With the natural type of feeding, young mothers often encounter the child’s refusal to eat. The reason for this situation is a change in the taste of breast milk, which becomes salty. If this problem occurs, nursing women need to find out the cause of the changes as quickly as possible and make every effort to eliminate them.
What shapes the taste of milk
The basis of the taste and beneficial qualities of this product is nutrition. The chemical composition of mother's milk depends on the completeness of the diet. Within the walls of the maternity hospital, the young mother is given recommendations regarding nutrition, which she must strictly follow. Before food components enter breast milk, they undergo a cascade of chemical transformations in the mother's body. Only after these substances enter the bloodstream do they accumulate in milk.
The consumption of certain foods affects the taste of breast milk. Similar changes are felt by a newborn baby, who ceases to perceive the mother’s breast. If the baby is not satisfied with the taste of milk, he becomes capricious and refuses to breastfeed. The following products influence the taste of mother's milk:
- vanilla sugar and vanilla;
- garlic, onion, hot pepper;
- radish, radish;
- confectionery products containing flavor and color improvers;
- spices and seasonings.
In addition to the characteristics of the diet, the taste of mother's milk is influenced by the emotional background of the woman. Excessive emotional stress and stress often cause changes in the taste of such a valuable product.
Why breast milk can be sweet or salty and what affects it
The health and lifestyle of a breastfeeding woman affect how breast milk tastes. Culinary preferences and product selection are of greatest importance. Changes in the composition and taste of milk may be affected by changes in eating habits.
Composition of breast milk
Breast milk is a balanced nutritional medium. Its content may vary depending on the time of day, general condition and mood (psychological comfort) of the mother. The composition of the liquid changes during feeding.
Milk contains:
- proteins, fats and carbohydrates necessary for the life and development of a child in infancy;
- enzymes that promote the absorption of nutrients;
- immunological defense factors responsible for the formation of the body’s immune response to the presence of antigens and the development of acquired immunity;
- vitamins and minerals, micro- and macroelements of which regulate metabolism, help to optimally use the constituent components of breast milk.
Breastfeeding, unlike artificial feeding, fully meets the growing body's need for water. Milk consists of 87% of it. If the feeding regimen is followed, the baby receives breastfeeding on demand; there is no need to give him additional water.
The most important component is proteins. Breast milk contains macromolecules with a balanced amino acid composition and easy digestibility. Their content can reach 1–1.8%. The main building material is casein (its amount in mature milk can be up to 40% of the total amount of proteins) and whey protein (up to 60%).
Fat in liquid – from 3.9 to 5.2%. Their finely dispersed structure allows molecules to easily penetrate cell membranes. This helps the absorption of substances and quickly saturates the child. The fat content of the nutrient fluid gradually increases during feeding. The last portion of milk is the fattest.
Carbohydrates are represented by di- and oligosaccharides. Lactose (6.8%) is necessary to provide energy to a growing body. This is especially important for the brain. Carbohydrate promotes calcium absorption. Oligosaccharides are a nutrient medium for bifidobacteria living in the child’s intestines. In addition, they neutralize some antigens.
Milk contains digestive hydrolytic enzymes necessary for the breakdown of all macromolecules. They participate in the formation of new vital compounds. Some of them block the activity of viruses and pathogenic single-celled microorganisms.
The nutritional fluid contains hormones and growth and development factors. They participate in the humoral regulation of metabolic processes in the child’s body and are responsible for the differentiation of cells and tissues of all organ systems.
What does breast milk taste like?
Normally, the nutritional liquid should be slightly sweet. This is due to the high sugar content in it.
Many women compare the taste of their milk with the taste of diluted condensed milk (if you dissolve 1 teaspoon of the product in 1 glass of clean water).
Sometimes the liquid resembles a sweet protein shake that athletes use to build muscle mass.
If there are no sharp deviations in the mother's diet, milk does not have strong flavors. It leaves a pleasant aftertaste. The predominance of creamy taste indicates a high fat content.
Many women report a salty taste to their milk. This may be due to the increased content of table salt in it. In some cases, it begins to taste bitter, causing anxiety in both mother and child. If the milk has acquired a bitter taste, this does not mean that breastfeeding should be stopped. It is better to try to find out the reason for the change and eliminate it.
What does taste depend on?
It is different for every woman. The taste may depend on the mother’s well-being at the time of feeding, her state of health, and the foods prevailing in the diet. The following products influence the appearance of a specific flavor:
- spices and hot spices (cinnamon, pepper, vanillin, cumin);
- vegetables with a strong taste and smell (onions, garlic, radishes);
- herbs containing essential oils (basil, mint, thyme).
The taste of a valuable product is negatively affected by the consumption of smoked products. Dishes high in sugar and salt, and coffee also affect the composition and taste of breast milk.
Flavors are affected by hormonal changes. For some breastfeeding women, menstruation occurs before the end of the lactation period. The beginning of the cycle is associated with strong hormonal changes, which are reflected in the taste characteristics of breast milk. During this period, it may become bitter or salty (depending on the level of hormones in the mother's blood).
Some medications can affect the taste of milk. In order not to cause unfavorable changes, medications should be limited or eliminated altogether.
Greater physical activity (for example, intense and prolonged training) leads to the accumulation of lactic acid in the body fluid. It is a breakdown product of glucose. Before the acid is cleared from the blood, it can make breast milk acidic.
Alcohol and nicotine lead to the fact that the nutrient liquid has not only a foreign taste, but also an uncharacteristic odor. Carcinogens and toxins can make milk completely unsuitable for baby food. In addition, such a product poses a potential threat to the child’s fragile body.
The taste may change if breast milk has been frozen. When frozen, changes may occur in the structure of the nutrient fluid. This sometimes happens even if all the rules for freezing and thawing the product are followed. Breastfeeding women note that when exposed to low temperatures, milk may develop a synthetic taste.
The presence of an inflammatory process in the mammary glands, for example, with mastitis, also negatively affects the taste of milk. It may become salty or bitter. The same happens with lactostasis.
If the child does not refuse the breast, you should not interrupt breastfeeding. You just need to monitor the color of the nutrient liquid.
This is necessary to prevent milk with purulent or bloody inclusions from entering the baby’s body.
Source: https://mammolog.guru/beremennost-i-laktaciya/grudnoe-vskarmlivanie/kakoe-na-vkus-grudnoe-moloko.html
Mastitis and lactostasis
A potential cause of the salty taste of breast milk is mastitis and lactostasis. Both conditions are characterized by the accumulation of sodium crystals, making the milk salty. If a woman has developed unilateral mastitis, then the salty taste of milk will be observed in the painful breast. With unilateral lactostasis, the taste of milk changes in each mammary gland.
If the cause of this phenomenon is stagnation of milk, then despite the discomfort, it is not recommended to stop feeding the baby naturally. If mastitis develops, complicated by purulent-inflammatory changes, feeding should be stopped to avoid infection of the child’s body.
Hormonal imbalance
Changes in hormonal levels often lead to the appearance of a salty taste in breast milk. The cause of such changes can be the restoration of menstrual function in a nursing mother. When a young mother’s menstrual cycle normalizes, the baby refuses to breastfeed not only because of a change in the taste of the milk, but also because of a change in the smell of the mother’s body.
Other hormonal changes include recurrent pregnancy. If a woman becomes pregnant while lactating, her milk acquires a salty taste and a specific smell. If this circumstance does not cause a refusal to breastfeed, then the woman is recommended to continue natural feeding of the baby.
Taking medications
Before using any medications, a nursing mother should obtain the consent of a medical professional. Many medications have the ability to penetrate through the blood into breast milk, affecting its taste and nutritional qualities.
When breastfeeding a baby, drinking alcohol and smoking is strictly prohibited. These substances not only change the taste of milk, but also have a detrimental effect on the child’s body.
Treatment
If the cause of this condition is errors in the diet, then the nursing mother is advised to reconsider her diet. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that affect the taste of milk. Treatment of lactostasis and mastitis must be done under the guidance of a medical specialist.
Treatment of mastitis involves the use of the following groups of drugs:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibacterial drugs;
- antipyretics;
- multivitamin complexes.
Hormonal changes in the mother’s body, as a rule, disappear on their own. If the reason for the change in the taste of breast milk was the restoration of menstrual function, then the nursing mother should not worry. Such changes will take place without outside help after some time.
In order for breast milk to retain its nutritional and taste properties, a woman must avoid nervous shock and stress. In a home where a nursing mother and her newborn baby live, a comfortable emotional environment and a favorable mood should be maintained.
A week ago I stopped breastfeeding my daughter. Before this, there were only night feedings - and it was difficult to call it feedings - so, more than anything, she applied to the breast just to calm down, apparently she liked the process itself, but there was little milk. So, for almost a week after completing breastfeeding, there was no heaviness or feeling of fullness. Everything was the same as always - my breasts had shrunk in size, and I thought that was it, the milk had gone.
But two days ago I began to feel pain in the lobes emanating from the center of the sternum (I don’t know how to write more precisely) - only in them. And I felt droplets of milk coming out. At the same time, the breasts are completely soft, there are no lumps, and it feels like they are practically empty. But at first the milk tasted sour to me, and then I realized that it was salty.
And for the third day now, it’s the central lobes that have been hurting. So I’m thinking - either my daughter trampled on me with her hands (she falls asleep on my chest, and before falling asleep she always crawls up and down me), or after all, some kind of stagnation of milk has formed and I need to try to express at least a little, but I’m afraid to stimulate a new flow of milk.
Maybe someone had a similar situation? What do you advise?
Sometimes it happens that the baby suddenly does not take the breast for no apparent reason. In this case, you can taste the milk; perhaps it has become bitter or salty to the taste, so the baby refuses the unusual food. When faced with this, you need to first find out why breast milk is salty or bitter.
Why does breast milk become salty?
Breastfeeding is a natural process that ensures the full development of the child. Mother's milk contains all the substances the baby needs.
Therefore, no artificial formula, even the most adapted, can replace breast milk. During the period of breastfeeding, some women taste the milk that the baby is fed.
Questions often arise about the taste of this natural food. One of them: why did breast milk become salty?
Before drawing a conclusion about the saltiness of milk, you should figure out: what should human milk be like? As a rule, it has a sweetish taste. But if a woman’s living conditions or nutrition change, breast milk may acquire a different taste and smell.
So, let's look at why breast milk tastes salty.
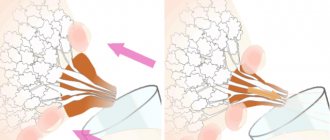
Lactostasis or mastitis
One of the reasons for this change may be any disease of the mammary glands, for example, lactostasis or mastitis. These diseases are associated with stagnation of milk in the milk ducts or the occurrence of an infectious inflammatory process. In case of such diseases, you will feel the following symptoms:
- Enlargement of the mammary glands.
- Redness of some areas (presence of red spots on the chest).
- Soreness to touch.
- Increased body temperature.
- Lumps may appear on the chest.
- Difficulty squeezing milk out of the breast.
- A change in the usual white color of milk to yellow, as well as the appearance of a salty taste.
If similar symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo all necessary tests. After all, mastitis is an infectious disease, and if it is not cured in time, it can lead to dire consequences, including infection of the baby.
Lactostasis is a fairly common phenomenon that many women encounter while already in the maternity hospital. To diagnose the presence of milk stagnation, you should analyze the symptoms and consult a doctor. If the doctor confirms the presence of lactostasis, then this disease is the cause of the salty taste in breast milk.
To completely heal your breasts, you do not need to stop breastfeeding. On the contrary, frequent suckling by the child of the sore breast is the best treatment. After all, during stagnation, it is important to empty the clogged ducts as quickly as possible. If the baby cannot cope with a large amount of milk, you will have to resort to using a breast pump.
With lactostasis, there may be salty milk in one breast, and normal milk in the other.
Despite the apparent harmlessness of lactostasis, it is its advanced state that is usually the cause of mastitis.
Fading lactation
The extinction of lactation does not occur immediately. The mammary glands gradually stop producing milk in the same volumes. Natural burnout of milk occurs after the child turns 2 years old.
The decline is accompanied by a decrease in the production of the sweet carbohydrate lactose. It is lactose that is responsible for the sweetness of human milk. At this time, milk contains a lot of sodium. And sodium is salt. This phenomenon can explain the saltiness of the milk.
Despite the appearance of such an unusual taste, children still do not give up their usual diet.
Taking medications
Unfortunately, during breastfeeding the female body is vulnerable. It is almost impossible to completely protect yourself from diseases. Taking medications becomes a reality for many breastfeeding mothers. Fortunately, there are drugs that do not pass into breast milk and are safe for children.
Despite this, breast milk may develop one or another flavor. Typically, medications give milk a bitter taste. But there are also those that contain many minerals, which increases the “salinity”.
If the milk has become salty due to medications or vitamins, and the nursing mother takes them as prescribed by the doctor, and the baby is still eating normally, then there is no need to worry.
Menstruation or pregnancy
These phenomena are accompanied by changes in the woman’s hormonal levels. Many people claim that during menstruation, milk becomes bitter or salty. As a rule, such a change in taste is short-lived. After a few days everything will be restored.
A new pregnancy is also accompanied by serious hormonal changes. The taste of milk may change, just like during menstruation.
If you do not need to stop breastfeeding during menstruation, then when a new pregnancy occurs, it is advisable to stop breastfeeding so as not to burden the body and to allow the fetus to fully develop in the womb.
Maternal nutritional characteristics
Babies remember the smell and taste of mother's milk from birth. Experts say that there is no direct relationship between the foods eaten and the taste of milk. However, milk acquires certain shades (“notes” of taste), especially after consuming various spices or foods with rich flavors and aromas.
Children enjoy drinking milk flavored with sweets and vanilla. But they are often scared off by the flavor of mother’s milk:
- garlic
- Luke
- radishes
- seasoning
Overly seasoned or overly salted foods can affect the taste of human milk. A child, sensing something is wrong, may refuse. Therefore, during breastfeeding, you should not eat foods that are too salty, fried, flavored with spices, or smoked. In addition to changing the taste, such milk carries the risk of developing an allergic reaction in the baby, as well as tummy problems.
Let's sum it up
One of the most unpleasant causes of salted milk is lactostasis. If, in addition to a change in the taste of milk, a nursing mother has breast pain, tightness and fever, you should consult a doctor. There are also other non-dangerous reasons for the saltiness of milk: menstruation, new pregnancy, taking medications, burnt milk, abuse of salty foods.
Source: https://grudnichokk.ru/zdorove-mamy/pochemu-grudnoe-moloko-stalo-solenym
What factors determine the taste of breast milk?
Breast milk usually tastes quite sweet - much sweeter than regular cow's milk. This is due to the fact that a child needs more carbohydrates for full development (especially of the brain). Therefore, breast milk contains a lot of lactose - milk sugar.
But in some cases, its taste properties may change, without always affecting the quality. First of all, the smell and taste of mother's milk are greatly influenced by the food that the mother eats.
- vanilla and other spices, seasonings;
- mint;
- sugar and sweet foods in large quantities.
In addition to nutrition, taste can be affected by exercise, the use of certain medications, alcohol, smoking, as well as hormonal changes in the body - menstruation or a new pregnancy.
Is breast milk salty?
Lyudmila, hello!
In recent days, my daughter has become restless at the breast. He will suck and release. Crying. It began to seem to me that my milk was bad, and I risked tasting it. It turned out to be very salty. What to do? Am I really unable to breastfeed and will I have to switch my baby to formula?
No, don’t worry and don’t switch your child to formula. Salty breast milk is a normal option, and now I will explain why the taste of milk can change and how critical this is for babies.
Taste of milk
Taste sensations depend on genetic predisposition, as well as on national food characteristics.
Most often, the taste of breast milk is described as sweet and creamy. What makes it so is its high lactose (milk sugar) content.
Some women find their milk bitter, even tasting soapy.
The following can have a negative effect on the taste of breast milk:
It may become bitter or salty. Very often, young mothers run to the gym to regain their figure. If you are one of them, then be prepared for the fact that your breast milk may also become salty.
This is caused by a substance that is released in the body during physical training.
Read the article about How to lose weight after childbirth>>>
Peculiarities of taste in infants and adults
When babies are born, they can react to 4 types of stimulation:
- Sweet.
- Sour.
- Gorky.
- Salty.
Many mothers become curious to taste their milk. And it doesn’t always leave a positive impression of itself. Thoughts arise: “How can you drink it?”
The fact is that the newborn did not swallow anything except amniotic fluid, and did not eat anything except breast milk. He is not familiar with other tastes.
An adult, on the contrary, already has quite a wealth of experience in learning tastes. Therefore, how you perceive your breast milk and how your baby perceives it are two different points of view. So breast milk is not a delicacy for him.
Why does breast milk become salty?
All of the factors listed above affect taste differently. But if breast milk has become salty, the reasons may be as follows:
- development of lactostasis or mastitis;
- completion of lactation (involution);
- drug treatment;
- restoration of the menstrual cycle or new pregnancy.
Usually, babies rarely refuse to breastfeed if their taste has changed a little, although they may show dissatisfaction - eat less actively, be capricious at the breast. If the milk has acquired a taste that can repel the baby, you need to determine the reason and try to improve feeding.
Many observations show that breast milk often becomes salty during menstruation. Babies can either refuse to breastfeed, or simply be capricious and eat poorly. Some breastfeeding consultants believe that the point here is rather that the mother’s smell changes, and this is very important for the child. During her period, mom needs to shower more often to reduce the impact of the odor.
Another reason that causes hormonal changes that affect taste may be the mother’s new pregnancy. Some babies may refuse to breastfeed, but if they are satisfied with the taste and there is no threat of interruption, you can safely continue feeding. And after giving birth, continue to feed two babies.
Lactostasis is a possible cause of taste changes, which occurs quite often. In this case, the milk in one breast becomes salty, while in the other the milk remains of normal taste. This is due to the fact that the disease causes the accumulation of sodium salts in the diseased breast. If the baby eats well from one breast, but is capricious from the other, this is a reason to suspect lactostasis.
Although the milk may taste salty, there is no reason to stop feeding. The best way to cope with congestion is to put your baby on the sore breast more often. No device can so effectively empty a mother’s breasts and rid it of excess that has accumulated in the milk ducts and causes inflammation.
In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between mastitis and lactostasis. The first is an infectious disease in which pus can also get into the milk. Therefore, if you suspect mastitis, you should consult your doctor about continuing to feed from the sore breast.
Many mothers have noticed that after playing sports, the baby may be reluctant to eat or even refuse to breastfeed. If you taste the milk at this moment, you will notice that it has acquired a specific salty taste.
During intense physical activity, a special substance is produced in the muscles - lactic acid. Because of it, muscles ache after exercise, and milk takes on a salty-sour taste.
During breastfeeding, many medications are prohibited for the mother, as they enter the breast. There is a small list of those drugs that are quickly eliminated from the blood and milk or enter it in minute quantities. But at the same time, they can affect its taste, causing objections from the baby. If he is capricious and refuses to breastfeed, you can try expressing salted milk or changing the medicine (after consulting your doctor).
Over time, lactation subsides naturally - the child grows, begins to eat regular food and needs less breast milk. It is no longer the main source of proteins, fats and carbohydrates for him. Therefore, the composition of milk changes, causing changes in taste - it contains more bioactive substances, less lactose, more sodium salts. There are also a lot of immunoglobulins necessary for the normal functioning of the immune system. In terms of their quantity, the milk again approaches the colostrum of the first days.
Breast milk has become salty: who is to blame and what to do
Sometimes it happens that the baby suddenly does not take the breast for no apparent reason. In this case, you can taste the milk; perhaps it has become bitter or salty to the taste, so the baby refuses the unusual food. When faced with this, you need to first find out why breast milk is salty or bitter.
What factors determine the taste of breast milk?
Breast milk usually tastes quite sweet - much sweeter than regular cow's milk. This is due to the fact that a child needs more carbohydrates for full development (especially of the brain). Therefore, breast milk contains a lot of lactose - milk sugar.
But in some cases, its taste properties may change, without always affecting the quality. First of all, the smell and taste of mother's milk are greatly influenced by the food that the mother eats.
Of course, it does not fully acquire the taste of the foods eaten, since they are first digested by the mother’s body, but some “echoes” reach the baby. For example, garlic, onions or radishes can make it bitter, and a large amount of salty foods will give the milk a salty taste. Taste is also affected by foods such as:
- vanilla and other spices, seasonings;
- mint;
- sugar and sweet foods in large quantities.
In addition to nutrition, taste can be affected by exercise, the use of certain medications, alcohol, smoking, as well as hormonal changes in the body - menstruation or a new pregnancy.
Previously, many nursing women believed that salted milk was spoiled and called it “burnt out.” But this is not so - milk cannot deteriorate in the breast, just as blood in the vessels cannot deteriorate.
Why does breast milk become salty?
All of the factors listed above affect taste differently. But if breast milk has become salty, the reasons may be as follows:
- development of lactostasis or mastitis;
- completion of lactation (involution);
- drug treatment;
- restoration of the menstrual cycle or new pregnancy.
Usually, babies rarely refuse to breastfeed if their taste has changed a little, although they may show dissatisfaction - eat less actively, be capricious at the breast. If the milk has acquired a taste that can repel the baby, you need to determine the reason and try to improve feeding.
During menstruation
Many observations show that breast milk often becomes salty during menstruation. Babies can either refuse to breastfeed, or simply be capricious and eat poorly. Some breastfeeding consultants believe that the point here is rather that the mother’s smell changes, and this is very important for the child. During her period, mom needs to shower more often to reduce the impact of the odor.
Another reason that causes hormonal changes that affect taste may be the mother’s new pregnancy. Some babies may refuse to breastfeed, but if they are satisfied with the taste and there is no threat of interruption, you can safely continue feeding. And after giving birth, continue to feed two babies.
For breast problems
Lactostasis is a possible cause of taste changes, which occurs quite often. In this case, the milk in one breast becomes salty, while in the other the milk remains of normal taste. This is due to the fact that the disease causes the accumulation of sodium salts in the diseased breast. If the baby eats well from one breast, but is capricious from the other, this is a reason to suspect lactostasis.
Although the milk may taste salty, there is no reason to stop feeding. The best way to cope with congestion is to put your baby on the sore breast more often. No device can so effectively empty a mother’s breasts and rid it of excess that has accumulated in the milk ducts and causes inflammation.
In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between mastitis and lactostasis. The first is an infectious disease in which pus can also get into the milk. Therefore, if you suspect mastitis, you should consult your doctor about continuing to feed from the sore breast.
During physical activity
Many mothers have noticed that after playing sports, the baby may be reluctant to eat or even refuse to breastfeed. If you taste the milk at this moment, you will notice that it has acquired a specific salty taste.
During intense physical activity, a special substance is produced in the muscles - lactic acid. Because of it, muscles ache after exercise, and milk takes on a salty-sour taste.
When taking certain medications
During breastfeeding, many medications are prohibited for the mother, as they enter the breast. There is a small list of those drugs that are quickly eliminated from the blood and milk or enter it in minute quantities.
But at the same time, they can affect its taste, causing objections from the baby.
If he is capricious and refuses to breastfeed, you can try expressing salted milk or changing the medicine (after consulting your doctor).
During involution of lactation
Over time, lactation subsides naturally - the child grows, begins to eat regular food and needs less breast milk. It is no longer the main source of proteins, fats and carbohydrates for him.
Therefore, the composition of milk changes, causing changes in taste - it contains more bioactive substances, less lactose, more sodium salts. There are also a lot of immunoglobulins necessary for the normal functioning of the immune system.
In terms of their quantity, the milk again approaches the colostrum of the first days.
What to do
If a mother is faced with the fact that the milk has changed in taste and the baby refuses to breastfeed, you should immediately try to determine the cause of such changes. A doctor, a breastfeeding consultant, as well as an analysis of the menu and lifestyle can help with this.
As a rule, babies rarely refuse breastfeeding due to changes in taste. Milk of any flavor is healthy and nutritious for them, so if the mother notices that the milk sometimes becomes salty, there is no need to stop breastfeeding.
It is enough to find out the reason and observe the baby’s behavior. If he calmly accepts this taste and its cause is not illness, you can safely continue feeding.
Otherwise, you should seek advice from specialists.
Source: https://ProGrudnoe.ru/trudnosti/grudnoe-moloko-solenoe.html
What to do
If a mother is faced with the fact that the milk has changed in taste and the baby refuses to breastfeed, you should immediately try to determine the cause of such changes. A doctor, a breastfeeding consultant, as well as an analysis of the menu and lifestyle can help with this.
As a rule, babies rarely refuse breastfeeding due to changes in taste. Milk of any flavor is healthy and nutritious for them, so if the mother notices that the milk sometimes becomes salty, there is no need to stop breastfeeding. It is enough to find out the reason and observe the baby’s behavior. If he calmly accepts this taste and its cause is not illness, you can safely continue feeding. Otherwise, you should seek advice from specialists.