For normal growth and development, every baby needs proper age-appropriate nutrition, which takes into account his needs for fats, proteins and carbohydrates at a certain period of life. However, not only the calorie content of food, but also its vitamin and mineral composition contribute to the proper maturation of all organs and systems.
The most common deficiency in children in the first year of life is hypocalcemia. A lack of calcium in a baby’s body can lead to very serious consequences – spontaneous fractures, convulsions, delayed development of the skeletal and nervous systems.
Causes of calcium deficiency
In order for the level of calcium in a child’s body to remain sufficient, this microelement must be present in his daily diet in a dose of 500–1000 mg. Breastfed babies receive it through mother's milk, so a nursing woman should eat well and additionally receive vitamin and mineral complexes throughout the entire lactation period. A critical decrease in the level of calcium in the blood causes rickets and its complications.
Infants receive calcium from their mother's milk, so a woman who is breastfeeding her baby needs to consume a sufficient amount of this element in her diet.
In the first year of life, calcium deficiency in children develops not only due to a low intake of calcium into the body, but also due to a lack of vitamin D3, which is involved in the absorption of the microelement. According to the recommendations of the World Health Organization, every infant who feeds on mother's milk must additionally receive a water-soluble form of vitamin D3 during the autumn-winter period. In the spring and summer, it is synthesized in the baby’s body independently under the influence of sunlight, so its excessive administration during this period leads to hypervitaminosis, which is much worse than a vitamin deficiency.
In older children, hypocalcemia can be caused by diseases of the digestive tract (gastritis, colitis, intestinal dysbiosis, etc.), taking medications that interfere with the absorption of substances in the gastrointestinal tract (antacids, sorbents).
Calcium norms depending on age:
- from birth to 6 months – 400–500 mg;
- from 7 months to 1 year – 500–700 mg;
- over one year and up to 10 years – 700–900 mg.
It is impossible to create an excess of calcium through nutrition; all of its excess is eliminated from the body through the kidneys and intestines. Additional intake of the microelement in ready-made tablet form very often leads to the accumulation of calcium salts in the kidneys.
Do children need to take calcium supplements?
During adolescence, when the body is rapidly developing, as well as after fractures, children may not have enough calcium contained in foods. In such situations, you need to pay attention to preparations of this macronutrient, since calcium is very important for children.
Currently, there are a huge number of calcium supplements for both adults and children. But before giving preference to one drug or another, you should consult your doctor. The doctor will determine the dosage and course of administration. The use of such drugs without consulting a specialist is dangerous for the child’s body.
After visiting the doctor, the question may arise: “Which calcium supplement should I buy?” Today, preparations based on calcium citrate, for example, Osteomed . Its important component is a natural product such as drone homogenate , which has virtually no competitors in terms of vitamins, minerals and amino acids.
When taking calcium supplements, you need to remember that they may not combine well with other medications (tetracyclines, iron and fluoride supplements).
Summarizing all of the above, we can conclude that calcium is one of the most important minerals for children. That is why it is necessary to ensure that the child receives it in sufficient quantities.
The drug Osteomed will help cope with the deficiency of this macroelement, and will also become a reliable protection against diseases of the skeletal system!
USEFUL TO KNOW:
ABOUT JOINT DISEASES
Joint gymnastics at home and in the office: simple exercises for ease of movement
JOINTS Author: admin1104.12.2020
Joint exercises are equally effective both as a warm-up and for the prevention of musculoskeletal disorders. Arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis and other diseases of this kind have long ceased to be the lot of the elderly. And at any age it is incredibly difficult to treat them. The set of joint gymnastics exercises presented below will be an excellent solution for anyone who has already encountered such a problem or wants...
Read more
ABOUT HORMONE THERAPY
The power of hormones. What active substances regulate cartilage restoration?
HORMONES Author: admin1110.12.2018 Leave a comment
A person’s condition and the coherence of the organs of his body are largely determined by hormonal balance. Cartilage restoration is also subject to the influence of ubiquitous life regulators. Without normalizing hormonal levels, complete regeneration of the joint is impossible. What strings does the invisible puppeteer, the endocrine system, pull, influencing cartilage tissue? Testosterone This hormone is produced by the gonads and the adrenal cortex, as in...
Read more
ABOUT BONE DISEASES
Fractured finger: how to speed up bone healing?
BONES Author: admin1102.12.2020
A fracture of a finger on the hand is not a fatal injury, but very unpleasant. It can significantly worsen the life of a modern person, depriving him of the opportunity to study, play, work, relax, and finally, use gadgets. How long such a fracture will heal depends on many factors. However, it is quite possible to accelerate the formation of callus. Let's talk.
Read more
ABOUT CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISEASES
ABOUT VITAMINS FOR BONES
May there always be sunshine! What is vitamin D for?
VITAMINSAuthor: admin311.12.2018Leave a comment
Sunlight for a person is not only a source of good mood, joy and happiness. When it comes into contact with the retina and skin, a large number of physiological processes are triggered in the body, for example, the synthesis of calciferol. What is vitamin D for, besides improving calcium absorption? How to compensate for its deficiency if exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun is undesirable for a person? For…
Read more
DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS
Clinical manifestations of hypocalcemia
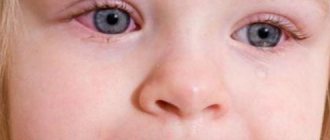
In young children who are not yet able to move independently, only a doctor can often suspect a calcium deficiency. The first signs of deficiency of this microelement in infants are:
- increased sweating of the skin, especially in the back of the head;
- rolling out hair in areas of prolonged contact with the pillow;
- tremor (shaking) of the chin when crying;
- flinching at loud noises.
If calcium deficiency is observed during the development of spinal curves and walking, then the baby develops curvature of the bones of the limbs and poor posture. At an older age, hypocalcemia leads to increased fragility of bones, splitting of nails, cracks in the corners of the mouth, cramps, anemia, and increased joint mobility.
Suspicions about a lack of calcium in the body and increased convulsive readiness can be confirmed using certain tests:
- If you lightly tap the baby’s cheek in the area of the corner of the mouth or cheekbone with the tip of your finger, and a twitching occurs in this area, then there may be a calcium deficiency in his body;
- If, when squeezing the baby’s hand in the middle third of the shoulder, his fingers cramp, then the likelihood of calcium deficiency is high.
Consequences of low calcium levels
Calcium is necessary for normal growth and functioning of the skeleton of a child and an adult.
Insufficient intake of this microelement into the body or impaired absorption in the intestines in childhood leads to the development of rickets. There are several stages of the disease, each of which has its own manifestations.
At the early stage of rickets, the baby develops all the symptoms of calcium deficiency - skin hyperhidrosis (increased sweating), hyperexcitability (shuddering), hair rolling due to prolonged compression or friction of the head on the pillow. At this stage of the disease development, no bone deformations are observed.
The lack of adequate therapy leads to the progression of rickets, and it enters the peak stage. Dyspeptic symptoms (vomiting, poor appetite, upset stool) and bone changes come to the fore. The muscle tone of the anterior abdominal wall also decreases, and it takes on the shape of a frog’s belly.
Among the bone disorders in the first year of a baby’s life are:
- flattening of the back of the head;
- asymmetry of the skull;
- softening of the edges of the fontanel;
- formation of frontal or parietal tubercles;
- deformation of the sternum (keeled or funnel-shaped);
- curvature of the spine (kyphosis, scoliosis);
- X- or O-shaped deformation of the lower extremities.
Ignoring the problem by parents can lead to disability of the child, delaying his physical and mental development. Frequent consequences of severe rickets in childhood are:
- severe deformation of the spine or lower extremities;
- tower skull, pronounced parietal or frontal tubercles;
- improper bite in the mouth;
- curvature of the legs, interfering with normal walking;
- deformation of the sternum, preventing the normal functioning of the lungs and heart;
- a flat pelvis, which does not allow women to fully bear a baby and give birth to him independently;
- visual impairment (myopia).
In children of preschool and school age, calcium deficiency manifests itself in the form of frequent fractures, joint hypermobility, and long-term anemia.
Children's vitamins from two years
- Calcium gluconate . This is the simplest option for replenishing the element's deficiency. The product dissolves well in water and does not cause discomfort to the stomach. The only negative is the taste; children may refuse to drink this solution. It is prescribed according to indications, for example, stunted growth, poor condition of teeth and gums.
- Multi-tabs. The complex contains seven minerals and 13 vitamins. It is prescribed to children from two to seven years old. The product replenishes the deficiency of minerals during the period of active growth and tooth change. The drug is produced in the form of chewable tablets with fruit flavors. The rate of consumption is once a day during meals.
- VitaMishki Calcium Plus . The drug is produced in the form of marmalade candies with natural fruit additives. Children love them because they do not look like pills and have a pleasant taste. There are no artificial colors in the composition; they are recommended for the growth of strong teeth.
- Calcemin . The drug is available in tablets and is recommended for use from the age of five. The composition is supplemented with vitamin D, copper, manganese and boron. It is recommended to consult your doctor about dosages.
Diagnosis of calcium deficiency
When the first signs of rickets or convulsive twitching appear, you should immediately consult your doctor. Such conditions require mandatory correction after examination.
It is mandatory to take a general blood test, which determines the level of hemoglobin. A urine test using the Sulkowicz test can detect calcium deficiency in young children. It shows the level of calcium excretion in the child's urine. The level of calcium in peripheral venous blood is also determined. In children under 6 months of age, this figure is normally 2.25–2.5 mmol/l.
Introduction
Calcium is an important macronutrient involved in various physiological processes.
Calcium accounts for up to 9% of total body weight. The main part of calcium is deposited in bones (99%), a small amount is deposited in teeth and soft tissues (1%), in intercellular fluid and plasma (0.08%) [1–5]. In blood plasma, calcium circulates in a free form and bound to albumin and chelate compounds. The indicated fractions collectively reflect the content of total calcium in the blood. Free calcium makes up approximately 50% of the total plasma calcium concentration and is a biologically active form involved in the physiological processes of neuromuscular conduction and blood coagulation. The concentration of total and free calcium is in a narrow range - 2.2–2.6 mmol/L and 1–1.2 mmol/L, respectively [1–7].