From the moment of conception, the female body begins to prepare for upcoming motherhood: the hormone progesterone is activated, the kidneys, liver, heart and other vital organs work in an enhanced mode. Therefore, many consider discharge during early pregnancy to be normal and do not rush to consult a gynecologist. However, not all so simple. The expectant mother should pay attention to the color, consistency and other characteristics of the vaginal secretion, so as not to miss the development of the pathological process. But you should not determine the normality of the discharge “by eye”. Only a qualified obstetrician-gynecologist will be able to identify or exclude dangerous conditions and, if necessary, place the expectant mother under observation.
What is considered normal discharge in the early stages?
Vaginal secretion is a complex product that contains mucus secreted by the glands of the cervical canal, desquamated cells of multilayered squamous epithelium located on the walls of the vagina and microorganisms (lactic acid bacteria predominate).
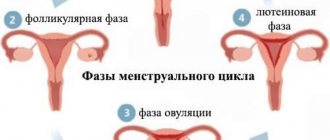
Vaginal discharge performs the most important functions: protection from pathological microflora, hydration during sexual intercourse and self-cleaning of the vagina. The discharge varies in color and thickness, depending on the stage of the menstrual cycle (the action of sex hormones). For example, on the eve and during the ovulation phase, the discharge is mucous, transparent, stretchy and resembles egg white (see mucous, transparent, stretchy discharge).
Some time after conception (approximately 10–14 days), the external indicators of vaginal discharge change. This is due to the “hormonal storm” occurring in the body of the expectant mother. The action of progesterone, the pregnancy hormone, explains the appearance of thick, opaque and scanty discharge.
White discharge in early pregnancy, usually called milky, is a physiological phenomenon. Thickening of vaginal discharge occurs with the aim of forming a mucus plug in the cervical canal, whose task is to prevent the embryo/fetus from becoming infected throughout the 40 weeks of pregnancy.
What secretion is normal?
Every woman of reproductive age should know what normal discharge during pregnancy looks like in the early stages. This will relieve unnecessary worries or help recognize the pathological process in its very embryo and save the child. Normal (physiological) causes of vaginal discharge include:
Hormonal changes
Hormonal levels fluctuate from the moment of conception. It stabilizes only at the end of lactation. After fertilization of the egg, the level of progesterone increases (this is necessary for the fertilized egg to attach normally to the uterine cavity). The hormone stimulates an increase in secretion volume. In this case, there will be cloudy discharge, like egg whites before the expected period. These are whitish or colorless mucous leucorrhoea, generously moisturizing the walls of the vagina, they are not accompanied by itching, burning and do not smell.
Formation of a protective plug of mucus (mucus plug)
Formed by the end of the first month, the plug reliably clogs the cervix, protecting the fetus from harmful factors. In this case, the transparent mucus has no odor and is secreted abundantly. The absence of discharge does not indicate the presence of abnormalities.
Implantation bleeding
After the fertilized egg penetrates into the mucous wall of the uterus (days 11–14 from the moment of conception), a third of women experience acceptable, barely noticeable short-term scanty pinkish or brown discharge. Upon careful examination, you can see streaks of blood. They are odorless and asymptomatic.
If white thick discharge appears before your scheduled period, this may indicate pregnancy.
- Irritation from hygiene products (panty liners, intimate soap). In this case, the appearance of transparent vaginal secretion is accompanied by itching and irritation of the labia. The symptoms will disappear as soon as the woman switches to natural, odorless pads and hypoallergenic intimate gel with a gentle pH value.
- Menses. Relevant for women with hereditary bleeding in the first trimester. Small discharge may appear in the second, third, or even fifth week of pregnancy. To confirm the “interesting position,” Doppler diagnostics are performed, which shows how the fetus is washed with blood.
The processes listed above do not indicate the presence of pathology, and therefore do not require medical attention.
If you know the difference between normal and pathological secretions in the first trimester of pregnancy and follow basic rules of personal hygiene, the chances of a healthy pregnancy, natural birth and a full-fledged baby increase significantly. Doctors recommend: underwear made from natural breathable fabrics, daily contrast showers and washing the external genitalia twice a day.
When should you contact a gynecologist?
A pregnant woman should carefully monitor her health, notice any warning signs and report them to her doctor. This is especially true for changes in the color of vaginal leucorrhoea and/or the occurrence of other symptoms. Do not delay visiting a antenatal clinic if you experience:
- itching and burning in the perineal area
- change in the color of vaginal discharge (bloody, brown, green, etc.)
- the appearance of pain
- feelings of discomfort in the lower abdomen
It is important to realize that self-medication of discharge that is suspicious in color and has an unpleasant odor can negatively affect both the health of the expectant mother and the health of the unborn child.
Mechanical damage
Not all discharge during pregnancy comes from the uterus. Sometimes, during an examination by a doctor or after sexual intercourse, damage to blood vessels in the vagina can occur. If the damage is minor, then such bleeding usually does not mean a threat to the baby and does not require special intervention. If there is any discharge in the first weeks of pregnancy, you should consult a doctor. The longer you wait, the less chance you have for timely treatment. Remember that time in such a situation works against you and your unborn child.
What does spotting at the beginning of pregnancy “signify”?
- Threat of miscarriage
Bloody discharge in early pregnancy occurs due to various reasons. First of all, it is necessary to exclude a miscarriage that has begun in a short period of time. Bloody discharge in such a situation is bright, scarlet (fresh detachment of the ovum), accompanied by nagging, aching pain in the lower abdomen and/or in the sacrum and lower back.
If conservation therapy is not started in time, the spontaneous abortion that has begun flows into the phase of abortion in progress, when the process can no longer be stopped. At the same time, the nature of the painful sensations changes, the woman feels cramping pain, which indicates powerful contractions of the uterus. The discharge becomes profuse, in some cases leading to profuse bleeding that is life-threatening.
- Pseudo-erosion of the cervix
Also the cause of discharge with blood is: pseudo-erosion of the cervix. In this case, spotting occurs after coitus, hygiene procedures (see douching - dangerous during pregnancy) or after a gynecological examination, and is called contact.
- Hydatidiform mole
Vaginal discharge with blood is a sign of hydatidiform mole (the disease is quite rare). Hydatidiform mole is the degeneration of chorionic villi into cysts and the death of the fertilized egg. Treatment consists of prompt removal of the hydatidiform mole, that is, curettage of the uterine cavity. The disease is dangerous not only with life-threatening bleeding, but also with the transition to a malignant tumor - chorionepithelioma (more about hydatidiform mole).
Other reasons that cause spotting in the first 4 weeks of pregnancy may be:
- myomatous nodes (in case of implantation of the fertilized egg on their surface)
- cervical canal polyp
- blood coagulation diseases
- abdominal injuries
Pathological
Discharge in the first days of pregnancy requires special attention. The body gets used to the new state and perceives the fetus as a foreign body. Natural mechanisms suppress a woman’s immunity, which causes frequent colds and the development of inflammation in the genitals. You can find out about infection by symptoms characteristic of this condition, such as:
- change in the nature of discharge in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- itching and burning;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- swelling and redness of the external genitalia.
Some diseases occur in a latent form and are asymptomatic. A woman can learn about health problems by the changed nature and color of vaginal secretion. This can happen at any time, so it is necessary to constantly monitor the mucus secreted and inform the doctor about any changes.
White
White discharge during pregnancy is observed at all stages and is rarely pathological. Without odor, color and additional symptoms, they are not dangerous, but in cases where, in parallel with the appearance of white cheesy mucus during pregnancy, flaky discharge, a woman detects a sour odor and feels itching in the genitals, medical attention will be required. Most often these are signs of candidiasis and bacterial vaginosis.
Exacerbation of thrush during pregnancy is the body’s reaction to weakened immunity. Pathogenic microflora begins to multiply uncontrollably and leads to candidiasis. Vaginal bacteriosis also develops due to decreased immune defense and can be triggered by hormonal imbalances.
Regardless of the causes of the disease, the risk of miscarriage and premature birth increases. To avoid complications, it is advisable to undergo an examination and stop the progression of the pathology at the initial stage.
Reds
Such discharge is among the most dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, especially when the secretion contains lumps and clots. Such manifestations can be caused by an ectopic pregnancy, cervical erosion, the presence of a malignant tumor, or the development of a hydatidiform mole. There are many reasons, the most harmless being late menstruation.
The growth of the pregnancy hormone in the body is observed only after the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. This usually happens in the first days after conception. Sometimes the embryo attaches to the uterine surface at the end of the cycle, and the hormone that suppresses menstruation simply does not have time to be produced in sufficient quantities. The woman begins to experience minor and short-term bleeding. They are not dangerous for bearing a child, but for the sake of your own peace of mind, it is better to tell the doctor about everything and do an ultrasound.
Red discharge is observed in women with fibroids identified before pregnancy and in the presence of cystic formations. Everything related to tumor conditions must be strictly monitored by a doctor.
The most dangerous thing that can happen is the necrosis of the neoplasm tissue. In such cases, miscarriage is inevitable. In the later stages, doctors save the child and mother, but often the uterus is removed after childbirth. There are many examples of successful pregnancy outcomes with fibroids. If a diagnosis has already been made and pregnancy has occurred, the woman should monitor her health and respond to any manifestations of discomfort and changes in the nature of the secretion.
Another cause of red discharge is detachment of the fertilized egg. This condition is considered a sign of an impending miscarriage. In the early stages, the appearance of bloody mucus is accompanied by discomfort in the lower abdomen; in the later stages, the pain is stronger and similar to contractions.
Even if the red discharge is scanty, a woman should seek medical help. With timely intervention by doctors, the loss of a child can be prevented.
The appearance of bleeding after the 28th week of pregnancy is classified as prenatal complications. Red discharge can be caused by rejection or malposition of the placenta, where the entrance to the cervix is blocked. The abnormal condition of the embryonic organ provokes an increase in blood pressure, which leads to the appearance of a red spotting secretion.
Brown
In the first month of pregnancy, scanty brown discharge does not pose any danger. They are often observed during the period of implantation and attachment of the fertilized egg, as well as in the later stages, when the mucous plug that covers the cervix throughout pregnancy comes off. In other cases, the appearance of brown mucus is attributed to pathological conditions. Sometimes they are accompanied by pain, unpleasant odor, increased urination and irritation in the genitals. All these are signs of infection and inflammatory processes that have begun in the body.
Unfortunately, very often such discharge is discovered when it is no longer possible to save the pregnancy. This occurs with the development of a genetic abnormality called “hydatidiform mole”, ectopic and frozen pregnancy.
Excessively dark discharge, similar to black, characterizes ectopic and uterine bleeding.
Less dangerous and correctable conditions include brown discharge in the early stages of pregnancy, provoked by hormonal disorders and diagnosed cervical erosion. In such cases, doctors help the woman preserve and give birth to a healthy child.
Green or yellow
The most harmless reason for the appearance of green and yellow discharge can be external irritants. Elementary uncleanliness and lack of intimate hygiene contribute to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which contributes to the formation of yellow-green mucus.
Secretion of this color may indicate an exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary area. As a rule, mucus has an unpleasant odor and is accompanied by burning and itching in the genitals.
Also, the causes of the appearance of greenish or yellow discharge are diseases caused by nonspecific bacteria (staphylococci and E. coli) and sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis). The symptoms of these pathologies are largely similar. In addition to the atypical secretion, women experience itching, pain in the lower abdomen, and problems with urination.
If you notice any of these signs, consult your doctor. Complex diseases accompanied by yellow-green discharge can provoke miscarriage at any time, so it is necessary to be treated immediately after identifying harmful microorganisms.
Cream
Abundant cream-colored leucorrhoea can be a sign of developing thrush, but in most cases, such a secretion is associated with the formation of an ectopic pregnancy, when the fertilized egg attaches outside the uterus. The abnormal location of the embryo is accompanied by severe pain and requires surgical intervention.
Why did brown discharge appear - is it dangerous?
Brown discharge can also be due to a number of reasons. One of the etiological factors is bleeding during the period of attachment of the fertilized egg to the endometrium of the uterus. This type of bleeding is called implantation bleeding and does not pose a threat to pregnancy.
- Implantation bleeding
Dark brown discharge during early pregnancy appears after 7–13 days after the fertilization of the egg, which is exactly how long it takes for the egg to travel the path “fallopian tube - uterine cavity.” Typically, these discharges are short-term, lasting only a couple of hours (extremely 2 days) and are scanty.
A woman may not notice such discharge, since the size of the stains on her underwear is no larger than a pea or bean. During the implantation stage, a pregnant woman may feel slight discomfort in the lower abdomen. The color of the discharge during implantation bleeding varies, and the appearance of light brown discharge is not excluded.
- Chorionic detachment
Brown discharge is also a sign of “old” chorionic detachment (future placenta). For some reason, the fertilized egg has detached in one place from the uterine wall, resulting in blood accumulating between the chorion and the wall (retroplacental hematoma). With further detachment, the hematoma is emptied and its contents pour out. This condition requires therapy, the goal of which is to maintain pregnancy (see calculator for calculating gestational age).
- Ectopic pregnancy
A single or periodic appearance of brown discharge at the beginning of pregnancy may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, which occurs as a tubal abortion (see ectopic pregnancy: symptoms). As a rule, discharge occurs after an attack of moderate or severe pain in the iliac regions and is explained by desquamation (rejection) of the decidua in the uterus.
- Non-developing pregnancy
A frozen (non-developing) pregnancy is also characterized by the appearance of brown discharge from the genital tract. During a frozen pregnancy, the embryo dies, but the fertilized egg remains in the uterine cavity for some time, gradually peeling off from its walls, which provokes the appearance of dark discharge. Treatment for frozen pregnancy is only surgical (removal of the fertilized egg).
What does yellow discharge mean in the short term?
Yellow leucorrhoea signals problems in the woman’s reproductive system. Abundant yellow discharge during early pregnancy, as a rule, accompanies the inflammatory process in the genital organs (see yellow discharge during pregnancy).
Often such discharge indicates the presence of sexually transmitted infections, but is erased or asymptomatic in the “pre-pregnancy period”, and worsens during pregnancy. The causative agents of genital infection can be chlamydia (see chlamydia in women: symptoms, treatment), ureaplasma, cytomegalovirus (see cytomegalovirus and pregnancy) and other bacteria.
Urogenital infections are dangerous for the developing ovum, as the risk of spontaneous abortion increases. Such discharge is accompanied by an unpleasant odor (see discharge with a fishy odor).
The likelihood of yellow leucorrhoea increases when exposed to irritating factors in the perineum and vulva:
- allergic reaction to panty liners
- frequent use of soap during intimate hygiene
- wearing synthetic underwear
Small light brown discharge is one of the variants of implantation bleeding.
Deviations
Minor variations in color and density are considered normal. But there are signs that cannot be ignored. Therefore, expectant mothers need to ask the gynecologist at the first consultation what discharge during pregnancy in the early and late stages is considered normal.
By smell
A sharp, specific sour, putrid, fishy smell.
By consistency
Foamy, excessively watery or thick, pasty. Whether flakes, an admixture of pus, or blood are present or not. Curdled discharge during pregnancy is the main symptom of thrush.
By intensity
If the secretion is clear, the gestation period is over 13 weeks or at 36 weeks - this is the norm. In all other cases, an increase in intensity is a signal of the need for immediate medical attention.
What does white, cheesy, copious discharge mean?
Often, expectant mothers suffer from thrush (urogenital candidiasis, see how to treat thrush in women, suppositories for thrush during pregnancy). The disease can develop at any stage of pregnancy and often recurs, but the onset of thrush is observed in the first weeks after conception. The high incidence of urogenital candidiasis during pregnancy is explained by two factors.
- Firstly, immediately after the fertilized egg settles in the uterus, the woman’s body’s defenses weaken, and so-called immunosuppression (immune suppression) occurs, which is necessary to prevent rejection of the fetus as a foreign agent.
- Secondly, with the onset of pregnancy, the production of estrogens increases, which increases the secretion of vaginal leucorrhoea, which is necessary to remove pathogenic microbes from the vagina.
But along with pathological bacteria, normal lactic acid bacteria are also washed out, which provokes the growth of fungi. Vaginal discharge takes on the character of cheesy white lumps, becomes abundant and is accompanied by a sour odor.
Why do they appear?
Women always have vaginal secretions. But after conception, their structure and appearance changes. At this time, their occurrence is regulated by progesterone - it is characterized by transparency. Then estrogen enters the active phase - the nature of discharge during pregnancy changes, its volume increases.
Discharges perform important functions during pregnancy. They inhibit the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and protect the fetus from infection, and maintain vaginal moisture.
What does greenish or foamy discharge mean?
Often the cause of pathological vaginal leucorrhoea in the early stages of gestation can be trichomoniasis. The causative agent of the infection is Trichomonas, which “feels at home” in the vagina (see trichomoniasis in women: symptoms, treatment).
Discharge from trichomonas colpitis is greenish or yellowish-green, foams, has a specific unpleasant odor, and its quantity is significant. In addition to pathogenic leucorrhoea, the expectant mother notes severe itching, burning and even pain in the vagina and vulva.
Trichomoniasis in the early stages is very dangerous for pregnancy, and can cause miscarriage or failed abortion. Treatment of this infection is prescribed only by a gynecologist; you should never try to get rid of the disease yourself, since all anti-trichomonas drugs taken orally are toxic to the embryo.
Author:
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna obstetrician-gynecologist
How to determine deviation from the norm
If you notice discharge in the first, second or third month of pregnancy, listen to your body. What you should be wary of:
- there is pain, itching, burning and other discomfort;
- general health has worsened;
- color, consistency, volume and duration are not normal.
To accurately determine the color of your discharge, use white plain panty liners from the first trimester of pregnancy.
The main thing is not to start self-medication, because the consequences can be disastrous. The only right decision is an immediate visit to the doctor and strict compliance with his requirements. Remember, from the moment of conception you are responsible not only for your life, but also for the life of the unborn baby.
Read about whether the lower abdomen can hurt during pregnancy, like before menstruation, in the article at the link.