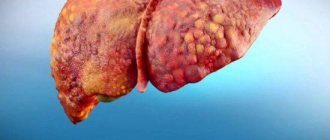
Responsible dog owners monitor not only the appearance, but also the contents of the tray. If you notice that your pet is depressed and has foul-smelling green poop, seek veterinary help immediately.
When a dog, at first glance, is healthy, but is choked with greens, you yourself are obliged to take action. Which? I'll tell you.
The article discusses the main five reasons why a dog has green stool. And specific recommendations for each option.
What affects the color of stool
The normal color of stool can be dark or light brown depending on the diet (presence of vegetables, chemical dyes in food). The stool turns brown due to the breakdown of bile.
There are several main reasons that contribute to the change in the color of feces to green with different shades:
- Food;
- medications;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
If you have green stools, it is necessary to analyze the diet in the last 2-3 days, since this is the time it takes for food masses to pass through the small and large intestines from the esophagus to the rectum.
Foods that can turn your stool green usually consist of significant amounts of chlorophyll, a greenish substance found in the leaves and stems of plants. Changes in the color of stool are possible after eating the following foods:
- broccoli;
- Brussels sprouts;
- celery;
- spinach;
- sorrel;
- chard;
- green smoothies;
- sprouted wheat with sprouts;
- green algae;
- juices from vegetables and fruits;
- red fish;
- red meat and products made from it;
- Red beans.
Also, a green tint of feces is observed after eating food with chemical dyes in the composition: carbonated drinks, caramels, filled candies, colored ice cream, etc.
Diagnostics, what tests to take
A change in the color of stool from normal to green, not related to food preferences, should be the reason for the following studies:
1 coprogram to determine the cause of stool of a green tint or color - a laboratory study of stool, which allows us to identify their physical, chemical and microscopic characteristics. Decoding the results of the analysis in most cases allows you to establish a diagnosis and find out the reason for the unusual color of stool;
2 general blood and urine tests, as well as microscopic examination of stool. The latter makes it possible to identify the presence of various parasites and their metabolic products in the body, which also often leads to a change in the color of stool;
3 bacterial culture for both the intestinal group - allows you to identify pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms inhabiting the human intestine.
Causes of green stool in adults
Medicines and dietary supplements (dietary supplements) can have a significant impact on the color of stool, in which changes in color occur without diarrhea and abdominal pain and other symptoms accompanying diseases of the digestive system.
The following groups of medications can affect changes in the color of stool:
- preparations with iron for the treatment and prevention of anemia (Totema, Ferrotab, Sorbifer, Tardiferon, etc.);
- multivitamins with iron;
- herbal remedies for constipation (Laminarid, Mucofalk, Senade, Rektaktiv);
- preparations containing iodine (Iodomarin, Antistrumin, Micro-Iodine, Iodbalas);
- Dietary supplements with chlorophyll (NSP Liquid chlorophyll);
- Dietary supplements with iron (Fersinol-3, Medefer, Spaton).
Light green stool
The cause of light green stool may be insufficient digestion of food in the gastrointestinal tract, when there is a deficiency of digestive enzymes, as well as an increased rate of movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract.
If liquid green stool is observed for a long time, this indicates diseases such as:
- celiac disease;
- maldigestion;
- chronic entrocolitis;
- disaccharidase deficiency;
- fermentative dyspepsia;
- liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatosis).
Dark green
Dark green stool is a serious symptom in combination with abdominal pain, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, and indicates internal bleeding of the upper gastrointestinal tract in the following diseases:
- stomach ulcer or erosion;
- duodenal ulcer;
- chronic gastritis;
- hypertrophic polydemat gastritis;
- varicose veins of the esophagus or stomach;
- angiodysplasia of gastric vessels;
- rupture of an aortic aneurysm into the lumen of the duodenum;
- pancreatic tumors;
- damage to the bile ducts.
Green stool with mucus
The presence of mucus in feces is an additional symptom of pathological processes in the organs of the digestive system. The main reasons for the appearance of excrement with mucus are the following gastrointestinal diseases:
- dysentery;
- rotavirus (intestinal flu);
- helminthiasis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
These diseases often cause not only changes in color, but also in the consistency of excrement: diarrhea and undigested food residues in the feces are observed.
Smell
The unpleasant smell of feces indicates a violation of the digestion of nutrients at different stages of the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates:
- a decrease and even absence of odor indicates accelerated movement of contents through the small and large intestines;
- a sour smell appears with fermentative dyspepsia;
- the smell of rot is noted with ulcerative colitis;
- an unpleasant fetid odor reminiscent of rancid oil indicates a violation of the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and a deficiency of bile acids in the intestines.
In addition to the color and smell of stool, you should also pay attention to the consistency of the stool, since the density of the stool can also be used to assess the functioning of the digestive system:
- formed stool indicates normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but is also observed with insufficient digestion in the stomach;
- mushy feces in combination with a green color confirm chronic enteritis, colitis, increased evacuation of colon contents;
- ointment-like feces are observed with insufficiency of bile in the large intestine, with insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes;
- diarrhea is observed with colitis and enteritis.
If, along with a green tint of intestinal secretions, bloating, fever, sharp or dull pain in the abdomen, diarrhea or vomiting are noted, this indicates poisoning and serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diseases with green diarrhea
In this case, inflammatory or infectious processes occur in the body.
This:
- intestinal infections;
- dysbacteriosis;
- enteritis;
- diseases of the biliary tract;
- liver pathologies;
- gastrointestinal bleeding.
All of these diseases have specific symptoms that help determine the cause and facilitate diagnosis.
When diarrhea occurs due to illness, overall health always worsens. Symptoms of intoxication appear: increased body temperature from 38 ° C to 39 ° C, nausea, vomiting, dizziness. There is discomfort and bloating in the abdomen, and appetite worsens.
With prolonged diarrhea accompanied by vomiting, dehydration develops. Blood pressure decreases, the skin turns pale, pulse and breathing increase.
These are common signs of all pathological diarrhea, but each disease has its own markers.
Intestinal infections
The manifestations of green diarrhea and additional symptoms depend on the causative agent of the disease.
Chair Features:
- salmonellosis: abundant, foul-smelling, contains mucus and blood, has a swamp color;
- rotavirus: watery, foamy, yellow-green diarrhea;
- staphylococcus: the appearance of green diarrhea with mucus.
Signs:
- antispasmodic, acute or aching pain in the abdomen;
- painful bowel movements;
- false urge to defecate;
- cough, snot, sore throat;
- redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes.
If the infection proceeds without complications, then the acute period lasts from 3 to 7 days. All diarrhea pathogens are contagious, so contact with people should be avoided.
Pancreatitis
A group of diseases with inflammation of the pancreas and disruption of the flow of enzymes into the intestines. Characterized by alternating constipation and gray-green diarrhea. Complete clarification of feces is possible.
More signs:
- constant or paroxysmal pain in the left hypochondrium;
- heartburn;
- debilitating, frequent vomiting;
- yellowness of the eyeballs and skin.
Drugs used for treatment are proteolysis inhibitors. In the acute stage, the patient is hospitalized; in complex cases, surgical treatment is required.
Bleeding
The causes of bleeding are ulcerative pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, Crohn's disease, cirrhosis of the liver, polyps, cancerous tumors, hernias, hemorrhoids, ulcerative colitis. This usually causes the stool to turn red or black. But sometimes the blood mixes with bile, which is manifested by dark green diarrhea.
Additional signs:
- dark brown vomit;
- pale skin;
- profuse, cold sweat;
- fainting;
- with cirrhosis: skin itching, jaundice, nosebleeds.
Patients with these signs are hospitalized. Treatment is given to prevent bleeding, and in some cases surgery is required.
Viral hepatitis
Inflammatory liver diseases after damage by viruses. Diarrhea occurs due to stagnation of bile. In an adult, loose, light green stools appear with an unnatural oily sheen.
Specific symptoms:
- itching;
- yellowing of the eyeballs and skin;
- darkening of urine;
- headache and muscle pain.
For the main treatment, antiviral drugs and hepatoprotectors are used.
Enteritis
A group of diseases with inflammation of the small intestine, impaired enzyme production and nutrient absorption. They develop in cases of severe infections, helminthic infestations, food poisoning and allergies.
Symptoms:
- the appearance of watery diarrhea with greens, pieces of undigested food, flaky inclusions are possible;
- dry and pale skin;
- white coating on the tongue;
- headache.
The underlying disease is treated, often with antibiotics and sulfonamides.
Dysbacteriosis
This is a change in the intestinal microflora with a significant increase in the number of pathogenic microorganisms. The cause can be all of the diseases listed above.
Symptoms:
- liquid, foaming yellow stool with a green tint, sometimes alternating with constipation;
- belching, rumbling in the intestines;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- sharp pain in the abdomen.
Dysbiosis also develops after treatment with antibiotics, cytostatics, sulfonamides, stress, poor nutrition, immune and hormonal disorders.
A doctor is consulted if there are 3 or more episodes of loose stools per day or the appearance of any suspicious symptom. Even a greenish tint to the stool indicates inflammation or infection. If you have a high body temperature and feel unwell, call an ambulance.
Diseases that lead to green stool
The most common causes of green stool are poisoning, dysbiosis and fermentative dyspepsia.
Poisoning is an acute digestive disorder, which is manifested by fever, diarrhea with green feces, vomiting and nausea. The causes of poisoning may be:
- low-quality products, which lead to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora;
- poisonous mushrooms;
- intoxication of the body with toxic substances found in alcohol, medications, plants, etc.
In case of poisoning, the stomach should be emptied of contents by lavage, general intoxication of the body should be eliminated with the help of medications and water balance should be restored.
Fermentative dyspepsia is a digestive disorder caused by a large amount of carbohydrates with coarse fiber in the diet, as well as a decrease in the amount of gastric juice.
The appearance of dyspepsia is also accompanied by poor chewing of food, eating at a fast pace, and drinking carbonated drinks. Symptoms of the disease appear as follows:
- bloating;
- feeling of transfusion and rumbling in the stomach;
- constipation and diarrhea;
- light green stool.
To eliminate discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to adhere to a protein diet for 7-10 days with the exception of vegetables and fruits, since foods with a large amount of fiber (white cabbage, apples, etc.) provoke increased gas formation.
Dysbacteriosis is a violation of the digestion of food in the intestines due to a lack of lactobacilli and an excess of putrefactive bacteria.
The development of dysbiosis is accompanied by abdominal disorders, bloating, and abdominal pain. In addition to the change in the color of the feces to yellow and green, you can see many undigested pieces of food in the stool.
To eliminate symptoms, pre- and probiotics are used to replenish beneficial lactobacilli, and you should also follow a special diet to maintain normal microflora.
What to do
If a green tint to the stool is observed for a long time (from 2 weeks), then it is necessary to identify the exact cause of the pathological processes in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. For this purpose, laboratory tests should be taken, namely:
To detect the causes of changes in the color of excrement, a stool analysis is required to determine the following indicators:
- reaction (pH) – alkaline and sharply alkaline (pH more than 8.0) for colitis, acidic (pH less than 5.5) for impaired absorption of fatty acids in the small intestine due to pancreatitis, liver diseases, pancreatic insufficiency;
- the presence of mucus in the stool, which indicates inflammation, infectious intestinal diseases and poisoning;
- blood impurities in stool;
- food residues in the stool indicate reduced stomach acidity;
- reaction to bilirubin.
Bacterial culture of stool when green feces appears is used to detect dysentery and intestinal flu pathogens.
To identify pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, the following is used:
If diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are detected, it is necessary to carry out appropriate drug treatment and adhere to a therapeutic diet:
- for stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis - diet 1 table;
- for fermentative dyspepsia and dysbacteriosis - table 4a;
- for enteritis and colitis - diet table 4.
During pregnancy
Light green stools during pregnancy can be a dangerous sign of gastrointestinal disease, since the enlargement of the fetus puts pressure on the gastrointestinal tract, which in some cases leads to the following digestive disorders:
- abnormal transit of feces through the large intestine, which is manifested by frequent stools, regular diarrhea with green or yellow excrement;
- colitis - inflammation of the intestines, the symptoms of which are abdominal pain, green stools with mucus, and in severe forms, blood in the feces;
- dysbacteriosis;
- allergy to lactose and gluten.
Also, the reason for the appearance of green excrement is sometimes the use of vitamins and dietary supplements for pregnant women with iron in their composition. Some of the iron is not absorbed and is excreted from the body, causing the stool to turn green.
Green stool in an adult is a signal of trouble in the body and a reason to immediately consult a specialist. There are many reasons for the appearance of green in the stool, and you should not always worry right away. However, such changes in bowel movements may be a symptom of a serious illness that requires immediate treatment.
What does green stool mean in adults?
Changes in the color of feces are associated with a variety of reasons, from fairly harmless ones, for example, the predominance in the diet of foods that have a coloring effect, to very dangerous ones - pathological disturbances in the functioning of vital internal organs and systems. Be that as it may, the unusual color of stool should alert you and become a reason for diagnosis, as well as treatment if necessary.
If green feces were noticed in an adult once, then this is almost always a physiological cause or consequence of eating certain foods. You can determine the exact cause of stool turning green only by contacting a gastroenterologist and undergoing all prescribed examinations.
Main causes of stool changes
Normal stool is brown in color due to bile pigments. The shades vary, but it is always shaped and not runny. Green stool in an adult can appear for physiological reasons related to errors in the diet, the use of “coloring” products, as well as due to diseases that provoke changes in the color of the stool. Pathological causes are dangerous to human health by developing complications and require increased attention, sometimes taking emergency measures.
Physiological factors
Some physiological factors can influence the stool of an adult:
- A diet containing unusual or unusual foods containing iron, combined with insufficient water, produces dark green stool. These foods include: red beans, meats, herbs, saltwater fish and vegetable juices (purees). Green foods (fruits, vegetables, herbs) also change the color of stool. In such a situation, no other symptoms appear. There is no pain, no dyspepsia, no nausea, no fever. There is no unpleasant odor, the stool does not change consistency and shape. Often, wanting to lose extra pounds, a person begins to fast, replacing all food with greens and vegetables. The result is marsh-colored feces. In this case, you need to switch to a balanced diet, and your stool will improve. The green color of stool in infants may be due to the treatment of colic with dill water, which is also not a pathology.
- Food dyes change the color of stool. Carbonated drinks, chewing gum, candies, jellies, red wine and much more contain similar additives. Unusual, brightly colored bowel movements in such cases are not accompanied by any unpleasant sensations. The situation returns to normal after foods with food dyes cease to be the basis of the diet.
- Dietary supplements and medications can cause a light greenish tint to stool: antibiotics, vitamins, glucose, preparations containing iodine, activated carbon, sorbitol, herbal extracts, algae, etc.
All this suggests that greenish feces are not always a cause for concern. Rather, it is a reason to normalize your lifestyle. However, if subjective sensations accompany the change in stool color: bitterness in the mouth, diarrhea, nausea, you should consult a specialist.
Pathological factors
Uncharacteristic color of feces can also be caused by pathological reasons. The green tint of stool, combined with a change in consistency and painful bowel movements, is a symptom of dangerous diseases.
This state of affairs requires examination and timely adequate therapy. Pathologies that cause the appearance of a green-tinged color include:
- An autoimmune intestinal disease is Crohn's disease, which requires surgical intervention in the case of a malignant course that threatens the patient's life. Food poisoning with fever, pain, diarrhea, vomiting, which requires gastric lavage, diet, or hospitalization to combat dehydration.
- Foodborne intestinal toxic infections, the hallmark of which is not only a change in the color of the stool, but also the appearance of a large amount of mucus in it. The most common causative agent of infection is salmonella. It is found in raw eggs, poorly processed meats, and all dairy products. Salmonellosis is also transmitted through contact with an infected person. This pathology is characterized by: diarrhea, hyperthermia, pain, profuse vomiting. The most dangerous thing is dehydration of the body, which can lead to serious consequences, including death. The patient has green, liquid, and foul-smelling stool.
- Dark green stool can appear when there is bleeding in the stomach area. The greenish tint depends on hemoglobin, which interacts with gastric juice. This is a very dangerous symptom: weakness rapidly increases, cold sweat, pain, black vomiting, tachycardia appear, blood pressure drops, and the skin becomes unnaturally white. Need emergency help. It is worth noting that bleeding makes the stool black and green, but can occur latently, then the color of the stool is the only sign of a disorder.
- Food allergies are another pathological cause of changes in the color of stool. In this case, undigested food particles are often visible in the feces.
- Peptic ulcer (peptic ulcer) is an extremely common and most unpleasant cause of changes in the color of stool, since it indicates the progression of the pathology and requires medical intervention.
- Rotavirus changes the color of the stool to dark and green, defecation is accompanied by a disgusting odor and the release of mucus. Severe intoxication requires immediate medical attention.
- Dysbacteriosis. Foamy, watery stools with an unpleasant odor after a long course of antibiotics are a reason for medical consultation.
- Pathology of the biliary system, gallbladder and biliary tract often causes green stool. An increase in bile pigments in the stool, when it becomes gray-green, is a harbinger of an exacerbation of the disease.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of an inflammatory nature: gastritis, colitis, enteritis, erosive processes. In this case, the light green tint is given to the stool by leukocytes, which are localized in areas of inflammation. The disease is always accompanied by pain of varying intensity, sometimes fever, and constipation.
- Lactase deficiency is caused by the lack of an enzyme that breaks down milk sugar. This may be a hereditary pathology that produces liquid green stools at the slightest ingress of milk into the intestines. After adjusting the diet, the stool becomes yellow or brown and hard. In young children, the pathology is often transient in nature.
If green feces appear in an adult for some unknown reason, you should not deal with it at home. It is better to go to the doctor for advice and diagnostic measures.
Physiological causes of green excrement
This group includes the factors described above, namely the predominance in the diet of certain foods that have coloring properties or are rich in iron. These are fairly harmless reasons, but every person should be aware that their eating habits can have such a side effect.
In addition to the dyes contained in food, changes in the color of stool often occur due to the use of various medications. What pills and medications can change the color of stool from light brown to green:
1 herbal mixtures aimed at combating constipation and other pathological conditions;
2 sweeteners, for example, glucose or sorbitol;
3 iodine-containing drugs aimed at maintaining the functioning of the thyroid gland;
4 complex vitamins and minerals may change stool color;
5 preparations not based on kelp, spirulina and other seaweed.
Such drugs do not threaten human health, of course, if they are used in the required dosage and under the supervision of a doctor.
What reasons can be considered dangerous for the appearance of green poop in an adult? First of all, if an adult begins to have green stools, then you should monitor subsequent bowel movements for the presence of mucus and other inclusions in the stool. If an adult has green poop and it does not stop for more than 3 or 4 days, then this can already be considered a cause for concern. Also, if there is mucus in light green or dark green stool, then there is a high probability that the cause of the change in stool color is pathological.
Green stool during pregnancy
During the process of carrying a baby, many women are faced with the problem of green stool. Most often this is due to taking vitamin complexes in the early stages of pregnancy or changes in diet over the trimesters. Iron supplements prescribed to expectant mothers with low hemoglobin also make the stool greenish.
In addition, pregnant women experience food poisoning and intestinal disorders that affect the color of the stool. Hemorrhoids and their injury during defecation can give an admixture of dark green color, since when blood and bile are mixed, this is exactly the shade that is obtained. Pathology of the large intestine also causes a change in the color of stool: microorganisms cannot break down bilirubin in time. Finally, antibiotics cause dysbiosis and accordingly change the color of stool. During pregnancy, a woman is under the supervision of a doctor, and there is no need to worry too much about the color of the stool. But if the color of stool does not change after childbirth and the period of adaptation of the body to breastfeeding, you should consult a gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist.
Necessary examinations and treatment
The condition in which the stool turns green cannot be ignored. We need to find the cause of this phenomenon. If something green was eaten the day before, and the general condition was not disturbed, then there is no reason to worry. However, if objective symptoms of intoxication or inflammation appear (nausea, diarrhea, headache, abdominal cramps, temperature), medical attention is needed, sometimes emergency.
Dangerous conditions that require immediate action include salmonellosis. The infection quickly provokes dehydration and can cause toxic shock and death. If you have symptoms of salmonellosis (vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the lower abdomen, fever, foul-smelling stools of all shades of green), you need to call an ambulance. Before the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to give the patient sorbents orally and provide plenty of fluids. Do not hesitate in case of intestinal bleeding. This condition threatens human life. You need to promptly call an ambulance, explaining to the dispatcher the reason for the call. The patient should not be given anything until the doctors arrive. You need to lay it horizontally with a cushion under your head and cold on your stomach, this will reduce the bleeding.
Necessary research
If the pathology does not require emergency care, then you need to contact a specialist to determine its cause. The clinic will conduct a full clinical and laboratory examination, which includes:
- UAC and OAM.
- Blood chemistry.
- Bacterial culture of feces or vomit on nutrient media.
- Ultrasound, CG or MRI of the abdominal organs.
- ECG.
- Colonoscopy.
- FGDS.
- Determination of blood electrolytes.
The examination is prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis, so the list can be supplemented or shortened depending on the suspected pathology. In parallel with the examination, treatment is usually prescribed. If the patient is hospitalized in a hospital, then examination and treatment are carried out under the supervision and careful supervision of a doctor.
Treatment
Therapy for green stool depends on the cause of the pathology, its severity and the general condition of the patient. Salmonellosis, food poisoning, and acute intestinal infections require hospitalization in the infectious diseases department of a hospital. Bleeding - to surgery. Treatment is comprehensive and consists of:
- A diet with the exclusion of alcohol, which is prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis (fasting is one of the options).
- Antibiotic therapy with preliminary culture of feces or vomit on nutrient media to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial therapy. Before receiving the results, two antibiotics from different pharmacological groups are prescribed at once to ensure the widest possible spectrum of action on pathogenic microbes.
- Choleretic agents, which are designed to eliminate congestion in the biliary system of the liver (chophytol, allohol).
- Detoxifiers that remove toxins and waste from the body (Polysorb), antidiarrheal drugs (Smecta).
- Probiotics, prebiotics, symbiotics that restore normal intestinal microflora (atsipol).
- Droppers with saline solutions, glucose, plasma, stopping dehydration, restoring blood loss.
- Symptomatic remedies.
In severe cases, direct blood transfusion, plasmapheresis, hemodialysis and surgery are possible. Self-medication is unacceptable and can lead to the most dire consequences, including death.
Changes in the color of stool do not only occur in children. Green stool in adults is often a cause for concern; the reason for the change in color of stool depends on many factors.
Healthy stool has a well-shaped appearance and medium consistency. Normal feces are brown, brownish-yellowish, or light brown in color. Feces do not emit the smell of rot, decomposition or fermentation.
Treatment, what to do, how to treat green stool?
The diagnosis provides the basis for prescribing a course of treatment. Depending on the severity of the pathology, it can be either conservative or surgical. If a person’s stool has turned green, then treatment should be carried out only after determining the true cause of such a pathology. In any case, for treatment of digestive and intestinal problems to be effective, it must be based on an individual approach.
If the reason for the change in the color of stool to green is certain foods, no treatment is required, just balance your diet and in a few days you will forget about the problem. Coloring stool green while taking medications may be a reason to reconsider treatment tactics and replace medications with others. The decision in this case remains with the specialist.
Pathological abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs, which affect the color of stool, must be treated under the supervision of a specialized doctor, since most of such pathologies are quite dangerous and can lead to the development of serious complications.
When green stool is combined with high body temperature, stool upset and deterioration in general health, first aid can be provided to the patient independently. First of all, such a clinical picture can lead to dehydration, so the basis of treatment should be rehydration therapy. For this purpose, it is recommended that the patient be soldered with pharmaceutical glucose-saline solutions or their analogue prepared at home or boiled water, soap, granulated sugar and baking soda.
If infectious vomiting occurs, it is recommended to perform gastric lavage with a large volume of boiled water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate. In this case, it is advisable to adhere to a fasting diet for the first day. From the second day, it is allowed to eat light food, for example, rice porridge with water, baked apples or white bread crackers. It is forbidden to prescribe medications to yourself without consulting a specialist, since inept treatment can aggravate the course of the disease.
Reasons for the formation of green stool in adults
Green or marshy stool appears in adults for various reasons. These are physiological reasons when feces are colored by natural green dyes, chemical compounds found in vitamins and medications, food additives, foods, and food coloring. Pathological causes include diseases.
Products that change the color of stool
Many foods influence the composition of fecal excretions of adults and adolescents. After consuming them, green feces are formed; the reason for this coloring of excrement is chlorophyll. This group includes:
- green onion feather;
- parsley;
- wild garlic;
- green peas;
- green beans;
- dill;
- broccoli;
- spinach;
- blueberry, serviceberry, blueberry;
- sea kale.
Why don’t “green poop” appear in all healthy people who eat fresh vegetables, berries and seasonings? The reason lies in the different course of metabolic processes in the body. The amount eaten is also of great importance.
The more food rich in chlorophyll and bright green pigments, the more green appears in the stool. The stool may be green (or swamp-colored) after eating red fish, beef, horse meat, and beans.
Greenish, gray-green, dark green fecal discharge often appears in people on strict vegetable diets. The meal kits of strict vegetarians and people who eat only raw fruits and vegetables are also loaded with greens, causing the color of the feces to change. This is often observed among lovers of carbonated drinks and confectionery products colored with food pigments.
Food colorings
Natural food colors are made from natural plant pigments and obtained by synthesis. There are several dyes that give creams, pasta, candies, jellies, drinks, marmalades, ice cream and other products a greenish tint (color).
Consumption of foods colored with pigments and special nutrition for athletes is one of the reasons for the formation of greenish-colored stool. Fecal discharge, colored with pigments, may acquire a greenish-yellow tint; it may be yellow in color. Due to the synthetic pigment, which is poorly decomposed in the liver, the color of poop can be similar to the color of kiwi.
HELP: High-quality products and food dyes, which cause excrement with a greenish tint, do not change its consistency. There is no putrefactive or other fetid or unpleasant odor during bowel movements. The stool is moderately hard, thick, and formed.
Vitamins, dietary supplements and medicines
Manufacturers of medicines and supplements indicate in the instructions information about possible changes in the color of fecal matter when taking the drug. The list of drugs that cause greenish and green-black feces includes:
- drugs to combat iron deficiency anemia;
- vitamin complex products containing iron;
- medications to relieve constipation;
- iodine-containing drugs;
- biologically active food supplements containing iron, chlorophyll concentrate and iodine;
- seaweed food supplements;
- medications for the treatment of hyperacid gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers (Vicair, De-nol);
- antibiotics.
Diseases that cause green stool
If an adult does not eat food or dyes, and the stool turns greenish, this means that pathological processes are occurring in the body.
As a rule, other symptoms also manifest themselves with diseases. This means that the sick person requires treatment. The list of pathologies includes:
- Intestinal infectious diseases.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Poisoning (including the toxic effects of alcohol).
- Recovery period after poisoning.
- Lactose or fructose intolerance.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Colitis.
- Intestinal neoplasms (benign and malignant).
- Enteritis.
- Celiac disease.
- Inflammatory process in the intestines.
- Diseases of the thyroid and pancreas, gall bladder.
- Hepatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Individual reaction to the product.
For different diseases, stool has a different consistency, smell, color, and inclusions. The frequency of bowel movements will vary. The development of the disease is indicated by the increasing severity of the condition and the worsening of symptoms, and the rapidity of development of the disease. By the coloring of the discharge, one can first suspect the presence of a particular disease.
Green stool with liquid consistency
Liquid, green-colored feces occur with intestinal infections - salmonellosis and dysentery. These infectious diseases are accompanied by a number of painful symptoms. They begin quickly, from two to three hours to three days after bacteria enter the stomach, and lead to loss of water by the patient’s body.
Salmonellosis is often severe. Typical signs of the disease:
- diarrhea up to ten times a day;
- abdominal pain (in the navel area);
- high temperature (up to 38-40 degrees);
- nausea and vomiting.
Feces with salmonellosis are liquid, foamy and watery, green lumps with mucus are visible in the discharge. The fecal matter resembles swamp mud. The smell of feces is pungent and unpleasant. On the 3rd day, diarrhea with blood in the form of streaks begins, causing the pain to intensify. In some forms of the disease, in severe condition, a rash may appear, a decrease in blood pressure, and tachycardia, from which the patient’s condition sharply worsens.
Dysentery occurs with similar symptoms. With this disease, stool is frequent, but not very abundant. The stool is yellow-brown mixed with green, or dark green. The fecal matter contains streaks of red blood, a lot of mucus, and possible pus. With this disease, frequent ineffective urges, vomiting, and headaches are observed.
Liquid greenish stool is formed due to dysbacteriosis and enteritis. Similar feces are formed in some blood diseases.
Green thick stool and constipation
In some adults, stool changes color due to constipation. During this period, fecal discharge is difficult to pass; it resembles pellets and balls of green or gray color with greenery.
If the poop of infants turns green when changing their diet or introducing inappropriate complementary foods (due to the imperfection of the child’s digestive system), then in adults it is not easy to identify the cause of such changes. The patient needs to visit a local physician and gastroenterologist.
Before treating constipation, you need to undergo tests prescribed by your doctor. The cause of the malaise may be dysbacteriosis, taking medications that destroy bacterial flora, or constantly eating food colored with green pigments. A medical examination should not be postponed if constipation is accompanied by bloating, pain, or blood is visible in the feces.
Light green fecal matter
Light green excrement, brown feces “with greenery”, appears when taking certain antibacterial medications. It is not dangerous, but you should consult your doctor. The consistency of fecal discharge is thick and shaped. Due to the fact that the microflora dies, the excrement is almost odorless.
An alarming sign in this case is vomiting. If the patient has a fever or stomach pain, you should visit a doctor immediately.
Black and green chair
Dark, fairly well-formed stool occurs after taking activated carbon. But often black, black-green, dark green feces appear when there is bleeding in the walls of the intestines or stomach. The blood has time to clot by the time of defecation, as evidenced by the dark, almost black color of the feces.
The cause of bleeding is a burst vessel or neoplasm, which requires an immediate trip to the doctor, or even calling an ambulance. Intestinal bleeding is treated in the hospital.
Yellow-green stool
With pancreatitis, the stool is yellow-green or gray, it can be whitish or light yellow. Feces are liquid, they emit a pungent, fetid, nauseating odor. After defecation, feces are poorly washed off, the surface of the discharge is smooth and shiny.
There is a lot of plant fiber in the feces, and fatty inclusions are observed. Fats in them appear due to a lack of lipase (a digestive enzyme) that breaks down these compounds. The amount of fat in feces increases if the patient eats a lot of fat-containing foods.
Pathological causes
If the diet has not changed recently, but a person nevertheless notices a change in the color of the stool, the cause should be sought together with a gastroenterologist. You cannot do without emergency help in cases where green stool is accompanied by severe abdominal pain, stool upset, vomiting and hyperthermia. In such cases, you need to be prepared for hospitalization and treatment within the walls of a medical institution.
Attention. If a person has black-green stool, very dark greenish stool, and the color of the stool is not caused by food or medication, then there is a risk that these symptoms are signs of a serious illness. Such a condition can be very dangerous, so self-diagnosis and, even more so, self-medication can lead to tragic consequences. Gray-green stool in an adult or green stool after alcohol also does not mean anything good. If the stool has acquired a gray color with a green tint, then with this color of poop, if it lasts longer than 2 days, you can safely make an appointment with a doctor. If the stool does not become a normal color a few days after drinking alcohol, after 3, 4, 5 days, then this is also a good reason to consult a doctor.
Let's take a closer look at diseases, one of the symptoms of which is the coloring of stool in a green tint:
1 Crohn's disease is an inflammatory process in the intestine, accompanied by the formation of granulomas on its mucosa.
2 Infectious diseases that provoke the development of inflammation, for example, enterocolitis. Such ailments are often accompanied by bloody or mucous impurities in the stool.
3 Internal bleeding may change the color of stool. Minor hemorrhage in the upper digestive tract causes the stool to turn dark green. Heavy bleeding can lead to tar-black stool.
4 Individual intolerance to certain foods. In this case, the stool is not fully formed, contains pieces of undigested food and a large amount of mucus.
5 Erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach.
6 Rotavirus infection or the so-called intestinal flu is a rather dangerous disease that requires immediate hospitalization and symptomatic therapy aimed at correcting water and electrolyte balance, as well as stopping vomiting and diarrhea.
Thus, the combination of green stool with other warning symptoms may signal the development of a serious pathology, so it is necessary to immediately visit a specialist and undergo all the proposed examinations.
If the poop has become dark green in color, and the person has not eaten foods that could color the feces, then you should definitely seek help from a specialist doctor. Very dark and green stool, especially if it contains mucus, streaks of blood or pus, is a very dangerous symptom.
Green stool - what to do
The coloring of feces in an unusual color should alert you. But this is no reason to panic. Perhaps the reason was menu errors. Remember your diet in the previous two to three days. If the discharge is of normal consistency and you are feeling well, there will be no need to worry. After a couple of days, the intestines will restore the normal brown color of the feces.
If the cause of the color change is food poisoning, but the person feels quite healthy, it is recommended to buy over-the-counter medications at the pharmacy: activated carbon, Enterosgel. They are taken after cleansing the stomach with two to three liters of water, according to the instructions.
In the future, Regidron is indicated to suppress the gag reflex, normalize water-salt metabolism and restore intestinal function . To restore the microflora, you will need probiotics (Lactobacterin, Colibacterin, Bifikol or other drugs).
A gentle diet will help restore the body. Fatty foods (animal oil, lard), sausages, smoked foods, soda, bread, pastries, herbs, foods colored with pigments, and milk are removed from the diet.
The menu during the recovery period includes pureed vegetable soups, mashed potatoes and porridge cooked in water, jelly, herbal tea and compotes, yogurt, kefir. You can eat low-fat protein foods - lean fish, meat (pay attention to the amount of kcal).
When medical attention is needed
What should be done if the usual color of the stool is not restored? Of course, visit your local doctor without waiting for the body to cope on its own. What to tell the doctor? You need to say it like it is: “I don’t go to the toilet the way I always do, green, and I’m worried about my health.”
A visit to the clinic should not be postponed if changes in the color of excrement are accompanied by changes in blood pressure, lethargy, poor sleep, indigestion, fever, vomiting, and pain.
An extremely dangerous situation is when black-green feces are combined with severe weakness, chills, sweating, and vomiting with black masses. These are symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding. The patient needs to call the ambulance service, as the pathology can lead to serious consequences and even death.
The appearance of unusually colored stool is not always a sign of illness. Green shit often only speaks of errors in the diet. But this is a reason to carefully monitor your body so as not to miss the development of a serious pathology.
Gastroenterologist, PhD. Graduated from the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenov in 2010. Place of work - Medical