Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease. Due to disruption of biochemical processes, excessive dryness, peeling, redness occurs, inflammatory processes develop, and itching is felt. It develops under the influence of allergens, and is often combined with bronchial asthma, food allergies, and allergic rhinitis. It appears in the first years of life, most often before 12 months or at the age of 2-3 years, when the children's diet expands and many allergenic foods enter it. With proper treatment and care, the disease enters the stage of stable, long-term remission, but can manifest itself in adolescents, young and elderly people during contact with allergens, a weakened immune system, and after stress.
Symptoms
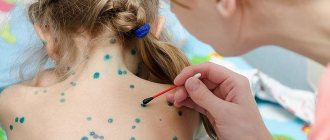
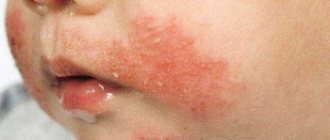
With atopic dermatitis in children, skin tightness, redness appears, the skin flakes, feels rougher to the touch, and thickening may appear. Microscopic bubbles form, around which moisture is released. The child is worried and scratches the affected areas. When an infection occurs, local inflammation develops and the wounds heal poorly. With significant spread in young children, general intoxication of the body manifests itself: the temperature rises, the peripheral lymph nodes enlarge. Due to severe itching, sleep and appetite are disrupted, and the child often cries. Dermatitis most often affects the face, neck, armpits, scalp, groin, areas under the earlobes, popliteal fossae, and elbows.
Dermatitis on the face of a child: photo, treatment
Dermatitis is a skin disease characterized by localized areas of rash and redness on certain parts of the body. It appears due to infection, toxicity or an allergic reaction. Infants are most often affected; less often, the pathology is found in schoolchildren and adolescents during puberty.
Signs of the disease:
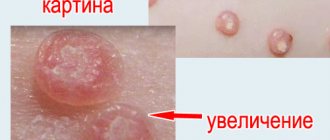
The rashes are vesicular-papular in nature (vesicles and papules form on the skin). They are preceded by erythema - this is the name given to the appearance of redness in the affected areas. When the bubbles burst, the skin underneath gets wet, dries out after a while and becomes a crust that later peels off.
From the first days of the onset of dermatitis, the skin remains inflamed and swollen. Inflammations cause the baby severe discomfort and pain because the affected area burns and itches. After stopping the inflammation and removing the crusts that have formed, new, healthy skin is generated under them. Sometimes traces in the form of hypo- and hyperpigmentation are noticeable, but they are temporary.
The origin of the characteristic rashes is the same as other types of rashes. But most often, dermatitis in the facial area is the result of an allergy to any products.
Causes of dermatitis on the face of a child:
- improper diet of the mother during pregnancy or breastfeeding, in particular the intake of citrus fruits, strawberries, and confectionery products;
- infectious or viral diseases during pregnancy;
- complications during childbirth, prematurity;
- inherited predisposition;
- dry air in the child’s room, elevated temperature;
- improper complementary feeding, feeding the baby prohibited foods, inappropriate formulas, undiluted cow's milk;
- hygiene products that cause allergies;
- use of synthetic detergents;
- immunodeficiency, weakened immunity due to viral and bacterial diseases.
- Contact dermatitis in children. Occurs after certain irritants - low or high temperature, intense rubbing, exposure to acid or alkali, plants. Manifestations are noticeable in areas in contact with the irritant. They look like spots, bubbles. Itching is possible, but not necessary, but pain is always present. If the lesions are severe, scars or scars may form. Relapses are unlikely.
- Allergic. This type of dermatitis develops after contact with a certain substance or object. Visually it appears after some time. The rash occurs in the contacted area or beyond. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms, accompanied by severe itching. A second contact with the allergen provokes a relapse.
- Atopic dermatitis in a child. It is one of the forms of the previous type of dermatitis and is caused by genetic factors. It is characterized by recurrent course and protracted treatment. Hyperkeratosis appears on the skin, but it does not go into remission. The skin becomes dry, thickened, often cracks and flakes. The child constantly cries and is nervous due to incessant itching and burning. In addition to traditional therapy, competent facial care is prescribed.
- Seborrheic. It develops due to the activation of the sebaceous glands and fungus, which is part of the pathogenic flora of the skin. Dermatitis is caused by hormonal or endocrine disorders, stress, lack of vitamins, and bad habits. Seborrhea most often affects older children, mainly teenagers. Signs reveal themselves in excessive fat and greasiness of the skin in the area of the upper part of the face, it also swells, and pale yellow scales are visible. In this case, severe itching and burning is felt. Lack of proper treatment leads to a chronic form.
- Perioral. The rash is localized in the mouth area, under the nose. The affected areas become covered with spots and scales and turn red. Due to the appearance of the symptoms and their location, the disease is easily diagnosed. It is provoked by a lack of nutrients or the use of inappropriate hygiene products.
In infants and young children, dermatitis of atopic or allergic nature is observed. More often it affects babies who are fed with baby food rather than breastfeeding, and those whose parents are atopics or allergy sufferers. Kindergarten and schoolchildren get contact dermatitis due to excessive curiosity. It is common for teenagers to suffer from seborrheic disease, as hormonal changes and puberty occur.
If a rash is detected in a baby, it must be shown to the treating pediatrician or dermatologist so that the doctor can prescribe adequate treatment. As a rule, diagnosis of dermatitis occurs quickly due to the presence of obvious external signs.
The process of diagnosing dermatitis on a child’s face involves examining and listening to complaints. Rarely, it may be necessary to take a skin scraping for analysis or biopsy. If allergic dermatitis is detected, testing for the allergen is indicated.
Treatment of dermatitis on the face of a child always begins with diet. It can be prescribed to a newborn or a mother who is breastfeeding.
Now on sale there are special mixtures for atopic children, where the main components are soy and protein hydrolysates. Among medications for oral administration, sorbents are prescribed, for example, Enterosgel, antihistamines.
For external use (in the dry form), creams with a moisturizing effect and emollients (retaining moisture) are used.
Treatment of dermatological diseases on the child’s face is supplemented with hormonal ointments if we are talking about numerous lesions of the skin.
The skin of very young children is thin, with an abundant capillary network, so hormones are prescribed in short courses under the strict supervision of a doctor. For the treatment of facial dermatitis in children, medications such as Advantan (from 4 months) are approved.
), Afloderm (from 6 months), Cutivate (ointment - from 6 months, cream - after 12 months). Ultraviolet irradiation will also benefit.
With severe dermatitis, inflammation and swelling are observed, accompanied by itching, pain, and discomfort. If blisters are present, pyoderma may occur. Through opened papules, with improper treatment or lack thereof, infection penetrates. Children scratch itchy areas, so the course of the disease is complicated by infection.
Dermatitis, unfortunately, cannot be cured in one day. Drugs for external use only relieve visual manifestations of the disease. Practice shows that the best way to avoid a rash is to carefully monitor the diet of the baby and his mother. The second most important thing is the selection of a suitable mixture (for “artificials”).
Maintaining cleanliness and normalizing the climate, a careful approach to the choice of washing powders and other hygiene products, using only natural fabrics - all this will help prevent an unpleasant disease. By the way, with age, when the intestinal flora stabilizes and the immune system strengthens, children stop getting dermatitis.
Source: https://dermatit.su/types/dermatit-na-lice-u-rebenka/
Prevention
Atopy is translated from Latin as strangeness. The causes of the disease cannot always be determined. But long-term observation of patients and members of their families has revealed that it develops more often:
- with a genetic predisposition - if the parents are healthy, the probability of developing dermatitis in the child is 20%, if one of them is sick - 50%, if both are sick - 80%;
- in case of unfavorable pregnancy, active or passive smoking of the expectant mother, consumption of food that provokes allergy attacks, use of certain medications;
- when a newborn is in a dusty room, insufficient care for his personal hygiene;
- with prolonged exposure to allergens that enter the child’s body with food through the respiratory tract.
Breastfeeding for up to 6 months and avoiding allergy-provoking foods reduces the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis and vaccinations
Parents often have a question: is it possible to get vaccinated if there are rashes and other signs of atopic dermatitis on the skin or frequent occurrence of allergic reactions? Often, doctors do not pay special attention to the presence of slight hyperemia on the cheeks of children and send them for routine vaccinations, after which quite serious complications can arise.
Of course, many vaccinations are necessary to create a protective reaction in the immune system, but children with atopic dermatitis need to be properly prepared for the procedure in advance in order to minimize the risk of a possible allergic reaction.
The baby is prescribed to take antihistamines and avoid many foods that can cause a negative reaction. And only after a month of preparation, provided there are no manifestations of dermatitis during this period, vaccinations can be given.
What to feed a child with atopic dermatitis
In order not to provoke an exacerbation of dermatitis, to relieve itching and redness of the skin, you need to follow a diet. Foods that burden the immune system are excluded from the children's diet: citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, honey, seafood. Red (strawberries, cherries, currants, apples) and exotic (mangoes, coconuts, pineapples) fruits are dangerous.
Split meals are recommended: small portions every 3-4 hours. It is better to boil, stew, bake, but not fry. Do not use spices, black pepper. The diet should be balanced and contain enough protein, vitamins, and microelements.
Avoid giving your child sugary carbonated drinks, chips, crackers and other snacks for as long as possible. If the infant is receiving breast milk, introduce new foods carefully. Add the product once a week to make sure it doesn't cause breakouts. After meals and between meals, offer your baby clean boiled water.
How to recognize dermatitis on the legs
Dermatosis at the initial stage of development makes itself felt by redness of the epidermis and small rashes. As the pathology develops, the symptoms intensify. Signs of the disease depend on the type of disease.
Allergic dermatitis is characterized by:
- a small rash on the lower extremities, accompanied by itching and redness;
- blisters on the epidermis containing liquid inside;
- cracks that most often appear on the feet and between the toes.
Neurodermatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- itching of the epidermis occurs, which is later accompanied by a rash on the entire inflamed area of the skin, in addition, the rashes are often accompanied by peeling;
- compaction of formations;
- weakness and apathy or aggression;
- lowering blood pressure;
- decrease in blood sugar concentration.
Dry dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of scaly rashes. In the weeping form of the pathology, there is liquid inside the formations.
It is not difficult even for people without medical education to recognize dermatitis on a child’s legs. If the disease begins with itching, the baby will constantly scratch the skin, leaving characteristic marks on the epidermis.
Next, formations will appear that indicate problems with the skin. These are the symptoms of dermatitis. However, only a doctor can diagnose pathology after conducting appropriate studies.
If dermatitis is detected on a child’s legs, it is recommended to show it to a specialist as soon as possible. Only a doctor will determine the form of the pathology and recommend what to do in such a situation.
Skin care
To relieve itching and prevent infection of the affected skin, you need to properly care for your skin:
- It’s better not to take a shower, but to take a cool bath for about 10 minutes; use medicated bathing products with a soft base that cleanse but do not dry the skin;
- moisturizing and softening – the skin should not be dry to prevent flaking and cracking; regularly apply a moisturizer recommended by a dermatologist;
- Do not let your child scratch the affected areas to avoid infection - apply anti-itching products to the atopic areas.
Cream or gel relieves discomfort during an exacerbation and allows you to sleep, eat, and play peacefully. Apply the drug to cleansed skin, treat atopic lesions and the areas around them. Do not exceed the recommended dosage and frequency of use.
Diaper dermatitis in children - how to treat the little ones?
One of the most common and early ailments in a child under 1 year of age is atopic diaper dermatitis. Irritation appears on the butt and in the groin area - that is, in places that come into contact with diapers or diapers. Most often, diaper dermatitis occurs when diapers are not changed on time. The skin cannot breathe, plus it is affected by aggressive substances from excretory products. This is how swelling, peeling, redness and itching appear. The best remedy for diaper dermatitis is to give your baby air baths, wash him more often, use powders for weeping irritations and creams for dry ones.
Rating of the best remedies for atopic dermatitis
To treat atopic dermatitis, use special children's products recommended by a dermatologist. During exacerbations, medications are prescribed for oral administration, application to atopic areas and general body care:
- preparations for removing allergens from the body - Enterosgel, Lactrofiltrum, Enterodes;
- skin softening products – Atopic cream for daily care;
- drugs that relieve itching - Panthenol spray;
- bathing products - soft shower gels for atopic dermatitis should be purchased at the pharmacy: dermatologists recommend using Atopic bathing gel from head to toe.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children under one year of age
The first signs of the disease appear at the age of 2-3 months. Characteristic signs of illness in a baby:
- moodiness;
- sleep problems;
- loss of appetite;
- irritability;
- intense itching, burning;
- redness, swelling in the affected areas;
- the appearance of serous papules;
- getting wet;
- erosion;
- dense crusts;
- peeling;
- cracks;
- dry skin;
- purulent foci.
Involuntary scratching can cause the development of a secondary infection, aggravating the course of the disease. When atopic dermatitis transitions to a chronic form:
- the appearance of scratching;
- skin thickening;
- the skin pattern intensifies;
- formation of pigmentation on the eyelids.
The disease affects:
- legs;
- hands;
- torso;
- buttocks with groin area;
- neck;
- face.
Quite often, parents confuse the symptoms of atopic dermatitis with other skin diseases and begin to self-medicate, which negatively affects the overall health of the baby.
Bathing
After a light shower to thoroughly cleanse your entire body, apply Atopic Bathing Gel to damp skin from head to toe, massage lightly and rinse thoroughly. Dry your baby with a soft towel using blotting, but not rubbing, movements. After water treatments, apply Atopic skin softening cream for daily care. Apply it several times throughout the day: after washing your hands and washing your face.
When taking a bath, the water temperature should not exceed 36 degrees. Place your child in the water and offer him toys or other entertainment. After 5-7 minutes, apply Atopic Bathing Gel from head to toe and rinse well. After bathing, use Atopic cream for daily care, and if itching bothers you, let the cream absorb, and then treat the affected skin with an anti-itching drug.
Prevention of dermatitis in infants
Most types of dermatitis in children in the first year of life can be completely prevented by following simple rules. The famous doctor Komarovsky gives many recommendations on this matter:
- to prevent the development of allergies in the baby, the mother needs to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet while breastfeeding;
- the room where the child is located must be regularly cleaned and ventilated;
- Do not use air fresheners, perfumes, or grow flowering or fragrant plants;
- instead of regular gauze diapers, it is better to use disposable ones with a moisture-retaining layer, this will help the baby’s skin always remain dry;
- all children's cosmetics must be hypoallergenic, like washing powder;
- Every day you need to arrange air baths for the child - let him be naked in a warm room (this will allow the skin to breathe and prevent the appearance of wet rashes);
- You should not wrap your baby too tightly - excessive sweating leads to diaper rash and diaper dermatitis;
- Children's clothing should be purchased from natural fabrics and ironed after each wash.
By following these simple rules, you can reduce the risk of skin rashes in your baby to a minimum.
Dermatitis in infants is a common occurrence. Almost all young parents have to go through this test. But if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations for caring for your child and preventing rashes, you can reduce the likelihood of developing this disease in all its manifestations.
How to choose products that are right for your child
A dermatologist may recommend not one, but several drugs to choose from. They have a similar mechanism of action, but their prices may differ significantly. It depends on the active and auxiliary substances, manufacturer, and release form. When choosing a cream for a child’s atopic skin, you need to take into account possible individual intolerance to individual components.
You need to purchase drugs from well-known manufacturers with a good reputation: Russian, European, American. It is equally important to contact large pharmacy chains that work directly with manufacturers and control the quality of drugs on sale - this will protect you from purchasing counterfeit drugs. Consider the age of the child: choose creams and gels with a pleasant smell so that the child enjoys going to the shower.v
When choosing drugs for oral administration, it is preferable to buy syrups, powders, drops, rather than tablets and capsules that are difficult for a child to swallow.