Sleep disturbance
As you know, any pain is especially acute during sleep; this problem is not spared during the teething period. At night or during daytime sleep, the baby begins to be capricious, often wake up, cry, and sob.
Many parents have had to go through sleepless nights, because in this case it is extremely difficult to calm their child down, he refuses to eat, and is not soothed by rocking or lullabies.
In this case, pain-relieving gels, tablets or a chilled teether can help, which will temporarily soothe the pain and itching, giving the baby the opportunity to sleep peacefully for a while.
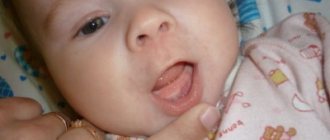
In rare cases, teething in babies is accompanied by the appearance of small hematomas on the gums - bluish-colored tubercles.
Doing anything to eliminate this symptom is highly undesirable; doctors do not recommend touching the tubercles or lubricating them with ointments.
The only effective way to speed up the process of hematoma resorption and reduce discomfort is to apply a cold compress to the inflamed area.
Another extremely unpleasant symptom is pain in the gums.
A small child is unlikely to be able to tell his parents that something hurts, so it’s worth paying attention to the baby’s behavior. The main feature of teething toothache is its direct connection with other organs and parts of the body: ears, chin, cheeks
The main feature of teething toothache is its direct connection with other organs and parts of the body: ears, chin, cheeks.
As soon as a sharp tooth comes as close to the gum as possible, nerve impulses spread and radiate to the ears and cheeks. The baby may begin to constantly rub his cheeks, pull his ears, or scratch his chin - this indicates that he is in severe pain.
As a result, the child becomes more irritable and restless. If such symptoms continue for a week or longer, but there are still no hints of a tooth, then parents should consult a pediatrician, because similar signs occur with otitis media.
If a child is cutting his first teeth, it is difficult to imagine this process without increased salivation.
The baby has not yet learned to quickly swallow the saliva accumulated in the mouth or spit it out, which leads to mucus running down the back of the throat. This may cause a frequent cough that coughs up.
Children especially often cough in their sleep, when snot and saliva caused by teething flow into the throat.
In this case, you can help the child by turning him on his side for better removal of mucus or by picking him up in an upright position.
Another way to understand that your baby is teething is to observe the discharge from the baby's nose.
A runny nose during teething occurs due to the fact that the baby’s immunity decreases, and saliva often gets into the nasopharynx.
To get rid of a runny nose, just rinse your nose with saline solution, sea salt-based drops, or use an aspirator.
If the baby still gets sick with a respiratory disease due to teething, then you should contact a pediatrician who will prescribe a good medicine for nasal congestion.
You may also be interested in
Many problems can arise when children lose their molars. The most common complications include:
- Lack of permanent teeth.
- Growth of a permanent tooth before the loss of a temporary one.
- Pain in a molar tooth.
- Molar tooth loss.
For every case, dentists have a solution; you just need to detect the problem in time and seek help. The last two phenomena arise due to low mineralization of hard tissue, and such anomalies appear regardless of how old the molars are.
As soon as a child’s primary incisor, canine or molar falls out, it is usually possible to feel the molar on the gum. Even if this is not the case, it should appear within a week. If there is no seal, it means that the baby tooth fell out too early. Many children loosen their teeth, and sometimes parents themselves take part in pulling them out.
In the worst case, such a symptom may indicate adentia. This pathology is extremely rare; it is caused by a serious violation of mineralization even in fetal age. Sometimes the disease appears during life due to infectious diseases. The problem is easily solved by prosthetics.
Another cause of the disorder may be a physiological delay in tissue growth. With this pathology, the eruption of all permanent teeth ends much later than usual. If the dentist finds such a defect, he will recommend making a removable denture. If you do not take advice, the permanent incisors and canines will grow crooked.
Typically, the growth of a molar tooth leads to the loosening of a primary tooth, but there are exceptions. It is possible to understand that the bite is changing incorrectly if all the signs of teething that were mentioned earlier are present, not accompanied by loosening of the primary incisors or canines.
This problem when a permanent tooth grows can lead to a number of problems:
- The incisor or fang begins to look for another path to cut through. In this case, children’s molars grow as in the photo on the right. Molars and premolars usually still come out of the gums, bending the entire dentition.
- The incisor or canine itself may become severely curved. It begins to bend in different directions, even before complete germination.
- Redness, itching and pain become more noticeable. Because of this, bacteria very often enter the damaged area. An infection may begin that will develop into a cyst or fistula.
- If your child's molars appear while the baby teeth are still in place, contact your dentist. He will be able to immediately detect the problem and remove the “milk jug” that is preventing the growth of the permanent tooth.
Signs of pathology
Blue gums during teething sometimes indicate the presence of pathology. It could be:
- hematoma requiring medical intervention;
- anemia;
- gingivitis;
- stomatitis.
If the bruise is more than 2 cm in diameter, then you should consult a doctor. This hematoma is often dark, almost black, due to accumulated blood. It is accompanied by fever and local pain. The doctor makes an incision and releases blood to avoid the development of pathology. Otherwise, it can lead to suppuration, inflammation or cyst formation.
Anemia is caused by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, which causes changes in the color of the skin and mucous membranes. Blue discoloration will be noticeable not only on the gums, but also in the area of the lips, nails, and eyes. Anemia is also indicated by: weakness, loss of appetite, susceptibility to infections, cold extremities. This condition is usually caused by a lack of iron and occurs regardless of whether the tooth is erupting at the time or not.
Gingivitis is an inflammatory process in the gums. It usually occurs due to insufficient oral hygiene and is accompanied by itching, bleeding, and swelling. If the child already has teeth, then gingivitis can be caused by carious teeth, mechanical injuries, malocclusion, or a weakened immune system. Sometimes the fact that a tooth is erupting is itself the cause of this type of inflammation, because damaged gums become vulnerable to various bacteria. With gingivitis, the gums turn blue or red, and small ulcers may appear.
Stomatitis is another type of inflammation of the oral mucosa. Sometimes there is a blue tint against the background of redness, which affects not only the gums, but also the oral cavity. It, like gingivitis, is usually caused by the penetration of pathogens into weakened or damaged mucosa and is accompanied by ulcers and pain.
The fact that the gums turn blue during teething may indicate various diseases, while often remaining within the normal range. It is necessary to monitor changes in the child’s behavior and well-being, then it will be easier to determine the root cause of the deviations and take action if necessary
Children do not yet have a strong enough immune system, so it is important that from the first days of life they receive everything they need to develop it. Pediatric dentistry will help clarify any questions and doubts that arise when teeth begin to cut.
What are baby teeth used for?
How does a child cut teeth?
Teeth eruption and replacement
Why you need to treat and protect baby teeth
While the child is still small and does not understand why he needs to take care of the health of his teeth and oral cavity, this is one of the important tasks of his parents
Moreover, you need to pay attention not only to the condition of the teeth, but also to the health of the gums, because many diseases of the oral cavity begin with them
Yellow, white or gray plaque, white or dark spots, and even ulcers may appear on the gums. Each of these symptoms has different causes and characteristics. Let's find out in more detail why a black spot may appear on a child's gum and how to cure such a pathology.
There are different reasons for the appearance of stains on the gums.
When do the first teeth cut?
Every mother should know how to help her child. First of all, parents should pay attention to changes in the baby’s behavior. If he has become restless and salivation has increased, we can expect the first incisors to appear soon. The moment when a child gets his first tooth depends on several factors. First of all, it is heredity. If mom and dad started teething late in infancy, you shouldn’t expect anything different from the child. The baby's nutrition is also important. A small body must receive a sufficient amount of calcium. If the child is breastfed, the mother should eat more dairy products.
Oddly enough, climatic conditions can also affect teething. In hot countries, babies' first primary incisors appear much earlier. Also, if a child was born at the end of May and the first months of his life fall in the summer, his teeth may appear a little earlier. The process is also influenced by the gender of the child. As a rule, girls become the happy owners of their first baby teeth earlier.
Which teeth cut first for a child? All pediatricians are unanimous on this. The lower incisors appear first. Although, of course, there are exceptions to the rules. If your baby's molars or eye teeth begin to appear first, you should consult a doctor for advice.
How to reduce discomfort?
Methods to reduce discomfort during teething are different and their effect is individual. Often used:
- special anesthetic gels containing various local anesthetics (Dentinox, Kalgel, Bobodent and others);
- teethers (various models made of soft plastic, filled with water), which reduce discomfort but do not injure the mucous membrane;
- in case of severe anxiety and pain, the use of painkillers with ibuprofen and paracetamol (suppositories or syrup) in an age-appropriate dosage is allowed;
- the use of anti-inflammatory decoctions of medicinal herbs - treating the gums with a soda solution, a decoction of sage, chamomile or oak bark.
How to relieve a baby’s condition if his gums are swollen and painful?
When the gums are swollen and unpleasant symptoms appear, many pharmacological innovations come to the aid of children and parents that relieve pain and discomfort. You can use traditional medicine recipes that also helped our mothers and grandmothers.
First of all, you need to get a teething toy. It is first placed in the refrigerator or freezer - the cold rubber toy dulls the pain and safely scratches the gums.
If symptoms are intense, especially when the child does not sleep at all and cries a lot, a variety of gels, suppositories or suspensions are suitable.
Homeopathic medicines are popular and should reduce general symptoms.
Medicines
Medicines for children are divided into the following groups:
- local painkillers;
- complex homeopathy;
- painkillers for oral administration.
Local analgesics are presented in gels; almost all modern parents have them in their medicine cabinet. The advantages of such gels include convenient application to the gums, quick effect and antiseptic properties. During the first minute, the mucous membrane “freezes” and becomes insensitive. Among the disadvantages are the short duration of the effect and unpleasant sensations in the mouth. However, the pain relief effect is sufficient until the child falls asleep.
The most famous gels:
- Kamistad Gel (Baby);
- Kalgel;
- Dentinox Gel-N;
- Holisal.
Homeopathic medicines act comprehensively. They affect the entire process as a whole, speed it up and alleviate the baby’s condition. Such products contain only natural and safe ingredients, so they are suitable even for the smallest children. They must be used strictly according to the instructions.
Homeopathic medicines:
- Viburkol - candles;
- Dantinorm Baby - drops (composition of Dantinorm Baby and instructions for use);
- Dentokind - tablets (instructions for use of the drug Dentokind);
- Pansoral - gel, etc.
Analgesics and antihistamines intended for internal use are prescribed only by a doctor. Unlike the first two groups, taking these medications is indicated in the presence of serious symptoms or complications:
- Fenistil drops (from birth) and Parlazin (after 1 year) are antihistamines. They are prescribed to relieve and reduce swelling of the mucous membranes in the mouth and nasopharynx, and eliminate itching or burning of the gums. Antihistamines help reduce runny nose and inflammation.
- For severe pain or fever, taking antipyretic drugs (they also act as painkillers) is recommended. Children's (necessarily age-appropriate) suspensions or suppositories based on ibuprofen or paracetamol (Nurofen, Panadol, etc.) are suitable. Before starting to take the medicine, you should consult your pediatrician. He will assess the need for its use and also select the most suitable product.
Folk remedies
- Tea based on chamomile, lemon balm, lavender and catnip will calm the baby and reduce pain. Dry ingredients must be mixed in equal proportions. Pour a tablespoon of the prepared mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave for 10-15 minutes, then strain. You can drink this tea throughout the day.
- Wipe your mouth with a strong decoction of chamomile or make compresses. If the decoction is diluted with water, it can be drunk as tea.
- Clove oil helps children and adults in dentistry. It disinfects and relieves pain. Pure clove oil will burn, so it needs to be diluted with olive or almond oil in a 1.5:1 ratio. Treat the inflamed area with the resulting solution.
- For rubbing or compresses, a decoction of sage, calendula, and oak bark is used. You can use one component or prepare a mixture. The ingredients relieve inflammation, disinfect, reduce pain and itching.
Chamomile tea is a very effective teething soothing remedy.
How to help your baby?
Many people are familiar with the pain of wisdom teeth erupting. Young children who have their first incisors experience approximately the same sensations. Parents should know how to help their children get through such a difficult period. At what age do the first teeth cut? Symptoms may appear as early as 2 months. Massage helps relieve pain very well. Parents can do it with washed hands. Use your thumb or index finger to press lightly on the gums. With such manipulations, most babies immediately calm down.
Cold helps relieve itching and pain. There are special teething toys on sale. They are a small container filled with liquid. Before giving this toy to the baby, you need to place it in the refrigerator. The baby will bite the teether and cool the sore gums.
There are also medications. It is recommended to use them in the most extreme cases. If the baby is very capricious and does not sleep well at night, you can use special cooling antiseptic gels. Before using any medicine, you should consult your pediatrician. The specialist will tell you at what age the first teeth begin to cut and how to alleviate the baby’s suffering.
Causes
To detect pathology or even minor irregularities, you need to know what a child’s gums look like in normal condition. To do this, look into his mouth, and you will find that the mucous membrane has a predominantly pale pinkish tint, and the gums do not in any way resemble an inflammatory process.
But with whims and changes in behavior, especially if the temperature rises, you can notice painful signs:
- the color of the mucous membrane becomes red;
- sometimes cyanosis is added to this, as a result of bursting small capillaries;
- the gums themselves swell and become inflamed;
- sometimes bubbles, spots, plaque and other formations appear on the surface of the soft tissues.
Teething occurs most often before one year of age and explains most of the child’s reactions. At this time, the baby is capricious, pulls all objects into his mouth, and has increased salivation. A runny nose may appear and the body temperature may even rise. In the mouth you can see that the gums are swollen, sometimes a blue tint is added to this, since the process of eruption causes small vessels to burst. You can feel the hard lump with your finger. The first baby teeth are usually expected at the age of 6-8 months, but depending on individual characteristics, this period can be reduced to 3-4 months or extended to a year. Caries occurs even in the youngest children. Why do teeth hurt immediately after teething? This may be due to dirty nipples or spoons that the parents licked before. An abundance of sweet drinks and foods. A common cause is the habit of falling asleep with a bottle of milk. Then bacteria multiply very quickly on the surface of teeth, which are not yet sufficiently protected and strengthened to resist pathogenic destruction of enamel
It is important to show your child to the dentist in a timely manner so that he can prescribe competent and adequate treatment. Stomatitis is an infectious disease transmitted by contact with an infected person. It is caused by viruses, bacteria and fungi
In each case, other methods of therapy and influence are needed. But pathology is always manifested by swelling of the gums, elevated temperature, various rashes and formations on the surface of the mucous membrane. Mechanical damage - if a child pulls various objects into his mouth and any of them turns out to be too sharp or hard, then a wound forms on the gum. The site of injury may become red, slightly inflamed, and blood may be released when the soft tissue ruptures. Lack of vitamins and microelements - most often, this is how the gums react to a lack of vitamin C in the body. With an unbalanced diet and low levels of important substances in the diet, a number of diseases develop, among which gum problems are popular. In this case, they become loose, bleed, increase in size, and swell.
At what age do the first teeth begin to appear?
Doctor's recommendations often imply additional administration of beneficial vitamins to babies along with the consumption of breast milk. In these children, teething occurs as early as 3 months.
.
No one will tell you the exact timing of teething - they simply do not exist and they must erupt without external influence. They depend on the baby’s race, heredity, body condition and other factors. Pediatricians take average periods into account when assessing the overall development of a child.
The normal period for the appearance of the first teeth is 6-8 months. By the first year of life, a baby may already have 8 teeth. By the age of 3, children should already have 20 teeth. If teeth are cut 2-3 months after birth, this should not frighten parents
— this indicator does not go beyond the norm.
What could be the reason for the early appearance of teeth in a baby? This is caused by the mother taking mineral complexes and multivitamins during pregnancy, which include calcium and vitamin D. This is caused by increased consumption of cottage cheese and dairy products.
There are rare cases when the first teeth can appear already in the first month of a baby’s life.
. This should be a reason to contact your pediatrician, who will issue a referral for testing. Abnormally early teeth may indicate disturbances in mineral metabolism in the body.
Teething in children after one year
Even with changes or slight disturbances in hormonal levels, by the age of one year, babies should have 1-2 teeth. If they are absent, then this is a reason for parents to be wary. The delay in the eruption of baby teeth in infants is influenced by the following factors:
- rickets;
- weakened immune system;
- pathology of the endocrine system;
- early or too late introduction of complementary foods;
- allergy to cottage cheese and eggs;
- prematurity;
- hereditary predisposition;
- edentulous
We have already written about a detailed teething scheme, so it would be a good idea to further familiarize yourself with this information to complete the picture.
Edentia in a baby
If after a year your baby still has not developed teeth, it is recommended to consult a dentist. In most cases, the specialist detects swollen gums at the appointment. Thanks to a small massage, it is possible to stimulate the process. The doctor will immediately notice which teeth are cut first. But in rare cases, a diagnosis of edentia may be made. This is the complete absence of tooth buds. There are several types of this disease. With complete edentia, the baby may be left without teeth altogether. There may be several causes of the disease. For example, a congenital feature caused by genetic factors or an infectious disease suffered by the mother during pregnancy.
In case of complete or partial edentia, children undergo prosthetics from the age of three. Such children must be constantly registered with the dentist and come regularly for examinations. The fact is that the pressure of the prosthesis can contribute to a lag in the development of the jaw. In the future, the child may have problems chewing food. When treating a disease with prosthetics, complications may arise. They are associated with jaw atrophy. Bedsores and inflammation may also develop. Parents will have to carefully monitor the child's oral cavity. Proper hygiene is of great importance.
Edentia is a complex disease with unpleasant consequences. You can't let the disease take its course. First of all, the baby is at risk of psychological discomfort. A child without teeth will not be able to fully attend school and communicate with peers. Therefore, you should definitely think about installing a high-quality prosthesis.
Symptoms ↑
The severity and frequency of symptoms accompanying the appearance of baby teeth in children are variable and individual: for some they may be complete, while for others eruption occurs without any discomfort at all.
The main signs of teething:
- local changes (inflammation and looseness of the gums);
- temperature increase;
- excitability;
- runny nose, cough;
- diarrhea.
Gum inflammation
Swollen gums make the baby have a strong desire to scratch them, and he constantly “drags” something into his mouth, actively chews various objects - a pacifier, toys, clothes, a blanket, his own fingers, and can bite the mother’s breast when feeding.
Immediately at the moment of cutting into the tooth, you can see the separation of the gum tissue, accompanied by redness. At this time, the gums are extremely painful, sometimes easily injured (blood appears when you tap a spoon over an emerging tooth, bleeding is possible when chewing).
In some cases, when fangs or molars erupt, even a hematoma (bluish-colored tumor) occurs above the tooth, requiring surgical intervention.
Excitability
Pain, burning sensation, tension in the gums, drooling, and increased temperature during teething are very painful for infants.
Children become restless, capricious, constantly demand attention, and sleep is often disturbed. Many babies become more sensitive to external stimuli: they begin to react painfully to bright lights or loud sounds.
Heat
The increase in temperature during teething is caused by biologically active substances released during the development of local inflammation in the gums.
Prolonged or severe fever in an infant with a temperature greater than 39°C is always suspicious for other illnesses.
Runny nose and cough
A runny nose and cough occur due to a large amount of saliva that flows into the nasopharynx, causing soreness and irritation; at the same time, the glands of the nasal mucosa are activated.
The cough is rare, usually wet, with the release of mucous sputum or saliva. Characteristically, the cough intensifies when the child is lying on his back.
Nasal discharge is also mucous in nature (liquid or semi-liquid, transparent). They flow from the baby’s nose, the baby “grunts” and “squishes,” especially during sleep and while eating. Nasal congestion should not appear.
Digestive disorders
The appearance of the first teeth may be accompanied by a decrease in appetite up to a complete refusal to eat and drink, diarrhea, regurgitation and vomiting.
Decreased appetite is associated with the child’s poor health and pain in the mouth. When the tooth erupts, gum inflammation stops and appetite is restored. Breastfed babies may either refuse the breast or require the breast more frequently than usual, every 15 to 20 minutes.
The stool acquires a semi-liquid or liquid consistency, but its yellow (yellow-brown) color remains. There should be no impurities of blood, mucus, or greenery. Watery stools often cause irritation on the skin of the perianal area.
Regurgitation and vomiting occur as isolated episodes, usually accompanied by high fever. Persistent repeated vomiting, vomiting like a fountain, constant regurgitation is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
What does gum look like when teething?
- By the time the baby is born, the crowns of all twenty baby teeth are already fully formed.
- They are located deep in the alveolar processes of the upper and lower jaw.
- The process of eruption is a kind of increase in their volume and a gradual pushing of the crown outward.
- First, they move upward, overcoming the resistance of bone tissue, and then the soft mucous membrane.
- It is during this period that the swelling of the gums and the appearance of itching at the site of their growth are first noted, and then pain and other signs of teething appear.
- In normal condition, infants' gums are pale pink in color, without any signs of inflammation or other changes (swelling, plaque, lumpiness, bleeding).
During teething, the following changes are noted:
- the gums first become loose, a slight bumpiness and redness appear;
- after a certain period of time, the swollen gums become more sensitive, small hemorrhages appear;
- then a small wound forms at the site of growth and the tip of the tooth crown appears.
At this time, the baby becomes more restless, refuses to eat and sleeps poorly.
But in some cases, all these general manifestations may be absent - it all depends on the degree of discomfort in the oral cavity. Often the first teeth erupt easily and parents notice this fact only when it begins to knock on the spoon or the tooth has erupted well and becomes noticeable.
A slight bruise on the gum during teething is not a reason to panic. This is due to injury to the blood vessels as the tooth crown passes to the surface of the tissue. In most cases, this phenomenon goes away completely after a short period of time.
How to reduce discomfort? Methods to reduce discomfort during teething are different and their effect is individual.
Often used:
- teethers (various models made of soft plastic, filled with water), which relieve discomfort but do not injure the mucous membrane;
- in case of severe anxiety and pain, the use of painkillers with ibuprofen and paracetamol (suppositories or syrup) in an age-appropriate dosage is allowed;
- the use of anti-inflammatory decoctions of medicinal herbs - treating the gums with a soda solution, a decoction of sage, chamomile or oak bark.
Possible local complications
Parents often use special pain-relieving gels containing various local anesthetic substances (Dentinox, Kalgel, Bobodent and others), but you must be extremely careful with these products - many international medical organizations urge pediatricians and parents to completely abandon the recommendations and use of these products.
Mothers often simply don’t know how many times to apply and how to properly treat the baby’s gums, and lidocaine as a medicine is extremely dangerous! Often such unreasonable use of them leads to anesthesia of the respiratory tract and respiratory arrest during sleep.
- An allergic reaction to lidocaine is also dangerous - swelling of the nasopharynx and even anaphylactic shock are possible.
- In some cases, complications during the growth of baby teeth are possible.
- These include:
- Blue gums in a child during teething and/or bruising.
- These signs indicate the difficulty of teething in the area of the soft mucous membrane - the gums turn blue during teething, a hematoma and persistent swelling of the soft tissues appear.
- It is necessary to remember that the baby is in severe pain, does not sleep, and is constantly restless.
- Signs of infection
- Signs of a local infectious process (viral, bacterial or fungal flora) on the mucous membrane of the gums at the site of eruption and in the oral cavity include:
- white or grayish-yellowish coating;
- rashes in the form of millet grains;
- minor erosions.
Treatment options
The choice of one or another treatment method is made by the attending dentist based on the diagnosis and visual examination of the small patient.
Treatment of a bruise from an injury on the gum
If you are sure that the bruise on the child’s gum is the result of an injury, you can try to provide the child with first aid, which consists of using the following methods:
- applying cold compresses to the injured half of the jaw;
- rinsing the mouth with decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage.
If the bruise does not resolve for a long time (more than 5 days), and the main symptom is accompanied by severe pain and a rise in temperature, then most likely an inflammatory process has begun deep in the gums. In this case, medical assistance is necessary, which may include both the use of medications and surgical intervention.
Treatment of a cyst on the gum of a child
Treatment of the cyst is prescribed by the dentist after examining the child. There are two ways to do this:
- if the cyst formed during teething. In this case, experts recommend using special teething toys that help break the tissue and speed up the process of tooth extraction. If this technique does not help, and temperature is added to the main symptoms, it is possible to use the technique of dissecting the upper layer of the mucosa;
- if the cyst is large and accompanied by pain. In this case, the surface of the “blue bump” is usually dissected and the bloody or purulent contents are removed. After which the wound is treated and washed. In some cases, complete healing may require several visits to the dentist.
Medicines are usually not prescribed for blue gums. The only exceptions are those cases when the hematoma is accompanied by the formation of an abscess and an increase in body temperature.
Teether toy
Treatment of gingivitis
In this case, experts recommend resorting to plaque removal and prescribing anti-inflammatory rinses. In some cases, antibiotics are used as a rinse solution.
Painkillers
If the blueness is accompanied by severe pain, the child can be given painkillers. The most popular are “Ibuklin”, “Ibufen”, “Nurofen” and many others. In addition, you can use analgesics in the form of suppositories, for example “Viferon” - suppositories that, in addition to pain relief, have an antiviral effect. In addition, you can use special dental gels:
- "Holisal";
- "Kamistad";
- "Baby Doctor"
Treatment at home
It is worth understanding that any home therapy must be fully agreed with the attending dentist. In addition, sometimes experts themselves recommend supplementing the basic treatment with some folk recipes.
Mouth rinses
If the child is already quite independent and knows how to rinse his mouth, then this method will help to significantly speed up the process of relieving swelling and pain. The best options for preparing infusions are chamomile and calendula, which have an antibacterial effect.
To prepare the mixture you need:
- take 1 tablespoon of dried chamomile or calendula flowers;
- pour a glass of boiling water and leave for about an hour;
- Cool the infusion and strain.
You can rinse your mouth 4-5 times a day or after each meal.
Infusion of chamomile.
Teether toys
Such toys are sold in all pharmacies and children's stores. The teether contains distilled water inside, which allows you to significantly cool the toy by putting it in the refrigerator for a few minutes. This teether not only speeds up the process of teeth appearing, but also relieves swelling due to the cooling effect.
Applying compresses
Cold compresses help relieve swelling and inflammation. They have a special effect in the case of hematoma formation during dental surgery. To do this, you can take several lud cubes wrapped in a clean cloth and apply them for a while to the cheek or lip located above the injury.
Mistakes that parents often make
Falling into a real panic, parents often make mistakes when they try to help their child cope more easily with the appearance of his first teeth. Here are some of the most common bad advice you can find on the Internet:
- too frequent cooling: cold really helps to dull the pain for a while, but its abuse can lead to the development of a cold, because the baby’s immune system is already weakened,
- crackers instead of a teether: under no circumstances should you give your baby dry bread or cookies, as they can seriously damage the delicate mucous membrane of the oral cavity. There is no need to take risks, but it is better to purchase special teethers,
- soda solution instead of special anti-inflammatory drugs: sometimes young children are prescribed rinses with pharmaceutical preparations that help relieve inflammation. There is no need to replace them with a soda solution unless advised by a doctor. Otherwise, you can only aggravate the situation and give the baby an additional portion of unpleasant sensations,
- irritation and nervousness on the part of parents: it is obvious that during this difficult period in every sense, not only children, but also their mothers and fathers suffer. Of course, it’s difficult to maintain composure when you haven’t slept for several nights in a row, but parents need to gain strength and patience so as not to further injure the baby with their breakdowns.
It is important for parents not to panic.
Some experts recommend sleeping with the child, explaining that tactile contact with the mother will help him calm down faster. If teeth are cut at the age of 1.5-2 years and the child experiences severe pain, it is worth postponing for a while weaning him off pacifiers and diapers. Otherwise, the baby will have to experience double stress.
- According to information provided by WHO.
You can alleviate the symptoms of teething with increased attention and affection. You need to pick up the child more often, play with him, talk to him, read books. This is how the baby feels cared for and is distracted.
Adults need to know what activities will help alleviate the condition:
- Proper diet. Avoid sweet foods. It is worth including products such as cottage cheese, cheese, cauliflower.
- As soon as the first teeth appear, they need to be properly cared for. You need to buy a special brush with soft rubber bristles. Your baby should brush his teeth without toothpaste.
- The child should be offered rubber toys, teethers (corrugated or with water).
- Massage the gums with an adult's finger. Be sure to wash your hands with soap before the massage!
- For local anesthesia, gels and ointments are used (Kalgel, Cholisal, Kamistad).
- Antipyretic drugs based on ibuprofen or paracetamol (Nurofen, Panadol).
- You can use decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, lemon balm, mint, sage). They have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. The decoction is taken orally or applied to the gums.
- A solution of soda helps relieve inflammation. To do this, add 1 teaspoon of baking soda to a glass of boiled water. Gauze is wrapped around the finger and moistened with the solution. You can treat your gums several times a day.
- During the period of teething in infants, preventive vaccinations should be excluded.
The process of erupting molars is long and painful. During these periods, parents should try to be very attentive and tolerant towards their baby. To reduce pain and anxiety, pediatric dentists recommend using special gels that are cooled in teethers.
If your temperature rises or alarming symptoms such as runny nose or cough appear, you should definitely consult a pediatrician. The doctor will determine the exact cause and may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs.
Teething is a period when increased attention to oral hygiene is required. For this age, you need to choose the right toothpaste for your child. For example, children's toothpaste from the ASEPTA baby series for children aged 0 to 3 years significantly reduces the number of harmful microbes in the child's mouth, so that the difficult period of teething passes without unnecessary hassle.
Timing and symptoms of teething
In most cases, the first milk teeth erupt closer to six months, in the period from 4 to 7 months, but there is no single correct time for the start of their growth - everything is individual. Read more about the timing and order of teething→
Timing of eruption and factors influencing them
Often the sequence of appearance, the age at which growth begins and the duration of teething in children are laid down in utero during the formation of the fetal jaw (at 3-4 months of pregnancy). During this period, their size and structure, sequence and age of appearance of the first signs of growth are determined.
Therefore, the course of pregnancy during this period and the absence of unfavorable factors that could change their normal formation are of great importance. The greatest negative impact can be caused by:
- severe maternal illness;
- late toxicosis;
- neuro-allergic disorders;
- metabolic disorders;
- exposure to harmful factors on the embryo (smoking, alcohol, drugs, radiation, poor environmental conditions);
- genetic abnormalities of fetal development;
- intrauterine infection of a child;
- heredity - family predisposition to early and late tooth growth;
- climate features;
- somatic or infectious diseases in the baby.
Symptoms of teething in babies
Symptoms preceding the appearance of the first teeth can be detected long before their true eruption - from 3-4 months. During this period, the baby experiences active salivation, moodiness, and sometimes the gums change before teething - there is slight swelling, looseness, bumpiness and slight redness.
At the same time, the child puts his hands and various objects into his mouth, and his behavior becomes restless, especially in the evening and at night. This is considered the beginning of the passage of bone paths in the gum and the approach of the tooth to the mucous membrane.
Subsequently, repeated redness and swelling of the gums are observed and the following may appear:
- light, clear mucous discharge from the nose (snot);
- rare coughing;
- temperature increase;
- loosening of stool.
Why does it hurt so much for a child to grow teeth?
Pain during the eruption of baby teeth is a completely natural and quite common phenomenon. In rare cases, this period is asymptomatic. But why does the baby suffer so much at this time? As mentioned above, the child’s body undergoes certain changes, the growth and formation of the dentofacial apparatus occurs.
Erupting the first teeth is a test for a child
The situation is aggravated by the body's natural reaction to what is happening - the baby may develop a fever, cough and irritation due to excessive salivation. In addition, excessive saliva production leads to intestinal motility and diarrhea. All this combined turns the stage of growth of the first teeth into a real test for the baby, so parents should be as attentive and patient as possible during this time.