soaps when washing your breasts during pregnancy and breastfeeding less often than usual, so as not to dry out your nipples. There should be no pain in the chest with or without discharge from it. Causes for alarm: changes in the relief of the glands, the appearance of retracted areas, swelling, itching, redness, swelling or peeling.
Colostrum appears not only in women before childbirth, but also in non-pregnant girls, children and even men. The cause of a rare pathology called galactorrhea is a violation of prolactin synthesis. This may indicate congenital or acquired diseases of the pituitary gland or thyroid gland.
Properties and composition of colostrum in postpartum women
Colostrum, produced by the glands within 4-7 days after the birth of the baby, is more fluid and lighter than during pregnancy. In appearance, it is a translucent yellowish or grayish thick, slightly oily liquid, with a slight salty-sweet taste with a high content of protein compounds. After a few days, more fats and sugars appear in its composition, and there is less protein - transitional milk is formed. From the beginning of the second week after birth, the composition stabilizes - the milk becomes fully mature.
The properties of colostrum are unique, despite the fact that it is commonly called unripe milk. The substrate contains in an ideal ratio all the beneficial substances necessary for a newborn during the transition period from intrauterine to breastfeeding. Colostrum contains:
- A set of valuable proteins: albumins, globulins, enzymes.
- Natural antioxidants: carotene, zinc, selenium, tocopherol, vitamin C, blocking the oxidizing effects of oxygen contained in the air.
- Mature maternal immune factors: lymphocytes, macrophages, lactoferrin, immunoglobulin A, polysaccharides and oligosaccharides. At the same time, the concentration of immune cells in colostrum is much higher than in the blood of a woman in labor. They are not digested, remaining in the baby’s intestines and forming protection against pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi and other pathogens, promotes better absorption of iron, eliminating its excess, which supports the activity of microbes. Colostrum helps block cholera vibrio, salmonella, streptococci, rotavirus, enteroviruses, polio virus, encephalitis, herpes, and Candida fungi. At the same time, the child’s own interferon is produced, and the foundations of future immunity are laid.
- Growth factors: peptides, cortisol hormones, insulin, specific factors EGF, IGF-I. Under their influence, the formation of epithelial tissue of the stomach and intestines occurs, the synthesis of DNA cells, and overall physical development and growth are accelerated.
Each woman has different thickness, composition and color of colostrum. In general, it contains more than 30 different active biochemical elements.
Because colostrum contains less liquid, fat, casein and lactose than breast milk, it is not difficult to digest. At the same time, it has a laxative effect, helping to cleanse the baby’s intestines of original feces, helping to accelerate the excretion of congenital bilirubin, which prevents the development of physiological jaundice.
What affects the amount of discharge?
The secretion of colostrum may be insignificant or, on the contrary, excessively intense. In addition to the individuality of the body, there are a number of factors that provoke an increase in secretion:
Emotional background. The presence of positive emotions accelerates the appearance of colostrum. Low mood, depression, and stress, on the contrary, reduce the amount of discharge.
- Hot shower. When taking a bath, the flow of secretions increases.
- Hot food. If food or drink has a temperature above 37 degrees, then colostrum appears more intensely.
- Massage. Stimulating the mammary glands accelerates blood circulation in this area, which provokes an increase in secretion.
- Sexual intercourse. Excitement provokes an increase in the production of hormones, which increases the amount of discharge.
Breast care
When colostrum is released, a woman should pay close attention to her mammary glands. The important rules are:
- Buying a comfortable bra that will not put pressure on the gland.
- It is necessary to wash the breast area twice a day without using soap, so as not to dry out the delicate skin of the areola.
- After a shower, nipples should be blotted without rubbing with a towel.
- When feeding colostrum, it is worth purchasing a cream to prevent cracked nipples.
Squeezing out secretions is strictly prohibited; this can lead to serious pathologies of the mammary gland and increased uterine tone. When the substance flows, it is necessary to use special pads so that it does not leak onto clothing and does not irritate the nipples due to friction of the wet surface against the underwear.