This chapter is from the book “Purpose of Being a Mom” Read more »
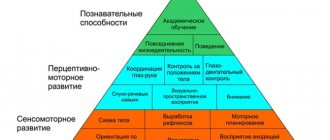
In the first year of life, a child goes through a huge path in his development. He is born as a small lump that sleeps almost all the time, does not walk, does not speak, his senses are imperfect at first - he perceives information like a huge soup, without distinguishing the individual ingredients in it. And by the end of the first year, he turns into a real little person, most often running around, starting to chat in his own way, building relationships with loved ones and with this world.
Is it surprising that the first year in the life of a child and parents is so difficult and filled with crises? Is it surprising that it is so difficult for us precisely in these moments, when a child screams, cries - and we do not understand what is happening to him? He can’t explain or show us anything, we can’t understand why he’s screaming? Everything seems to be as usual, as it was yesterday and the day before, but the child is different.
To be honest, the first time it all infuriated me. That I don’t understand at all what’s going on, why he suddenly becomes tame and whiny for no particular reason. Why does what worked yesterday no longer work, why does he suddenly sleep so poorly, why does he suddenly start eating so much - and so on. And one day I discovered a book that personally helped me a lot. And I want to tell you about it, because it can help you understand what is happening to the child.
It was published in Russian under the title “Being capricious means developing”, its authors were Hettie Vandereit and France Ploy. Her amateur translations are available online. This book is based on research by scientists who studied the development of a child's brain in the first year and a half of life. And they found that a child goes through a “growth spurt” several times in the first year and a half. Each leap is determined by the child's new skills and new information that he begins to receive from the world. And during this period it becomes more difficult with the child.
Children develop in leaps and bounds, not gradually, not a little bit every day, but in leaps every few weeks. Every jump is painful. Because the child is bombarded with new information, new sensations, new emotions, and skills. And he needs time to figure it all out, not to be afraid of new things - and to learn new things.
Believe me, if such a quantity of absolutely new things for you fell on you like that, you would also be capricious, and how! If even adult women cannot control themselves during PMS, although they know and understand everything, then what do we expect from a tiny little man who has not yet even understood where he ended up and why.
Calendar of developmental leaps in children: what is the normal height for infants under 1 year of age
The first year of a baby’s life is not only the most difficult for its parents, but also a record one for the number of changes observed, both in terms of physical development and psycho-emotional abilities.
Baby
Frequency of growth spurts
Growth spurts in children under one year of age are periods during which parents notice significant changes in the child’s behavior and skills.
It has happened to every mother that she woke up one morning and realized that today the child seemed to be replaced - he did not allow her to leave for a long time, demanded a toy or did not fit into her favorite onesie.
Before each new stage of development, the body gains strength and accumulates potential, so that at some point it can surprise itself and its parents with a new skill.
During the first year of life, up to 7 developmental leaps in a child can be observed:
- Parents will encounter the first immediately after the end of the newborn period - after the 28th day of life;
- The second time the baby will change behavior and become a little different at 2 months;
- By the middle of the 3rd month there will be another net that will not go unnoticed;
- At 5 months, the mother will begin to notice that it has become more difficult to walk with the baby. This is the most difficult fourth jump. It arises because the baby already holds his head well and wants to sit up, but he still can’t, hence the glaring crisis;
- The fifth leap will occur immediately after the baby turns six months old;
- For the sixth time, a crisis will occur after 8 months, when the baby confidently sits down and begins to perceive the world in a vertical plane;
- The very last, seventh leap occurs when the child turns 10 months old. At this age, almost all children can stand and have already tried to take their first steps, but they still cannot walk confidently, which becomes the cause of nervous crises.
If a mother keeps a diary of the baby’s development, her notes will automatically form a calendar of the child’s developmental leaps, based on notes that on certain days the baby was especially nervous for no apparent reason.
The baby is upset
Important! Adults should not lash out at children. Increased moodiness has nothing to do with character damage. Children themselves suffer from the fact that their psyche undergoes drastic changes, so at such moments the little ones need support and care even more.
Why are growth spurts called crises?
What to play with babies under one year old by month
The spasmodic development of the nervous system does not allow the child to sleep peacefully and disturbs the consciousness. The baby, learning more and more about the world around him, realizes his helplessness and every day becomes more and more emotionally attached to his mother.
Each new skill makes the baby very happy at first, for example, the first rollover from back to stomach. When this trick fails once again, the baby, with his characteristic maximalism, will begin to scream.
Growth spurts are called crises, because at certain moments the baby’s psyche cannot withstand the colossal load. The child is forced to react sharply with hysterics to changes in the body and endlessly incoming information in huge quantities.
Physiological development of children under one year old
Rapid development can be easily associated with the calendar of growth spurts in children under one year old. In just one year, infants grow by more than 20 cm. The girth of the head rapidly increases, by which one can judge how quickly the child’s brain is growing.
Norms of child development from the fetus in the stomach to the newborn year
Physical development of children in the first year of life
Age, months Acquired physical skills Distinctive features of age
| 1 | At this age, the neonatal period ends, the child no longer concentrates on unconditioned reflexes. He learns to lift his head while lying on his stomach. | The world around us opens up to the child. He realizes that, in addition to his personal needs, there is light and darkness, silence and sounds. This innovation becomes the impetus for the first crisis. |
| 2 | The child manages to hold his head longer, he begins to understand where the loud sound is coming from, and turns his head in its direction. | The first conscious smile indicates that the psycho-emotional perception of the world begins to develop. |
| 3 | Babies, lying on their stomachs, begin to try to lift themselves up on their arms, roll over from their back to their stomach and back. | Any unsuccessful attempts will be a real disaster for the baby. |
| 4 | At this age, children learn to pick up small objects and put them in their mouth. | Age is not characterized by a large number of nervous breakdowns. |
| 5 | For the first time, the child tries to take a vertical position, leaning on pillows or elbows. | There is a sharp change in the baby's mood, associated with an unwillingness to lie on his back. |
| 6 | The duration of sleep is significantly reduced, the child can sit with support. | The restructuring of sleep and wakefulness patterns, as well as the desire to sit constantly, cannot pass without leaving a mark on the baby’s psyche. |
| 7 | The ability to pick up toys brings significant variety to a child’s leisure time. | The baby is more often calm than irritated. |
| 8 | The skill of standing up with support captivates the child, and he does not get tired of practicing again and again. | Attempts to walk with a side step at a support are not always crowned with success, which significantly upsets the baby and often becomes the cause of hysterics. |
| 9 | The already minted step becomes the main activity. | Most of the time the child is happy. He enjoys being able to stand up and move around in an upright position. |
| 10 | I want to turn the boring side step into movement without support. | Unsuccessful attempts give rise to loud hysterics. |
| 11 | At this age, children practice walking upright. | Usually this age does not include any crisis moments. |
| 12 |
Important! The calendar cannot accurately predict each growth spurt in infants. We must not forget that all babies are individual and develop with some deviations from generally accepted terms.
Psycho-emotional development of children
A child gets sick in the car - what to do for children under 1 year old
The newborn spends most of his time sleeping and is hardly disturbed by sounds. Only a sharp loud sound or a bright light aimed directly at closed eyelids can wake up a child.
At 1 month, babies begin to see the world around them and use the movement of their eyeballs to track slowly moving objects.
At 2 months, children understand the sleep-wake schedule and are able to stick to it. The first emotional manifestation in response to external factors can be noticed precisely at this age.
First smile
A three-month-old baby begins to recognize his mother not only by smell, but also by appearance. The child is attracted to toys.
At 4 months, children can play independently longer if the toys are located close. The baby is not afraid to be alone and can calmly spend some time alone with bright objects.
At 5 months, children understand adults' intonation well and also recognize themselves in the mirror.
A six-month-old baby reacts to his name and tries to pronounce the first syllables.
From 7 to 8 months, the ability to distinguish between familiar people and strangers develops. Therefore, children of this age are reluctant to go to the arms of unfamiliar relatives.
At 9-10 months, children easily recognize their grandmother or mother among people and can express their joy by waving at them.
After 11 months, the child understands taboo words, which can greatly upset him. If he hears that he can't touch or do something, the frustration may become too emotional and lead to hysterics.
Symptoms of growth spurts
Growth spurts in children under one year of age are accompanied by characteristic symptoms. Each age may have its own distinctive characteristics; basically, the behavior of children during crisis surges includes the following points:
- Frequent crying for no apparent reason. It can be heard when the child is full and not suffering from heat or pain.
- Reluctance to let go of breasts. Having sucked all the mother's milk, the infant continues to hang on the mother.
- Apathetic attitude towards the game. After another emotional breakdown, the child does not want to explore the world through play.
- Constant desire to be in mother's arms. The child, going through difficult moments, refuses to be alone with his experiences. He needs tactile contact with his mother.
Begs to be held
Additional Information! Simultaneously with capriciousness, the baby finds restless sleep. Often waking up in a bad mood, he needs his mother's hugs. This is why psychologists sometimes advise parents to take their children into their bed to allow all family members to get some sleep.
How should parents behave during this period?
Parents should not be upset by their baby's frequent crying. It is difficult for a small person to keep up with a rapidly growing organism. Increased size of bones and muscles can cause unpleasant pulling sensations in a child. Mom does not need to look for hidden diseases and cures for them.
If parents manage to maintain composure and not turn into a bundle of nerves, it will be much easier for the child to survive each crisis. At this time, mom can:
- go outside more often in good weather to distract the baby from his difficult workouts;
- talk kindly to the baby, avoid a harsh tone;
- Hug your child more often so that he feels the support of his family.
Important! The hardest thing is for the mother, who in times of crisis for the baby must manage to cope with household chores. Therefore, it is precisely at these moments that mom needs dad’s help.
How can you help your baby?
During the period of active development, a child’s body can be helped by a well-composed list of activities that the mother organizes:
- Exciting games will help your child take his mind off the misfortune that has happened. The mother can be more active in teaching the child colors, shapes or sounds, depending on his age characteristics.
- Help in performing tricks will add confidence to your child. If the mother holds the hand or pushes when necessary, ensuring the successful completion of the trick, the baby will have no reason to be upset.
- Daily gymnastics aimed at training the muscular skeleton will help relieve physical pain that occurs due to the rapid growth of bones and tissues. Pediatricians consider exercising on a fitball an excellent option.
- Timely rest is what every workout should end with.
Fitball exercises
Children under one year old get tired 10 minutes after the start of classes. Therefore, it is necessary to take breaks every 5 minutes if the activity is not very interesting to the baby, and every 10 minutes if the game captivates the baby.
Growth spurt chart for infants up to one year old
Most babies are born between 48 and 52 cm tall. Boys are usually slightly larger than girls. Growth spurts occur in both sexes at approximately the same time.
Growth change by month
The table shows the average values for the increase in body length of babies up to one year old. The given data should not be taken as an exact schedule, however, significant deviations from the specified values can be considered as a reason to contact a pediatrician.
Infant growth jumps by month
Age, months Boys, cm Girls, cm
| 1 | 54,5 | 53,4 |
| 2 | 57,7 | 56,9 |
| 3 | 61,3 | 60,2 |
| 4 | 63,8 | 62,1 |
| 5 | 66,9 | 63,9 |
| 6 | 67,7 | 66,6 |
| 7 | 69,6 | 67,4 |
| 8 | 71,2 | 69,8 |
| 9 | 72,8 | 70,6 |
| 10 | 73,9 | 72,1 |
| 11 | 74,9 | 73,6 |
| 12 | 75,7 | 74,8 |
The table shows that the sharpest growth spurt occurs in the first month of a child’s life. He can gain about 3 cm in height in three to four weeks. The next significant jump occurs between 4 and 5 months for boys and 5-6 months for girls.
How to calculate the crisis week from the date of birth
Using special online calculators, you can calculate the dates on which particularly critical moments will fall. Knowing the numbers of difficult weeks, you can easily calculate and create your own calendar of emotional disorders.
Interesting! If the child was born early or late, with a difference of more than a week, then the countdown should begin not from the day of birth, but from the expected date of birth, which the doctor set during the ultrasound.
Mom's support
The calendar and symptoms of growth spurts in infants will help the mother competently separate warning signs of malaise from crises associated with the child’s development.
When calculating the numbers of difficult weeks, the mother should take the first day of such a week not as Monday, but as the day on which the child was born.
If the baby was born on Thursday, then the crisis week will last from Thursday to Thursday.
The following week numbers are considered the busiest:
Taking into account the calculation of critical periods, the mother will be able to adequately respond to a sudden change in her baby’s mood. Deciphering the baby's behavior will make it easier for the mother to find a cure for sadness and help her calm down. Only a happy and confident mother can ensure healthy growth and development for her baby.
Source: https://kpoxa.info/uxod-razvitie/skachki-rosta-detey-do-goda.html
Baby's developmental leaps. Myth or truth?
The material is taken from the application on child development up to one year. Let's consider his most important theses.
What are growth spurts?
Growth spurts are periods of intense physical and mental development.
Child development in the first year of a baby’s life does not occur evenly, but in so-called leaps.
In total, during the first year there are 8 jumps, in the next six months - 2 more. 10 leaps in 1.5 years.
During such leaps, increased moodiness, tearfulness, and demandingness are observed.
Calendar of developmental leaps
All babies have jumps almost at the same time, experts say. There is even a weekly calendar.
When using it, you should also take into account the time of birth of the baby relative to the expected date of birth.
If the baby was born, assume 4 weeks earlier, add 4 weeks to the date on the calendar. If later, on the contrary, it takes away.
Again, experts note that this calendar is a rough guide, since each baby develops individually.
The calendar will help you understand that a temporary capricious state is the norm and is associated with intensive development. This period will end and the baby will be in a good mood again.
If you look at this calendar, then my baby probably doesn’t fit into its periods. We see a clear growth spurt in the 20th week (moody, doesn’t want to be alone, wants to eat often, increased height, etc.) in the calendar, marked as a “quiet period.”
How to help your baby?
- The main thing
is to try to give what he needs: attention, physical contact, frequent feeding.
During such periods, the baby’s world changes, the only stable thing is MOM.
- It is likely that the baby will “ hang on the chest
.” And this is not only because he is hungry, but also to calm him down. - The child needs contact
with his mother. You will have to pick him up and hug him more often. You can sing a song and dance - this will distract the baby. - Change the situation
. Walking in the fresh air, going out to the balcony, swimming - all this will also reduce tension and tearfulness. - Don't get overtired
. During these periods, the baby’s psyche is especially sensitive to overwork. The baby gets tired more often and wants to sleep. Watch for signs of fatigue in your baby.
What does a developmental leap give?
After each jump, the baby’s world changes, a new skill or skill appears.
5 week
.
The baby recovers from childbirth and gains strength. The child begins to see and distinguish sounds better, and recognize the faces of his parents. The world becomes full of new sensations that he does not know how to cope with. The child begins to look at objects longer and listen. Some people give their mother their first smile this week. And those who already smile will do so more often.
What to do?
Talk to the baby, mirror him, repeat the sounds he makes.
8 week
.
The baby separates himself from another space, discovers his arms and legs, begins to control his facial expressions and hold his head. Now he can follow moving objects, the movements of his parents, turn his head to familiar sounds, and even imitate his parents.
What to do
? Teach to close your palm around the toy. Support the desire to explore your arms and legs. Show various objects, toys.
12 week
.
The child may notice simple changes in sounds, texture, taste, light, movement. The baby begins to understand that he himself can take the toy. Learns to make smooth movements. It is likely that the first rollover will occur.
What to do
? Maintain a “conversation”, a hum, respond to its sounds. Let's touch different textures, shapes, saying what it is. Play with an airplane, picking up the baby, flying and landing, or a pendulum, swinging from side to side, but not too much.
Week 17
.
The baby begins to play intensively with toys, pulling them towards him, squeezing, turning, trying to put them in his mouth.
The child begins to realize that the world exists from objects, even if he does not see them.
What to do?
Hang toys so your baby can reach them. Continue to let them touch different fabrics, objects, materials. For example, let the bag rustle. Stimulate the baby's activity, for example, rattle a toy on the side so that he turns towards the sound.
Week 26.
The child learns to coordinate the movement of arms and legs with the movement of the whole body, and begins to study the relationships between things. Realizes that there is a distance from one object to another. If mom moves away, he may be scared that he may not get to her.
What to do
? Teach your baby to clap. Sing nursery rhymes with gestures. Let them smell different smells. Teach to knock an object against an object, making sounds. Play hide and seek by placing a handkerchief on an object and showing how to find it.
Week 36
.
The child begins to see important similarities and differences between different objects. These changes affect all types of senses - vision, hearing, smell, taste, touch. Speech is developing intensively. The baby begins to understand a little more from the words addressed to him. You can notice concentration in your behavior. For example, carefully study food during meals.
What to do?
Give the opportunity to press buttons and switches. Ask for an item. Catch-up crawling and hide-and-seek. Provoke the child to imitate you, and you imitate him in return.
44 week
.
During this period, you can notice how the child is trying to create, and not just destroy. The child begins to understand that in order to achieve a goal, actions must be performed in a certain sequence. The baby is interested in everything you do around the house.
What to do
? Tell him what you are doing in the kitchen and around the house, give him a ladle or a rag. Name and show different parts of the body. Wrap the toy in paper so your child can unwrap it himself.
54 week
.
The child masters the tasks. They, unlike sequences, are more complex. The baby can think about goals, for example, about a walk and know what this means: he needs to get dressed, go out the door, go down the stairs. The child may insist on doing something on his own.
What to do
? Play with water. Allow you to do as much as possible yourself: undress, wash your hands, unpack bags, bring something, etc. Hide and seek with a glass. Hide something under one glass, move the glasses so that the child can use it and guess where the thing is hidden.
62 week
.
The baby's thinking becomes more complex and adult. He thinks over his moves, makes plans, weighs the consequences. Can check reactions to actions. Understands when to be friendly and when to throw a tantrum.
What to do
?
Let him jump on the mattress, run, climb. Ask the child to name the object. Do household chores together. Give them the opportunity to play with sand.
Week 73
The child begins to show flexibility. Understands that his actions lead to events, that he has power over things, that he is able to make decisions. All this is connected with the consciousness of one’s “I”. Notices that other people have different preferences from his. He can console, imitate. Fantasy develops. The concept of time becomes more complex, and speech develops.
What to do
? Balance exercise. Drawing, puzzles, books, soap bubbles, scooter or other baby transport. Opportunity to play with other children and feed animals.
Of course, you need to take into account that a child may be capricious for other reasons: gas, after vaccination, teething, from lack of sleep or hunger.
Blame everything on growth spurts
It’s simply not reasonable; in any case, it is always necessary to take a closer look at the child and monitor his behavior and well-being. And if in doubt, consult your doctor.
In our experience, it is a myth
It’s impossible to call growth and development jumps, but there are still obvious signs of behavior changes, excluding tummy problems and so on. So it’s worth taking a closer look at the calendar and expert advice.
Did your baby have growth spurts and causeless whims?
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/bodrum48/skachki-razvitiia-malysha-mif-ili-pravda-5ee889e57c13c822dba2aefe
Modern measurements
And everything would be fine, but inaccurately, there is no division into boys and girls.
Modern pediatricians use centile tables.
We have a separate article about how to read centile tables, but I’ll still leave the “cheat sheet” here. This is how the data of all indicators is read.
Growth of boys from one to two years
Growth of girls from one to two years
Weight of boys from one to two years
Watch the course “Children’s orthopedist: what mom does NOT need to worry about” (free at ViLine.Club)
Weight of girls from one to two years
Dependence of weight on height (indicators for boys from one to two years old)
Dependence of weight on height (indicators for girls from one to two years old)
Head circumference - boys
Head circumference - girls
Growth spurts in children after one year | Online school of motherhood and childhood
Your baby is one year old! From a tiny lump he has turned into a nimble toddler who moves around the house independently and even utters his first words. It is at this age that the baby goes through several more developmental leaps that will push him to new discoveries.
Time periods
In children aged 1-1.5 years, three developmental leaps occur:
- Developmental leap at 12 months (8th leap), duration 3-6 weeks. At week 55, the crisis reaches its maximum.
- The developmental leap is at 15 months (jump 9), lasting six weeks, reaching its peak at 64 weeks.
- A developmental leap at 17 months (10th leap), this crisis lasts about four weeks, reaching a maximum at the 75th week.
Causes:
As before, growth crises in children after one year have a number of similar reasons :
- A very large flow of information, which a small organism is sometimes unable to cope with.
- The emergence of new opportunities for independent exploration of the world.
- A sharp change in the perception of surrounding objects puts significant pressure on the child’s mental state.
Signs
Probably every mother has noticed sudden changes in the behavior of her baby, when a common action or situation caused a non-standard reaction from the child. Most often, this signals that another developmental leap is beginning.
Let's take a closer look at the general signs that characterize growth spurts in children after one year:
- The baby does not want to let his mother go, asks to be held, literally hangs on her. The toddler needs to be hugged and cuddled up to her periodically, this gives a feeling of security and reassurance.
- Decreased appetite. The child refuses his usual food and can only eat what he really likes.
- "My mom!" The baby gets angry and jealous of his mother towards anyone who tries to contact her.
- Frequent whims and tears for no reason. This also includes mood swings, when a cheerful, satisfied baby starts whining for no reason after a few seconds.
- The child requires entertainment and games with adults.
- Apathy. It can manifest itself in the child “getting stuck” on one object, as well as in sudden thoughtfulness in the middle of the game.
- The baby may show shyness even in front of people he knows.
- The baby shows self-will - he screams, falls to the floor, wanting to get his way.
Baby's sleep
As in any crisis, the quality of sleep noticeably deteriorates during this period. The baby has difficulty falling asleep, his sleep becomes shallow and restless. Frequent awakenings at night and reduction of daytime sleep reduces its total duration. Thus, a developmental leap often leads to lack of sleep in a child.
To neutralize the negative manifestations of the crisis, try to help your child calm down before bed. The best way out would be to prepare the baby for bed in advance, including checking the external sleeping conditions - temperature, humidity, darkness of the bedroom - and eliminating any shortcomings.
Your help for the baby
In order to make developmental leaps in children as comfortable as possible after one year, try to adhere to some rules:
- Give your child attention when needed. He may ask to be held, caressed and run with his tail, this is normal. In this way, the baby makes it clear that he needs your support and participation. Hugs and kisses will literally help you get through your baby's next growth spurt.
- Cooperative games. Here, not only the baby’s toys, but also simple household objects can serve as tools - little helpers love to imitate adults. Songs, nursery rhymes, puppet theater, finger play and role-playing - all this contributes to the development of the baby, helping to overcome the changes that are happening to him.
- The freedom of action. Try not to limit the little explorer in exploring the surrounding space and objects when this does not threaten his safety.
- Feelings and emotions. As a rule, a one-year-old baby cannot always correctly express his emotions, which literally overwhelm him. This results in crying and capricious behavior. Try to teach him to express his feelings, show surprise or regret, sadness or joy with facial expressions, when appropriate.
Growth spurt results
What changes occur as a result of growth spurts in children after one year?
Firstly , the baby becomes noticeably more active and independent. A one-year-old baby learns to walk independently, tries to eat by himself and imitates adults, being interested in household chores. Now the little one is able to play independently for a long time.
Secondly , the baby realizes that he can choose which direction to go and which toy to pick up. Actively builds logical chains in his head, sets goals and achieves them. The thought process itself becomes fascinating for the grown-up toddler.
The pace of child development after one year is not as pronounced as the rapid growth up to one year of age. But still, each growth spurt brings many interesting discoveries for the baby and his parents.
Additionally, growth spurts in children under one year old can be calculated using the following table:
Source: https://sonmalysha.ru/skachki_posle_goda
Newborn crisis
Among specialists, it is customary to consider the childhood crisis that a newborn is experiencing from the physical and psychological sides. From a physiological point of view, this means the process of adaptation of the baby to the new conditions of its existence, which is radically different from the prenatal period. After birth, a baby needs to do many things on its own to survive, such as breathing, keeping itself warm, obtaining and digesting food. To help the child adapt and make this process as less stressful as possible, parents should develop a calm daily routine, ensure regular sleep and good nutrition, and establish the process of breastfeeding.
Child development at one and a half years and the tenth growth spurt
September 28, 2018
A child of 1.5 years has already learned to walk, sit, speak a little - development is in full swing! At 75 weeks he will have another important growth spurt. Today we’ll talk about it in more detail, and also find out what games you can play with your child to help him develop intellectually and physically.
Week 75: new world - new systems!
Not long ago, after a previous developmental leap, the child discovered a complex world of principles.
However, it is still difficult for him to use them - they were not flexible and mobile, like in adults, and have difficulty “adapting” in accordance with rapidly changing circumstances.
At the 75th week, perhaps a little earlier or a little later, the baby suddenly realizes that the principles do not exist separately from each other, they form complex systems. He will be mastering the new world for many more years, but the first step into it will have to be taken at this age.
The acquaintance will begin, of course, with yourself. After all, the body is also a system with which the child will have to establish “contact” first.
After this, he will certainly realize that he is a member of a family consisting of himself, mom and dad, and will understand that his family is different from the one that his friends have in the yard.
Of course, this seems understandable to adults by default, but the baby “discovers” the simplest systems for the first time.
At the same time, the first moral principles begin to form: conscience, norms of behavior and even values. In addition, the child understands that all his actions lead to certain consequences, a sense of responsibility appears, and a system of his own self is outlined.
By the way, only at this stage does the baby develop a clear line between the concepts of me and you. Having survived the 75th week jump, the child begins to understand that in addition to his preferences, there are also the desires of those around him.
This is the first step towards successful socialization - and parents should certainly help ensure that it is successful.
At first, the new world seems incomprehensible and hostile. As during previous leaps of development, only one haven seems reliable and cloudless - this is mother. The child again strives to be close in order to recharge his confidence and take the first steps into adulthood.
.
And again, as during previous leaps, cloudless existence is replaced by an unexpected storm. If you notice at least one of the signs listed below, then you need to prepare for the fact that very soon the child will become smarter, smarter and more savvy, moving to a completely new level of life:
- whims, constant whining for no reason;
- sudden mood swings: from boundless melancholy to unbridled joy;
- refusal to play independently, the need to have someone nearby to entertain and share the game;
- the desire to constantly be close to mom, walking “by the tail”;
- manifestation of cuteness and affection or, conversely, mischief;
- manifestation of feelings of jealousy;
- scandals and hysterics;
- showing caution towards strangers;
- expression of protest against interruption of physical contact;
- sleep problems, nightmares;
- refusal to eat;
- dreaminess and thoughtfulness;
- showing love for soft toys.
What from the world of systems is available to a child at this stage?
After the 75th week jump, not all systems are available to the baby. He slowly but surely begins to discover only a few of them, to form his preferences and views.
- Conscience and boundaries of what is permitted.
At this age, the child seems to be trying out what he can and cannot do. He forms the rules of life for himself.
- I am me.
Having survived the next leap, the baby learns to control his body, begins to show strong-willed qualities, learns not only to make decisions, but also to bear responsibility for them. In addition, he is aware of the concept of “property” and divides the boundaries between his own and someone else’s.
- Far away is not forever!
Not so long ago, a child considered a person who disappeared from sight to be gone forever. Now he understands that this is not so. At the same time, the realization comes that the search for the missing person is not only around the corner where he turned, but also in other accessible places.
- You and me.
It is at the age of 1.5 years that the child realizes that there are certain differences between him and other people. He becomes interested in human toys that perform actions.
- Other living beings.
The baby studies them carefully, observing and drawing conclusions.
- Family.
Another truth that is revealed to a child is that his family is a single whole, and it may differ from the one that friends, relatives, and neighbors have.
- House.
The child begins to understand where his home is. He mentally creates a map of the surrounding space and marks his “home” point on it. This is one of the most complex systems to be discovered at this age.
- There must be order in everything!
This moment is one of the most pleasant for parents. The desire to put everything in its place and systematize will not “repeat” again soon.
- The great power of art.
Having survived the 75th week jump, the baby begins to truly “create” - not just hold a pencil in his hand, but also draw cars, houses, and other objects.
- Speech.
The system also comes into this area of a child’s life. He begins to connect words into sentences, and, accordingly, clearly express thoughts.
- Time.
At this age, the baby begins to understand what the past is and what the future is, and that there are certain differences between them.