Scaring tourists is the privilege of ancient castles: each one has a creepy ghost or at least a legend about it. But seaside resorts don’t need horror stories. But a few years ago, a terrible legend about the Coxsackie virus went for a walk in Turkey. Among the rumors and speculation, it was difficult to find the truth - but it turned out to be not so terrible. Firstly, this enemy of holidaymakers is not a new scourge, and doctors have long known how to treat it. Secondly, the body itself successfully fights the virus, and it only needs competent support. Kidpassage has collected truthful information about the Coxsackie virus: symptoms in children, treatment and prevention. Find out how to bypass the soreness and relax peacefully.
What is Coxsackie virus
Coxsackie viruses are infectious pathologies from the herpes virus family. With this disease, bacteria settle and begin to actively multiply in the gastrointestinal tract. Experts have recorded more than 30 forms of the disease.
One of the most common syndromes is “hand-foot-mouth”. The pathology is otherwise called vesicular stomatitis. In this case, Coxsackie infection affects the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
The pathology is transmitted from person to person through close contact with the patient or his personal belongings. The risk group for infection includes children from 3 to 10 years old. Newborn babies who are breastfed are immune to this disease.
Children over 10 years of age, as well as adults, can also become infected with the pathology, but for them it will not occur with pronounced symptoms. Such patients quickly and easily tolerate the disease, and they develop immunity to this form of the disease.
How often is the throat affected, what strain?
In practice, you rarely hear the diagnosis of “herpangina”. In order to diagnose it, it is necessary to conduct a complex laboratory test that would allow identification of the causative agent of the disease. Many clinics do not have such capabilities, so medical protocols often include o. The sick child is prescribed therapy to relieve the existing symptoms.
Herpangina is caused by the Coxsackie virus strain “A” or enteroviruses of the ECHO group. Their physical and chemical properties are similar to those of the polio pathogen. The disease is widespread; sporadic cases of infection and large epidemics covering cities and countries are observed all over the world. Children under the age of five, as well as older adolescents, are most often affected. After the disease, strong immunity develops. However, the Coxsackie A virus has about thirty seroviruses. Immunity is developed to one strain. If there is a virus carrier of a strain of another serovirus nearby, the possibility of infection remains.
Routes of transmission and main causes of the disease
The Coxsackie virus can be infected through poorly washed vegetables, fruits and hands. The pathology is also transmitted through tap water and from person to person, and contact does not necessarily have to be with a patient who has been diagnosed with the disease.
It is enough to communicate with someone who is a carrier to become infected. People often bring pathology from the resorts of Cyprus, Egypt and other hot countries.
Once infected, bacteria begin to multiply in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the infection is concentrated in the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx. For these reasons, the infection is transmitted through the fecal-oral route.
The incubation period for the Coxsackie virus ranges from 2 to 10 days. During this time, the infection must completely settle inside the body. After this, the period of acute pathology begins. Symptoms arise - rashes on the epidermis and oral cavity, intestinal disorders, and fever.
If such symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor, especially in cases where the person has arrived from a resort.
How does the infection progress?
Pathology has four forms of occurrence:
- Flu-like syndrome. Another name is Flu-Like. This pathology has the mildest form. Characteristic symptoms are fever, muscle pain, discomfort in the bones and general malaise. Signs of the disease are observed within three days. Next comes recovery. Influenza-like syndrome rarely causes complications, but only with qualified therapy;
- Intestinal infection. Children under two years of age most often suffer from this form of pathology. With such a disease, it is not necessary that other children will become infected from the child. In a group, this case may be exclusive and no one else may suffer from it. Characteristic symptoms are high fever, discomfort in the bones and general weakness of the body. In the first days of infection, other signs are observed - intestinal upset, nausea accompanied by vomiting. For this reason, the disease is often confused with poisoning. The period of exacerbation is 2-3 days for children of primary school age and a week for newborns. This disease can cause milk intolerance during the first time after recovery. This makes it necessary to give the child medical lactose before breastfeeding or to refuse it;
- Boston Pathology. The disease manifests itself in the same way as rubella, which makes it difficult to diagnose. A child, like an adult infected with the Coxsackie virus, in this case becomes covered with formations of a red hue. Symptoms: high fever, rashes on the epidermis in the form of blisters. The treatment period is 3-5 days. After this, recovery begins. With this form, relapse rarely occurs, and complications are most often not observed;
- Pleurodynia. Another name is Bronholm's disease. Symptoms: high fever, severe pain in the back, abdomen, muscles and chest. Spasms occur at regular intervals – once every 60 minutes. The duration of the attack is from 1 to 20 minutes. They cause spasms in the pleura and peritoneum, which cause pain during friction.
With any form of pathology, the patient needs urgent medical care.
Coxsackie viruses are divided into two large groups
There are two groups of pathology:
- Type A virus: Infection with the Coxsackie virus causes damage to the throat and may cause meningitis.
- Virus type B. Affects the brain, muscles and heart, causing irreversible changes in these internal organs.
Course options: mild, moderate and severe
Pathology has varying degrees of progression. The severity of the disease depends on how much the mucous membranes and internal organs are damaged. The degree is also affected by damage to the body by toxins.
The mild form of the pathology is characterized by a rapid course. Recovery occurs within a few days. In this case, the virus does not affect the patient’s internal organs and brain.
With moderate severity, therapy takes a little more than a week. The pathology has pronounced symptoms. The virus can affect internal organs, but with qualified treatment the problem can be quickly resolved.
The severe form of the disease is characterized by pronounced symptoms and a long course. This causes damage to the brain and internal organs.
Experts also identify the following variants of the pathology:
- smooth – recovery occurs quickly and the disease does not recur;
- wavy - the pathology either fades or flares up with renewed vigor;
- recurrent – after recovery, the disease develops again;
- with complications – the disease is difficult to treat and causes complications.
The virus most often causes a severe form of pathology in adults. To get rid of the disease without serious consequences for the body, it is necessary to begin therapy immediately after infection. Any delay and attempt at self-medication leads to unpredictable and irreversible consequences.
Forms of the disease
There are two forms of pathology:
- Isolated. The disease occurs in one syndrome.
- Combined. In this case, the Coxsackie virus affects several organs and systems at once.
Nutrition feature
In the initial stages of the disease, the child often refuses food: the throat hurts, itches, and any sip increases the intensity of such manifestations. During this period, there is no need to force feed the baby. The patient is advised to drink plenty of fluids, which helps remove toxins from the body in a timely manner. Rosehip decoction and green tea with lemon are considered beneficial. Juices and soda should not be given - they may contain components that can irritate the areas of the throat affected by the rash.
The painful condition passes quickly; already on the second day after the high body temperature subsides, the baby himself can ask to feed him. Until complete recovery, he needs to be given warm liquid food; it is important to first grind all solid foods to a mushy state. Doctors recommend that parents prepare easily digestible food rich in vitamins, moderately limit proteins and fats, and organize the diet so that the child eats five to six times a day in small portions.
Possible complications
The Coxsackie virus, like any bacterial infection, can cause complications. Since it has several forms of flow, various organs and systems can be affected.
Brain swelling may occur due to the Coxsackie virus. This is the main danger of infection. If such a situation occurs, the person requires immediate resuscitation measures. Untimely assistance can result in death.
The Coxsackie virus also has the following consequences:
- During infection, additional infections may join the virus. As a result, bronchitis, sinusitis, meningitis, pneumonia and other similar pathologies occur;
- Dehydration. Most often observed in children. This condition occurs due to intestinal disorders, as well as in the absence of a drinking regime;
- The risk of diabetes increases. The infection provokes the development of type 1 pathology;
- False croup. This makes breathing difficult and swelling of the larynx occurs. This can cause suffocation and death;
- The central nervous system is damaged. This leads to paralysis, epileptic seizures and other similar problems;
- Pulmonary edema. Occurs against the background of the development of pneumonia;
- Atopic dermatitis. An intestinal infection can trigger exanthema with the Coxsackie virus;
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system. In particular, heart failure and other similar diseases appear;
- Infertility. Occurs in young men during puberty due to damage to the testicles;
- Liver pathologies;
- Complications on the eyes. Vision deteriorates to the point of complete blindness.
With the Coxsackie virus, hair also suffers and nails peel off, but only in severe cases of the pathology.
Treatment
If the disease proceeds without complications, then it is treated in the same way as ordinary acute respiratory viral infections. In general, it is enough to undergo treatment at home. Pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy is carried out:
- If a child has a strong fever, then antipyretics should be taken: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Ibufen.
- To increase immunity, the use of immunomodulators is indicated: interferons or immunoglobulins.
- If the body suffers from severe intoxication, then sorbents are prescribed: Activated carbon, Enterosgel.
- With elevated temperature, diarrhea and other manifestations, the body becomes dehydrated. Therefore, the child must be given plenty of fluids.
- If blisters and wounds appear in the mouth, then Orasept, Tantum-Verde, Hexoral are used to treat them.
- For severe itching, antihistamines are prescribed. This is necessary, since scratching may cause a secondary bacterial infection. If this does happen, then taking antibiotics is indicated.
When treating an infection at home, you should pay close attention to the child’s condition.
An urgent call to a pediatrician is necessary if a child is found to have:
- Pallor of the skin;
- Appearance of blue discoloration on the body, near the ears, between the fingers;
- The appearance of signs of dehydration: lethargy, dry lips, decreased urination, increased drowsiness, delirium, dizziness;
- Severe headache;
- Refusal to eat;
- Long fever.
If the infection develops severely, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
Symptoms and photos
Characteristic symptoms of the Coxsackie virus:
- an increase in body temperature, and it rises sharply and does not fall below 380 for several days;
- general weakness of the body even without excessive physical activity;
- a sore throat;
- white plaque in the mouth;
- lack of appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
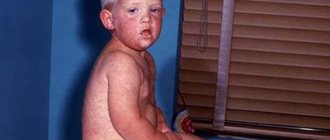
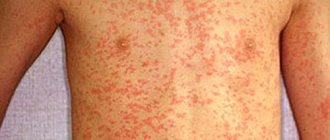
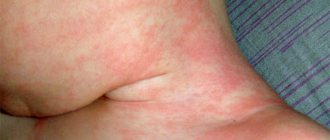
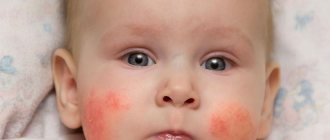
What the Coxsackie virus looks like is shown in the photo below.
There are several clinical forms of pathology. The classification is based on the predominance of the syndrome:
- Pharyngitis. When such an enteroviral disease occurs, rashes and white plaque appear in the oral cavity and tonsils;
- Exanthema. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of rashes on the epidermis;
- Myalgia. Symptoms – the appearance of pain in the muscles;
- Fever. With this form of infection, body temperature rises. There are no symptoms of colds. The child may also complain of weakness;
- Diseases of the nervous system. Brain damage occurs, severe headaches appear and intoxication of the body occurs. Sometimes paralysis develops.
If symptoms of infection are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor to prescribe treatment. Any delay can lead to complications and even death.
Coxsackievirus in children
Children are most often infected with the Coxsackie virus. The main danger of this pathology is that it can be confused with chickenpox or allergies due to the similarity of symptoms.
Particularly often, confusion occurs if the virus appears in infants, since it is difficult to identify additional symptoms due to the fact that the child is not yet able to complain of feeling unwell.
If the disease is incorrectly diagnosed, the doctor will prescribe the wrong treatment. Because of this, the virus will progress in the body, causing complications. For this reason, it is important to correctly diagnose the pathology.
What the Coxsackie virus looks like in children is shown in the photo below.
Symptoms of the virus in children
Signs of Coxsackie virus in children:
- increase in body temperature from 380 and above;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- pain in the head area;
- chills;
- weakness and fatigue even in the absence of physical activity;
- rhinitis;
- a sore throat;
- muscle pain;
- tachycardia;
- swelling of the larynx;
- lack of appetite.
If infection occurs, the child should be shown to a doctor immediately, without waiting for the disease to develop.
Preventive measures
Modern medicine does not have a medicine that can effectively fight enteroviruses; there is no vaccine that can be used to prevent epidemics. Therefore, the burden of responsibility for maintaining health falls on the shoulders of the person himself.
Even though Coxsackie is contagious, there are rules of conduct that help prevent infection. What should you pay special attention to?
- It is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene: it is useful to wash your hands more often, always do this after visiting the toilet, coming home from the street, and before eating.
- You should not drink untreated, unboiled water.
- Before consumption, it is useful to pour boiling water over all products.
- You should not swim in dirty ponds; when swimming in public pools, diving and swallowing water is strictly prohibited. Before and after water procedures, you must take a shower and wash with soap.
- During periods of outbreaks of enterovirus infections, doctors recommend avoiding staying in crowded places.
An important part of preventing infection is measures aimed at improving the health of the body and boosting immunity. Proper nutrition, long stays in the fresh air, physical activity, giving up alcohol and smoking, hardening, good sleep - this is what should become part of a person’s daily life.
On the part of the state - control over people working in children's groups, medical institutions, maternity hospitals, the field of public catering and tourism.
Coxsackievirus in adults
In adults, the disease is very rare, but the possibility of infection exists. The infection can be identified by the following symptoms:
- redness of some areas of the epidermis;
- pink rash on the skin;
- fever that is short-lived;
- rhinitis and cough;
- lack of appetite;
- problems with stool.
Pathology also requires timely qualified treatment. Only this will help avoid the development of complications and relapse of the disease.
How to treat
Your doctor will tell you how to treat the pathology and how to treat it. If the infection has not affected the internal organs and systems, then therapy is carried out in the same way as for any cold pathology.
A comprehensive treatment for the Coxsackie virus is prescribed, which is based on the use of antipyretics, analgesics and antiseptics.
The doctor will also prescribe antihistamines if symptoms of an allergic reaction are detected. Complete therapy is impossible without antibiotics and immunomodulatory agents.
If Coxsackievirus occurs, treatment of skin rashes is not prescribed. The doctor prescribes only medications for internal use. They also help get rid of the external manifestations of pathology.
How to care for sick people?
During the development of infection, the child must have personal hygiene products and cutlery. After use, they must be thoroughly disinfected. The child must be provided with bed rest.
When affected by the Coxsackie virus, children almost completely lose their appetite. You should not force feed your child, but he should receive at least small portions of food.
When treating Coxsackie virus, the following recommendations :
- The Coxsackie virus in most cases provokes dehydration of the child’s body, so the baby must be provided with the necessary drinking regime.
- Particular attention should be paid to the child’s immunity (not only vitamin complexes, but also food will help increase the body’s resistance to infection).
- During the period of infection, it is necessary to especially carefully monitor the child’s diet (vegetables and fruits must be appropriately processed before consumption).
- In most cases, parents cannot avoid infection when their child becomes infected, but frequent hand washing and disinfection will help reduce this risk to a minimum.