The anxious period of bearing a baby ends with the long-awaited birth of a toddler. Despite the woman’s great desire to meet her baby as quickly as possible, the expectant mother understands that the baby must be fully formed and go through the necessary stages of development. This condition is an essential condition for the successful birth of a child and his good health. Carrying two babies involves increased stress on a woman’s body. Expectant mothers pregnant with twins are usually more worried than others about whether they will be able to carry their babies to term. At what week is pregnancy considered full-term? What gestational boundaries for this period are established in cases of singleton and multiple pregnancies?
Urgent birth - what is it?
Pregnancy, according to medical reference books, lasts an average of 280 days. During this time, the baby manages to turn from one cell into a complex, multicellular organism, he gains the ability to feel, perceive, and think. From 22 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus is considered viable, but this does not mean that it will necessarily survive if born so early.
The fact is that a child’s body must prepare for coming into this world as best as possible.
The environment inside the mother's womb is very different from the one into which the child will find himself after birth, and the little body must be prepared for serious stress.
After 34 weeks of pregnancy, tiny alveoli in the baby's lung tissue begin to produce a special substance called surfactant. It, having accumulated in sufficient quantities, will allow the lungs to open and ensure free independent breathing. If there is not enough surfactant, distress syndrome and acute respiratory failure may develop, which is a common cause of disability and death in premature babies.
The child’s body weight is also important. From the second trimester, a thin fetus begins to gain weight due to an increase in the mass of subcutaneous fat. Weight gain lasts until the end of pregnancy. This is important not only to please mom and dad with a plump bottom and cheeks, but also so that the newborn can effectively retain his own body heat.
With malnutrition (low birth weight), the risk of systemic hypothermia and death of the child is higher.
The weight and readiness of the fetal lungs are two of the most important criteria for a baby to reach full term. It happens that even with premature birth, children are born with a normal weight, and it happens that even with a timely birth the weight is low. The readiness of the lung tissue may also be insufficient in a full-term baby, but more often this still happens with premature babies.
So, what kind of baby can be considered full-term? The answer is simple - born as a result of emergency childbirth. A term birth is a birth that occurs between 38 weeks of pregnancy and 42 weeks of pregnancy inclusive. This means that on any day of this period a full-term baby is born.
Childbirth from 22 to 27 obstetric weeks inclusive is considered premature. And the degree of prematurity is determined not by the duration of pregnancy, but by the weight and condition of the child’s respiratory organs.
From 42 weeks of pregnancy, there is a need for induction of labor - if it does not begin on its own, the woman is given stimulation, since postmaturity is also not the best option for the baby (the placenta has aged, it copes poorly with protective and nutritional functions, the baby’s head circumference is growing, which can make it difficult and complicate childbirth). After 42 weeks, one of the methods (Mifepristone, mechanical methods) provokes the onset of labor.
According to statistics, up to 80% of children are born between 38 and 42 weeks of pregnancy (at full term). 15-17% of births are premature, about 3% remain for “late” births.
It is difficult to say when labor will begin, unless, of course, we are talking about a planned caesarean section (surgically, on the recommendation of the Ministry of Health, you can give birth at any time according to indications, but usually from 39 completed weeks). In other cases (with or without a pessary, first birth or second - it doesn’t matter), doctors prefer to wait for the onset of natural labor contractions . It is through contractions that a woman’s body notifies that it is ready for a complex physiological process.
Do not confuse urgent labor with fast or rapid labor. A rapid birth is a birth that occurs too quickly, with a violation of the duration of the periods, and therefore this is considered a complication and can pose a danger to the woman in labor and the child. An urgent birth is an ideal option; it couldn’t be better (the baby is full term, the woman is ready).
Induction of labor during full-term pregnancy
The term “induction of labor” refers to the artificial stimulation of the onset of labor. This procedure is not absolutely safe, so the decision to stimulate should be made solely on the basis of precise medical indications, when the expected benefit outweighs the potential harm. In this case, it is necessary to establish the exact gestational age of pregnancy, study the woman’s history, conduct a clinical examination, and assess the maturity of the cervix.
Indications for induction of labor during full-term pregnancy
In what cases can a decision be made to stimulate labor during a pregnancy over 37 weeks?
- Treatment-resistant preeclampsia, gestational hypertension.
- Postterm pregnancy (obstetric period 42 weeks or more).
- The beginning of placental abruption.
- Premature rupture of amniotic fluid during full-term pregnancy. If the cervix is “ready” and there are no contractions, the introduction of stimulants occurs 6 hours after the water breaks. If the neck is immature, when it reaches maturity.
- Diseases that worsen the general health of the pregnant woman (for example, diabetes).
- Incompatibility of the blood of mother and baby according to the Rh factor or the ABO system.
Often during induction, the pregnant woman’s mobility is limited, and the woman experiences discomfort both from the manipulations themselves and from their consequences.
Methods of induction of labor during full-term pregnancy
During labor stimulation, one or more induction methods can be used.
- Mechanical (manual) separation of the lower pole of the amniotic sac from the uterine wall. The procedure does not cause severe discomfort. Can be performed during an appointment with a gynecologist to speed up the natural onset of labor.
- Taking medications to accelerate the process of maturation (smoothing, softening) of the uterine cervix. Medicines may be taken orally or inserted into the vagina. Therapy with drugs of this category is carried out exclusively within the walls of the hospital.
- Amniotomy is a puncture of the amniotic sac. The procedure is painless, it is carried out within the walls of the maternity hospital, when the cervix is already slightly dilated, it is thinned, and the baby’s head has dropped low.
- Oxytocin is a synthetic stimulant that provokes uterine contractions. Contractions caused by oxytocin are more intense and painful. It may make sense to discuss the use of spinal anesthesia with your doctor in advance.
Depending on the woman’s body’s response to stimulation, the induction period can last from several hours to 2-3 days.
Consequences of labor induction during full-term pregnancy
- Artificial induction of labor is associated with the risk of excessive impact on the uterus, as a result - the threat of rupture or perforation of the latter.
- Child distress syndrome is possible.
- If the gestational age of pregnancy is incorrectly determined, there is a risk of having a premature baby.
- A woman’s body does not always give the expected response to stimulation, and as a result, labor may be completed by caesarean section.
- Threat of umbilical cord prolapse during puncture of membranes.
- The use of oxytocin must be accompanied by monitoring the child’s heart rate (due to a decrease in the frequency of contractions).
Stimulation is carried out only with the informed consent of the pregnant woman, because administered stimulants provoke processes that differ from spontaneous natural childbirth. Violation of the physiological parameters of blood circulation in the uterus creates a threat to oxygen starvation of the child and damage to the central nervous system. The result of induction may be premature rupture of amniotic fluid when the cervix is not yet ready. As a consequence - weak primary and secondary labor.
A successful birth and the birth of a healthy baby are the result of a tremendous amount of work by a woman’s body. Listen to your feelings and the doctor’s recommendations, and then the birth of your baby will be as natural and gentle as possible.
Premature babies - features
Premature, according to the official standards of WHO and the Russian Ministry of Health, are considered newborns born before 37 obstetric weeks , with functional immaturity and weighing less than 2.5 kilograms. Height is also indicated - less than 45 cm, but in fact height is less important than weight and functional maturity.
Due to their gestational age (two weeks less than obstetric age), premature babies look disproportionately built, their skull sutures and small fontanel are open, they look thin due to a small amount of subcutaneous fat, and their skin is red. Premature babies are characterized by underdevelopment of the genital organs (with severe prematurity). Such children demonstrate either no reflexes after birth or weak reflexes (sucking, grasping), they cry weakly or do not cry at all. Such children require special care and attention.
The reasons why labor can begin prematurely, when the baby is clearly not ready to be born, are numerous:
- maternal age (before 19 years or after 40 years, the risk of premature birth increases significantly);
- bad habits during pregnancy;
- poor nutrition of the expectant mother, lack of nutrition;
- severe stress in the expectant mother;
- history of abortion;
- multiple pregnancy;
- gestosis;
- Rhesus conflict;
- the interval between this and previous births is too short (less than 2 years);
- gynecological diseases of the expectant mother, anatomical defects of the uterus;
- chronic diseases in women (diabetes, heart and vascular diseases, kidneys);
- fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, pathologies of the placenta.
Much depends on the degree of prematurity. is considered the most favorable - with it, the child at birth weighs from 2 to 2.5 kg, and birth occurs in the period 35-37 weeks . The most alarming is the fourth. Children with it weigh less than a kilogram at birth, and this weight is considered extremely low.
Premature babies are not only small babies with short stature. All organs and systems of the child are immature, the airways are narrow, the diaphragm is located high, breathing is shallow and weak, short-term stops (apnea) may occur, the lung tissue is immature, which increases the likelihood of distress syndrome and pneumonia. The immature heart beats dully, and the vessels are so fragile that a variety of hemorrhages cannot be excluded (most often, hemorrhage occurs in the brain). The stomach, kidneys, and liver have not fully matured.
Intrauterine development: at what stage is the fetus ready for life outside the mother’s body?
Throughout the entire period of gestation, the child is constantly developing. The first few weeks after fertilization, it bears little resemblance to a newborn. Throughout the first trimester, the baby develops internal organs and systems. By the 14th week, all the main organs have already been formed, but they are not able to function outside the mother’s body.
Physiological development continues in the second trimester. During this period, the nervous system and brain improve, the baby begins to hear and respond to loud sounds. After the 21st week, the process of formation of subcutaneous fat is activated. However, according to WHO, the minimum chance of survival in case of premature birth appears only after the 22nd week.
Despite the formation of the main organs and systems, during this period the child is still underdeveloped:
- the ability to breathe and digest food;
- swallowing and sucking reflexes;
- thermoregulation;
- brain activity.
Children born after 7 months of pregnancy are considered more viable. Provided that preliminary stimulation of lung maturation was carried out, with proper care such infants can be saved in 50% of cases. The baby is more prepared for life outside the womb after the 32nd week of gestation. During this period, those substances that contribute to the opening of the lungs are formed in the lung tissues. However, their level is still insufficient for full breathing.
Babies born at the end of the 36th obstetric week are also considered premature. Their development is sufficient to live outside the mother's womb. However, they require special care and are very vulnerable to the negative effects of the external environment. After 37 weeks, the fetus's respiratory and nervous systems fully mature. If born at this stage, the baby does not require increased attention from medical staff.
Low birth weight babies
Giving birth on time does not at all guarantee that the baby will be born with a weight that ideally corresponds to the tables and norms. The average body weight of a full-term newborn is from 2.5 kilograms to 4 kilograms. But sometimes low birth weight babies are born on time. If a baby weighs less than 2.5 kilograms at birth at term, he is called low birth weight.
The reason for the appearance of a toddler with a small weight within the prescribed period may be intrauterine growth retardation - the baby did not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. This can be caused by various abnormalities of the placenta, Rh conflict and other signs of trouble with the fetus during its intrauterine existence. In this case, some signs of physiological immaturity of a seemingly full-term baby are usually observed. Care is provided according to the same principles as in the case of premature babies.
A low-birth-weight baby can appear in women who did not eat well during pregnancy, in women with liver and kidney diseases, as well as in cases of gestosis, which is also called late toxicosis, and the amount of amniotic fluid different from normal (with oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios). The most favorable variant of the cause is a genetic predisposition.
If mom and dad are small in height and weight, there is a high probability that the baby’s height and weight will also be small. But at the same time, no signs of trouble or immaturity of organs and systems are observed.
Compared to premature babies, full-term babies with low birth weight have normal reflexes and can therefore be put to the breast immediately. Unlike a premature baby born, for example, weighing 2 kilograms, a full-term, low-birth-weight toddler with the same weight may not need intensive care, since he will breathe and eat on his own.
A child’s parameters at birth are not a death sentence at all. Doctors are well aware that both premature and full-term, but low-birth-weight children, with adequate care, gain weight more rapidly than their peers born with solid parameters. By 2-3 years, premature babies completely catch up with their peers. Low birth weight babies born at term are comparable in development to others by the age of one year.
For children born with low birth weight, breastfeeding plays an important role. It is its establishment, and not suffering over the lack of several hundred grams, that a new mother needs to worry about. Even if the baby was born at term, but his weight is small, it is worth ensuring that the baby is warm in the crib. Practice shows that in the first year of life, neurological disorders are possible - low-weight babies regurgitate more often and are more anxious. They are recommended to undergo hardening, but only with the knowledge and consent of the pediatrician.
Both premature babies and those who are simply low birth weight really need the warmth of the mother's body , so in the first month, doctors definitely recommend providing the baby with close skin-to-skin contact - holding the baby close to you more often. This is important not only from a physiological point of view, but also from a psychological one. Such contact allows the child to grow up in more adequate conditions for normal mental development.
Low weight children, regardless of full term, up to 3 years of age are registered with a neurologist. Parents should not miss visits to the pediatrician, since it is very important to monitor the dynamics and rate of weight gain and height.
For more information about when a baby is considered full-term, watch the following video.
From what week is a baby considered full-term: signs, timing and recommendations
In fact, this topic is very relevant in many women's forums, and future, as well as real mothers, are passionately discussing what period is considered normal for the birth of a child. Today we want to tell you the opinion of official medicine. Let’s make a reservation right away: despite clear data on what week a baby is considered full-term, there are exceptions to this rule. Moreover, the birth of a baby a little earlier or later than the average term almost never threatens his life and health. However, doctors will try to stop the onset of labor much earlier than expected and delay the time as much as possible.
Delivery on time
The ideal time for the birth of a baby is the fortieth week. It was by this time that he managed not only to completely complete the formation of internal organs, but also to build up a sufficient amount of subcutaneous fat for effective thermoregulation. Therefore, speaking about what week a baby is considered full-term, it seems logical to say 40 weeks. The child is completely ready to be born and live outside the mother’s tummy, and there should be no fears for his life and health. However, not all babies are born at this time. According to statistics, only 9% of women give birth at exactly 40 weeks.
Standard options
It is precisely because of the high variability that obstetricians-gynecologists and pediatricians have somewhat reconsidered the question of at what week a child is considered full-term. What can be considered normal or at least acceptable for childbirth? This is a fairly long period of time from the 37th to the 42nd week inclusive. However, the terminology is slightly different. Childbirth before the 37th week (the 36th is no exception) is considered premature, and babies born at this time are considered premature. From the 37th to the 40th week, the optimal period for the birth of babies begins, therefore, during this period, childbirth is called physiological. Finally, starting from the 41st week, the pregnancy is considered post-term, and by the end of the 42nd week, doctors will send the woman to the maternity hospital to stimulate labor. We have already answered the main question, from what week the baby is considered full-term, but there are still a number of points that need to be discussed.
What week do they give birth to their first and second child: statistics
The baby is considered full-term from the 38th week, so at this time the prenatal period begins. It continues until labor develops. If a woman is expecting her first child, then childbirth is considered normal at a period of 38 to 42 weeks.
The preliminary date of how many weeks labor can begin is determined by the doctor. Most often, during the first pregnancy, this period is 40 obstetric weeks. If the child is born later, they speak of post-term birth.
The range of when you can give birth to your first child is wide – 4 weeks. During this entire period, expectant mothers are very interested in the question of what week they give birth to a healthy baby and when he will be born. The answer is sought not in books, but in a woman’s health, the state of her body.
Depending on how many weeks they give birth, each woman’s body warns her 2 days before the onset of labor.
Woman at 37 weeks
You can be congratulated, the long journey of experiences is almost behind you. This is especially true for those whose pregnancy proceeded with the threat of miscarriage. Now you know exactly after what week the baby is considered full-term. Starting from the 37th week, the whole family should be prepared for the fact that the baby could be born at any moment. The remaining time will not play a role in the development of the baby, but he will be able to grow a little and accumulate subcutaneous fat, which is important for maintaining heat in a small body. At this time, some pregnant women are very balanced, while others, on the contrary, feel increasing anxiety before the upcoming birth. The cervix begins to slowly expand; as soon as it is ready, the mucous plug, which until now has protected the uterus from infections, will come away. This usually happens a few hours or days before birth.
Symptoms of approaching labor
Even knowing from what moment the baby is considered full-term, a woman is sometimes a little lost when she feels the harbingers of labor. Moreover, the better you imagine exactly what they should be and how to behave when they appear, the less time there will be for panic.
However, let’s make one more digression; it concerns packing things for the maternity hospital. Knowing at what stage a pregnancy is considered full-term, you need to start preparing in advance. By the 37th week of pregnancy, you need to buy a discharge kit, diapers and baby vests for the maternity hospital, collect a bag of personal belongings and put a separate discharge kit for yourself. Believe me, this is much better than trying to find a robe or other toiletries in the closet as contractions progress.
During this period, most women begin to experience insomnia. A big belly and the baby’s active life do not contribute to the mother’s sound sleep. However, it won't be long until he appears, so try to enjoy these last moments. Frequent urination may bother you, which can also be easily explained by the fact that a large fetus puts pressure on the internal organs. It is during this period that leg cramps often first appear. Be sure to monitor your vaginal discharge. Usually in the last week they become a little more abundant and lighter. And if you notice a significant amount of transparent mucus on your underwear, then labor is very close.
Indirect signs
It must be said that they are not found in all women, in addition, some note only some of them. However, in any case, you have no reason to worry. You already know which baby is considered full-term; the 37th week has passed, which means that whenever labor begins, he will be born completely ready for it. Remember this every day, so that sudden labor activity is not a reason for panic, but, on the contrary, a long-awaited event.
Diarrhea can warn you that labor is approaching. This is a normal physiological reaction that allows a woman in labor to cleanse her intestines. If this does not happen, then it is recommended to clean it yourself using an enema. It is no longer mandatory to do it in the hospital, but before calling an ambulance, you can easily do it yourself. Very often, just before giving birth, women experience a burst of activity. Suddenly you want to clean the windows and wash the curtains, wash the whole house right down to the entrance. It is our instincts that tell us that we need to prepare a nest in which a baby will soon appear.
Signs
The fact that pregnancy has reached its final stage and is full-term can be said by various signs. Some of them relate to the condition of the expectant mother, while others are observed in the child after birth. But each of them is important and is considered necessary to determine the degree of full term.
In a woman
With a normal pregnancy, childbirth should occur on time. And the fact that the baby will soon be born is indicated by the preparation of the expectant mother’s body. About 2-3 weeks before the expected date of the joyful event, the woman notices some changes in her condition. The following signs are signs of imminent labor:
- Descent of the uterine fundus.
- Reducing body weight.
- Removal of the mucus plug.
- False contractions.
Having reached 40 weeks, the uterus descends into the pelvic cavity. The height of its bottom is 34–35 cm, which is 1–2 cm less than a month ago. This circumstance significantly improves the woman’s well-being, because shortness of breath and heartburn go away, it becomes easier to move and sleep.
Due to the absorption of amniotic fluid by the placenta, a woman’s weight before childbirth can decrease by 1–2 kg. Swelling in the legs that appeared due to late toxicosis also disappears. The maturity of the uterus and readiness for the final stage is indicated by the appearance of false contractions (Braxton-Higgs). They are felt by a feeling of discomfort in the front of the abdomen or pressure in the pelvis. But these contractions differ from labor contractions in several ways:
- Irregular.
- Low intensity.
- Same frequency and duration.
- Stop after resting, walking or changing body position.
Before the baby is born, the mucous plug that covered the entrance to the uterus also softens and comes off. This is due to a decrease in the level of estrogen in a woman’s body and is manifested by an increase in the amount of discharge. But the cervix remains closed and the amniotic fluid has not yet drained - such signs indicate that labor has already begun.
The expectant mother senses the approach of labor by a change in her condition: some symptoms that have tormented the pregnant woman for a long time disappear, but instead others appear, confirming the readiness of the uterus.
Contractions and the onset of labor
You have already experienced them before, but if previously these were training contractions that did not last long and went away if you stood up and moved a little, now the situation is changing. Often the mucus plug comes off first, then your water breaks, and finally contractions begin. It also happens the other way around: the first symptoms are contractions. In this case, the main thing is not to panic. Double-check the bag you take to the hospital. Place your passport and exchange card nearby. Consider breathing exercises that will help relieve pain during labor and childbirth. You shouldn’t go to bed right away, walk around the house, you can even go outside and get some air. This will only intensify real contractions, and you will be sure that it is time to call an ambulance.
Memo for the expectant mother
The delivery room is not a place for panic, so even during pregnancy, mentally scroll through the whole picture of the events taking place several times in your head. Again, ask your doctor the question from what week is the pregnancy considered full-term. He will tell you that the lower limit of normal is 37-38 weeks. This means that from about this time you need to prepare yourself mentally. Close your eyes and imagine that contractions are starting, at the same time remember the breathing exercises during contractions, how you calmly get ready, go to the hospital and give birth to a healthy baby. This attitude will greatly help you overcome anxiety.
At what stage of pregnancy is the baby full term?
When assessing the full-term pregnancy, one cannot fail to take into account the degree of maturity, and therefore the full-term, of the child himself. It is the development of the baby that determines its readiness to come into the world and support life outside the womb of a woman. If the baby is not full term, it requires special care until the body gets stronger.
The signs of maturity were based on parameters at 38-40 weeks of pregnancy with a full-term baby:
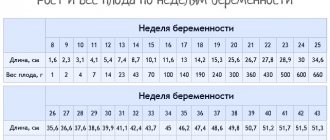
- The weight of the baby is 3000 - 3500 g (normal variations range from 2800 g to 4000 g).
- The baby’s body length, the most significant factor in assessing the baby’s full term, ranges from 45 to 55 cm.
- The head circumference is 1-2 cm greater than the baby's chest circumference. These values do not exceed 34-35 cm.
Important diagnostic criteria are:
- The first cry, which should be loud and quite intense.
- Color and condition of the skin. Full-term babies have smooth, elastic, pink skin covered with a specific white lubricant.
- The presence of a small and large open fontanelle.
- Increased muscle tone, causing the child's limbs to be slightly bent.
- Heart rate - 120 - 150 beats per minute.
Each parameter is assessed on a scale from 0 to 2 (Apgar scale) in the first minute and 5 minutes after the birth of the baby. This is why the Apgar score includes 2 numerical values, written separated by a slash (for example, 9/10, 7/8). A variant of the norm is an indicator of 8 points or higher. The interval 4 - 7 points indicates the average severity of the newborn’s condition. If the indicators are in the range from 1 to 3 points, the child’s condition is extremely serious.
When assessing the full-term birth of a child, both the gestational age at which the birth occurred and the maturity of the baby are taken into account. So the baby can be born at 37-38 weeks, but have signs of immaturity. In this case, the pregnancy will be full-term, but the child will not.
General information
Probably everyone knows that a woman carries a child for about 9 months. But according to obstetric terminology, a pregnancy that lasts at least 37 weeks is considered full-term. This is exactly the time necessary for the fetus to fully form and be ready for new conditions of existence. But even here, not everything is so simple. The fact is that children born at 37 and 40 weeks differ from each other in many ways. This became the basis for dividing the period of full term into several stages, taking into account gestational time. Based on the classification adopted by doctors of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, pregnancy occurs:
- Early term (37–39 weeks).
- Full-term (39–40 weeks).
- Late term (41–42 weeks).
- Post-term (more than 42 weeks).
Definition of deadlines
So that a woman can know how long she needs to carry a child until all systems of its body are fully formed, various methods are used in medical practice. But, unfortunately, none of them allows you to calculate the date of birth up to one day. Most often, several methods are used, and if taken together there are no conflicting results, then it is possible to determine with sufficient accuracy when labor will occur. For this purpose, anamnestic data and the results of instrumental examination are used:
- The date of the last menstruation is added to it by 280 days.
- The date of the first movement of the fetus is added to it by 20 or 22 weeks (for first- and multiparous women, respectively).
- Pregnancy period at the first visit to the antenatal clinic (up to 12 weeks).
- Ultrasound results.
Considering that term birth occurs between 37 and 42 weeks, the likelihood of making an error in the calculations can be quite significant. But the expectant mother should not worry about this - confidence in the normal course of pregnancy and a positive attitude will help carry the child to the due date, even if he is born on another day.