How to quickly help an adult with laryngospasm
In a child, breathing often recovers spontaneously, due to the peculiarities of age-related mechanisms of reflex regulation.
But you definitely need to call a pediatrician and start treatment.
If an attack of laryngeal spasm occurs in adults, without immediate medical intervention the person may die.
First aid for laryngospasm consists of the following:
Initially, place the person on a flat floor surface, this is necessary for possible subsequent resuscitation. Adults with laryngospasm should be asked to hold their breath for a few seconds so that the carbon dioxide accumulated inside the body triggers the mechanisms for relieving muscle cramps. During an attack, you can do a warm regime in the bathroom: fill a container with hot water, breathe in the steam for 5-10 minutes. Call an ambulance"
It is important to unfasten collars, bras, belts, remove tight elastic bands
During an attack, sometimes a person begins to get nervous, he is shaking from fear, it is necessary to immediately calm him down, mechanically remove convulsive reflexes: pinch, adults - prick with a pin or pull the tongue out of the mouth, press on its root to induce a vomiting reflex.
To relieve spasms, you need to give the person water, wet their forehead, temples, or sprinkle it on their face.
If any of the adults around you have an aerosol inhaler with Berodual or Salbutamol (fast-acting bronchodilators), you should try to take two breaths one after the other, followed by holding your breath.
In a situation of loss of consciousness in adults, you need to wave a cotton swab moistened with ammonia not far from the nose.
In case of cardiac arrest in adults, artificial respiration and indirect massage must be performed.
Further treatment is carried out exclusively by the doctor who came on call, since it is important to exclude the root cause of the occurrence and recurrence of laryngospasms. Usually in such cases, inhalations through a nebulizer using mineral water and saline are prescribed. In adults, inhalation treatment is carried out using drugs with combined anti-inflammatory, decongestant, antihistamine, antispasmodic action: Pulmicort, Berodual
In adults, inhalation treatment is carried out using drugs with combined anti-inflammatory, decongestant, antihistamine, antispasmodic action: Pulmicort, Berodual
Usually in such cases, inhalations through a nebulizer using mineral water and saline are prescribed. In adults, inhalation treatment is carried out using drugs with combined anti-inflammatory, decongestant, antihistamine, antispasmodic action: Pulmicort, Berodual.
In children, therapeutic treatment with Dexamethasone is prescribed.
If repeated attacks of laryngospasm occur quite often, and you live far from civilization, your doctor may recommend buying a laryngeal mask; its use will allow you to wait for the ambulance to arrive without much fear.
To prevent an attack, you can drink a cup of warm (38 degrees) milk, humidify the air in the room, and sit down for 10 minutes. into a bath with warm water diluted with soda solution. It is forbidden to spray aromatic substances near the patient, as well as to place mustard plasters.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of this condition should be aimed primarily at the mandatory elimination of the cause that caused it.
Since if the necessary medical measures are not provided in time, then death is possible.
It happens that an attack occurs after foreign objects penetrate into the lumen of the larynx, then they need to be urgently removed.
In this case, it is necessary to turn the child upside down and insert a finger into the mouth and remove the object. Treatment should be carried out and at the same time it is necessary to call an ambulance.
The child must be calmed down as quickly as possible, since children are predominantly in an excited state.
Be sure to provide access to fresh air, open windows, or take the victim out into the fresh air.
Moisten a cotton pad with a solution of ammonia and bring it close to the person’s nose to inhale ammonia vapor.
If the patient is conscious, give him something to drink.
You can resort to mechanical methods: patting the back, pinching a skin fold, causing a gag reflex, irritating the root of the tongue.
In the room where there is a patient with an attack of laryngospasm, be sure to provide air humidification. You can turn on a humidifier, or fill the bathtub with hot water and move the patient to the bathroom.
Dry air when inhaled can provoke the development of a second attack.
You can start treatment using a nebulizer. You can do inhalations with the following means:
- mineral water;
- saline solution.
You can also do treatment with inhaled medications:
- Pulmicort (hormonal agent);
- Adrenaline;
- Beroduala.
Inhalations using medications can only be done on the recommendation of a doctor.
In children, only Dexamethasone is used. The drug Dexamethasone is approved for use in children from the very first days.
Dexamethasone is used for laryngospasm to relieve swelling of the vocal cords, have an antiallergic effect, and an anti-inflammatory effect.
Dexamethasone is administered to the child as an intravenous or intramuscular injection. In this case, Dexamethasone must be dosed according to the weight of the children.
In severe cases, Dexamethasone is used for several days after the attack.
If the patient has asphyxia, then the parents urgently need to perform chest compressions and artificial respiration for the patient.
After discharge, children are under the supervision of a local pediatrician and an ENT doctor.
All children are at risk of developing a recurrence of the attack.
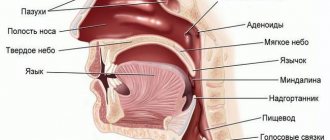
In childhood, when the baby’s systems and organs are not yet fully formed, there is a high risk of developing laryngospasm. This is the name for a disease during which involuntary contractile muscle movements begin. Because of them, partial or complete closure of the glottis occurs.
Manifestations of laryngospasm in children require emergency care, since an attack is caused by laryngospasm, which causes the baby to stop breathing, which leads to death.
How to behave as an adult during an attack of laryngospasm in children, what to do before the doctors arrive, and how to find out the pathology - questions to which you will find answers in our article.
What are the signs of laryngospasm
Regardless of the reasons that caused spasm of the laryngeal muscles in children, laryngospasm occurs in the same way and has the same symptoms.
The condition always has an acute development, all symptoms appear sharply against the background of well-being. There are no warning signs.
Laryngospasm in children has the following characteristic symptoms that occur in a child:
- the occurrence of sudden respiratory distress;
- in children, the head spontaneously tilts back, since in this position the maximum opening of the larynx is achieved;
- mouth opens;
- neck muscle tension is visible;
- during breathing, the patient can see retraction of the intercostal spaces (retraction of the intercostal spaces);
- when air passes through the narrowed lumen of the glottis, a whistle occurs;
- cyanotic coloration of the skin of the face appears, most pronounced in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- drops of cold sweat appear on the forehead.
If the lumen is reduced completely or the attack lasts a long time, the following symptoms may occur:
- consciousness is completely lost;
- convulsive twitching occurs in the arms and legs;
- presence of foam in the mouth;
- the patient urinates on himself;
- uncontrolled bowel movements occur;
- attacks of suffocation occur with prolonged laryngospasm.
Severe and prolonged attacks without timely help can be fatal.
Mostly short-term attacks of laryngospasms occur in children. It is also characteristic that after the restoration of normal lumen of the larynx and breathing, the child falls asleep.
In this case, the restoration of lost functions is necessarily accompanied by the fact that the child takes the deepest possible breath.
In a child, the amount of carbonic acid sharply increases and at the same time the receptor apparatus of the respiratory center is irritated, triggering the act of inhalation.
Children may have repeated attacks of spasms of the laryngeal muscles. When this condition develops, immediate assistance to the patient is required.
Possible complications
If laryngospasm occurs during colds of the respiratory system, then, as a rule, its attacks pass along with the disease. No cough - no attacks.
When the occurrence of laryngospasm is associated with more serious abnormalities (decreased immunity, metabolic disorders, nervous disorders), the elimination of the cause can often be delayed. This threatens to increase the frequency of attacks and increase their duration.
Against the background of frequently recurring laryngospasms, the most severe symptoms develop: loss of consciousness, accompanied by convulsions and incontinence. If the cause is not eliminated, the result can be tragic: asphyxia and death.
Main causes of seizures in children
Spasmophilia
This is a predisposition to the appearance of cramps, muscle twitching and spasms. As a rule, it is caused by a lack of vitamin D and calcium.
Main reasons:
- removal of the parathyroid glands;
- malignant neoplasms;
- diseases of infectious origin;
- nervous excitability;
- hemorrhage.
Allergic reaction
When an allergen or irritant enters the body, non-infectious inflammation of the larynx with spasm of its walls may develop.
The main provoking factors are as follows:
- animal hair;
- cosmetics;
- household chemicals;
- plant pollen, fluff;
- red fruits;
- chocolate;
- honey;
- milk products;
- some medications;
- industrial waste.
Reaction to anesthesia
Spasm of the laryngeal muscles can occur at the beginning of anesthesia, when cold ether vapors are inhaled. In this situation, it is assumed that laryngospasm occurs due to a high concentration of ether, irritation of the larynx with mucus, an endotracheal tube or food masses. Most often, spasm occurs when barbiturates are administered.
The surgeon's manipulations in reflexogenic zones (solar plexus, when pulling the mesentery or stomach) can also lead to reflex laryngospasm.
Extubation
This is the removal of the endotracheal tube after anesthesia, which is performed provided that the patient breathes normally on his own, that is, when consciousness and reflexes are restored. Laryngospasm is a complication of this procedure.
Laryngitis
This is an acute disease in which the patency of the larynx is impaired, which can result in respiratory failure. Spasm of the laryngeal muscles is one of the manifestations of this disease.
Laryngitis develops due to the following reasons:
- bacterial and viral infections;
- long stay in a dusty room;
- hypothermia.
Reflex spasm of the larynx
In children, reflex laryngospasm can occur against the background of the following conditions:
- artificial feeding;
- rickets;
- dropsy of the brain.
The main reason is increased neuromuscular excitability of the larynx. As a rule, a spasm is provoked by a psychogenic disorder and occurs under severe stress.
Epileptic seizure
During an attack, all muscles contract, including the laryngeal muscles. The spasm most often occurs when the focus of epileptic activity is located in the temporal lobe of the brain.
What it is?
Laryngospasm is a sudden contraction of the smooth muscles of the larynx. It develops more often in children, especially under 3 years of age, including in the first year of life.
This tendency in children is associated with the anatomical features of the structure of their respiratory tract - the lumen of the larynx is relatively narrower than in adults. In addition, children have a less stable nervous system, and muscle spasms may be associated with increased neuro-reflex excitability.
Here is a short list of possible predisposing factors:
- effect on the respiratory tract of irritating substances, dust, spraying;
- allergies, including Quincke's edema in the larynx;
- foreign body in the respiratory tract;
- laryngitis, possibly in combination with tracheitis, bronchitis and even pneumonia. In this case, laryngeal stenosis develops; we’ll talk about it separately;
- lack of vitamin D in the diet;
- spasmophilia;
- chorea;
- consequences of birth trauma, including hydrocephalus.
Treatment of laryngospasm along with tracheospasm of the throat
There are various methods, recipes, and drugs for eliminating attacks of laryngospasm in an adult. First, you need to provide emergency assistance. How to choose a cold powder and what types there are, read here.
How to relieve symptoms - first aid
The very first and most important measures to provide emergency care for laryngospasm in adults are as follows:
- It is necessary to place the person on a hard, flat surface.
- Facilitate easier access of air to the lungs by removing the top layer of clothing.
- Ensure the supply of fresh air and ventilation in the room in which the patient is located (ventilate the room).
- Eliminate possible irritants and create absolute silence.
- Influence the attack by sprinkling your face with water, inducing a gag reflex.
- Call emergency assistance.
Ambulance doctors will carry out the necessary measures for the victim, and it will consist of the following:
- Injection with calcium gluconate intravenously.
- The use of tracheotomy or intubation if all previous measures are ineffective.
- Performing chest compressions when the heart stops working.
- Carrying out oxygen therapy.
Drug treatment
When laryngospasm occurs due to a lack of calcium and vitamin D in the body, it is necessary to adjust the diet and follow a diet. In a situation with more frequent attacks, the use of warm baths and a solution of potassium bromide in oral doses helps to relieve exacerbation
It is important to remember that getting rid of laryngospasm in adults is monitored and adjusted by a doctor on an individual basis.
An effective way to counteract frequent attacks is inhalation using mineral water or pharmaceutical drugs prescribed by the doctor:
- Inhalation of ammonia vapors.
- Introduction of anticonvulsants into the body (chloral hydrate enema - 0.3-0.5 g per glass of water).
- In long-term cases, warm baths are used.
- Take a 0.5% solution of potassium bromide orally, a teaspoon twice a day (the doses of the listed drugs for children depend on age).
ethnoscience
You can eliminate attacks of laryngospasm using traditional medicine recipes. The main criterion when choosing products should be effectiveness and safety.
Inhalations
Frequent attacks of laryngospasm can be eliminated with the help of soda inhalations: add soda to hot water for procedures in the amount of 2 tablespoons per glass of boiling water. It is necessary to inhale the effective healing steam for at least 15 minutes; this method must be used for one month.
Tincture
Herbal wine tincture perfectly facilitates breathing and eliminates many causes of laryngospasm. To prepare it you need:
- Geranium herb.
- Thyme.
- Rosemary sprigs.
- Marian grass.
- Mint leaves.
- Grated ginger root.
- Ground red pepper.
- Red fortified wine (1 liter).
Mix all the herbs and pour warmed wine, leave for 2 days, strain and drink 50 ml before bed. The course is repeated with a break of a month.
Chamomile
Common and simple chamomile tea will strengthen the body and the nervous system in particular. For laryngospasm, it is recommended to brew the drink not in ordinary water, but in hot milk.
Pine resin
It is recommended to dissolve fresh pine resin in your mouth in the morning and evening. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. For an adult, the dosage should be 1 teaspoon. Resin can also be dissolved in warm milk and drunk every day at night.
Warm milk
Every evening the patient should drink warm milk with the addition of a spoonful of honey, cinnamon, nutmeg, cloves or propolis (according to his preference). Each of these components helps soften the respiratory tract and strengthen the body.
Laryngospasm in children - symptoms and emergency care for a child - ENT plus
A disease of the respiratory tract in children, which is accompanied by short attacks of suffocation, is called laryngospasm. With age, it can go away on its own, but still requires parents to take urgent measures to block spasms. Most often, children between 3 months and 2 years old suffer from them.
Laryngospasm in a child: emergency care, symptoms and algorithm of action
Diseases of the respiratory system are very common at any age. But laryngospasm is more common in young children due to the anatomical features of the larynx.
What is laryngospasm?
Laryngospasm is a sudden uncontrolled sharp contraction of the striated muscles of the larynx, occurring against the background of various pathologies of both the respiratory system and others (for example, with rickets, the nervous and skeletal systems are mainly affected).
Causes in children
The development of laryngospasm can be triggered by various reasons.
The main reasons include:
- Low level of calcium ions in the child’s body;
- Reduced immune reactivity of the body;
- Injuries during childbirth;
- Entry of a foreign body into the trachea/larynx (designer part, toys, pen cap, etc.);
- Violation of metabolic processes in the body;
- Developmental anomalies of the trachea, larynx, bronchi;
- Use in the form of medicines - adrenaline, for vasoconstrictor purposes;
- Chorea;
- Stress;
- Sudden joy;
- Spasmophilia;
- Rickets;
- Bronchopneumonia.
- Laryngospasm in children can develop during fright due to a stressful situation, during hysterical crying or laughter, or during a strong cough reflex.
Who is at risk?
At risk are:
- Premature babies;
- Children with developmental delays;
- Children whose breastfeeding has been replaced with unadapted infant formula from the first days of life;
- Children with birth injuries;
- Hyperactive children;
- Children with allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, etc.);
- Children exposed to stress (in children's groups, families);
- Children with pathologies of the digestive tract (malabsorption syndrome in the intestine);
- Poor nutrition, in which an insufficient amount of calcium enters the body with food and an insufficient amount of vitamins.
- Children who have not received rickets prophylaxis.
Important! Vitamin D3 deficiency in rickets leads to impaired calcium absorption, resulting in very little calcium in the child’s body. Low calcium levels provoke excessive synthesis of parathyroid hormone, which leads to even greater leaching of calcium
Calcium deficiency leads to the development of convulsive syndrome and laryngospasm.
Signs of laryngospasm in a child
Laryngospasm occurs in children under 2 years of age. The first sign of laryngospasm is a heavy, loud breath that sounds like noise. Inhalation resembles a wheezing whistling sound. This causes blueness of the skin and the area around the mouth (blue lips), and tension in the neck muscles. The child's head is thrown back. The reaction of the pupils to light often disappears.
As the symptoms progress, the symptoms intensify and the following signs can already be noticed:
- The child's mouth is open very wide, he greedily gasps for air;
- The level of sweating increases (beads of sweat appear on the forehead and in the armpits, and over time the whole body begins to sweat);
- The heart rate increases, the heartbeat can be heard without a phonendoscope, the pulse becomes threadlike (barely palpable);
Immediate Assistance Plan
At the first signs of laryngospasm in a child, it is important not to panic, call an ambulance, and before it arrives, try to help him on your own. What can you do?
- Make sure that no foreign object enters the respiratory tract. If you find that the airways are blocked by a foreign body, then try to reach it with your hands. If all else fails, turn it upside down. You can also press on the solar plexus using pushing movements, the child will start coughing, as a result of which the object will come out.
- Provide access to fresh oxygen (open a window, take the patient out to the balcony, turn on the air conditioner or fan, unbutton the collar or undress).
- It is very important to reassure the child, as his anxiety further increases the narrowing of the ligaments.
- Take a cotton swab soaked in ammonia and bring it to the patient’s nose. This will bring him to his senses.
- Distraction therapy is also effective - it helps relieve spasm. This can be done by lightly pinching. You can also pull on the tongue or press on the root of the tongue to trigger the gag reflex.
- Place a damp cloth or towel over your baby's face to moisturize and soften the dry environment.
- You can give it a little drink and moisten your face with cool water.
- Taking a warm (but not hot) bath also helps relieve spasms.
- If the child can understand the requests, then ask him to hold his breath, and then begin to breathe slowly and calmly.
When parents are aware that their child is prone to laryngeal spasms, they will need to purchase a nebulizer for inhalation with alkaline water, soda solution, or Pulmicort suspension. This is a great way to relieve choking.
First aid for laryngospasm in children - how to relieve a child at home
There are diseases that are not truly dangerous for adults, but in children, if events develop negatively, they can even threaten life. One of these diseases is laryngospasm. And if for middle-aged children it already poses a danger, then for infants it is a critical phenomenon that leads to the death of babies.
Definition of disease
Laryngospasm is a very sharp contraction of the muscles in the throat area that occurs involuntarily. As a result, quite severe shortness of breath begins with the closing of the gap.
Although many categories of children are at risk when the problem occurs, the highest mortality rate with this approach occurs before about one year of age.
Possible complications
Complications may vary depending on how severe the disease is.
In particular, in the initial stages, the child may experience convulsions, may foam at the mouth, and may lose consciousness.
At the same time, the work of the heart may weaken, the muscles may begin to spontaneously relax and, conversely, contract (this can, among other things, lead to uncontrolled urination or defecation).
If the attacks continue, if they increase their duration, then everything can lead to asphyxia and, as a consequence, the death of the child, therefore you need to react as quickly as possible and quickly take measures to eliminate the problem.
Medication method
Drug treatment for babies may vary depending on their age. If these are newborns, then you must resort only to suspensions, but if these are children over two years old, then you need to use tablets and drops of the appropriate type.
No-spa for laryngospasm in children
The use of medications depends on the nature of the disease. In general, the use of no-shpa or salbutamol is recommended to reduce spasm. If the nature of the disease is allergic or asthmatic, then dexamethasone is used. It helps to relax the bronchi well and ensure stable air circulation.
Some parents believe that prednisolone is a good drug choice, but this is not entirely true. Although this is a fairly powerful anti-spasm drug, it has a number of side effects that may affect children. It is recommended that it be given only to adults.
conclusions
Laryngospasm is not just a minor nuisance, it is a real problem that leads to a serious danger not only to the health, but also to the life of the baby.
Therefore, it is so important that all necessary measures to eliminate the problem are taken as quickly as possible so that no critical situations are created. As soon as you have the first suspicion of laryngospasm, immediately contact a doctor who will tell you what to do to protect your baby
As soon as you have the first suspicion of laryngospasm, immediately contact a doctor who will tell you what to do to protect your baby.
Symptoms
- sudden sharp change in breathing;
- throwing the head back (as if the child is trying to grab more air);
- mouth open;
- connecting additional muscles to breathing;
- neck muscle tension;
- a whistle is heard from the chest due to the narrowing of the laryngeal muscles;
- pale skin;
- cyanosis on the face (most strongly observed around the nasolabial triangle);
- cold sweat;
- loss of consciousness (during severe cases);
- cramps of the arms and legs;
- foam at mouth;
- incontinence, sudden embarrassment (walking) under oneself;
- the duration of the attack is several minutes;
- the child quickly falls asleep when breathing is restored;
- asphyxia - in the most severe cases.
Symptoms
The very first manifestation of progressive laryngospasm is noisy and quite difficult inhalation. Against the background of this symptom, cyanosis of the skin forms (especially in the lip area), due to which the neck muscles become tense.
Symptoms during attacks:
- The patient's mouth is constantly open quite wide.
- There is increased sweating.
- The pulse appears thread-like in nature.
- Due to the rapid increase in carbon dioxide levels in the body, the respiratory center is irritated, and the respiratory function itself comes to a stable state.
When laryngospasm becomes severe, the following symptoms are added in addition to the main clinical picture:
- Fainting.
- Convulsive syndrome spreading throughout the entire muscular skeleton.
- There is a discharge of foam from the mouth.
- The Patient may experience involuntary bowel and bladder emptying.
- Cessation of cardiac activity.
Laryngospasm in adults is quite specific. Hysterical laryngospasm is characterized by its simultaneous occurrence with convulsions of the pharynx, esophagus, and limbs. In patients with hysteria and other neuroses, laryngospasm may manifest itself when a laryngeal speculum is inserted into the pharynx, but such an attack quickly passes by itself.
Sometimes the attack is similar to epilepsy. In less serious cases, laryngospasm may be limited to a short-term narrowing of the glottis, prolonged inhalation with a characteristic whistle, pale or blue discoloration, noisy inhalation, or short-term shortness of breath, sobbing.
Acute stenosing larinotracheitis
Laryngospasm can occur in conjunction with tracheospasm, when the smooth muscles of the posterior membranous part of the trachea simultaneously contract.
The nature of the pathology
Contraction of the laryngeal muscles can occur in an adult or a child. Children suffer from this disease until they reach 2 years of age. The development of laryngospasm is caused by a sharp swelling that closes the throat slit.
There are no prerequisites for such an attack. With all the surrounding prosperity, it can turn bad at any moment.
Several factors can provoke it. As for children, those most often affected are those who are bottle-fed. Common causes of development may be:
- Metabolic disorders
- Hormonal disbalance
- Viral infection
- Spasmophilia
- Bronchopneumonia
- Diseases of the pharynx or trachea
Allergic reactions, affecting the laryngeal nerve, dust or smoke in the inhaled air, medications, as well as severe anxiety or stress can lead to muscle irritation.
It can happen during coughing attacks, hysteria, loud laughter or sudden fear. Children suffering from rickets are also susceptible to this kind of phenomenon.
The child develops much faster, since she is surrounded by soft and delicate tissues that are well supplied with blood. A child's glottis and its muscles become irritated much more quickly from any effort.
The photo shows the symptoms of laryngospasm
What to do first
The emergency action algorithm for laryngospasm in children includes a number of measures aimed at restoring normal patency of the upper respiratory tract and normalizing the psycho-emotional state of the baby.
This is where the range of acceptable first aid measures ends. All other interventions and use of medications can only be carried out by medical personnel. In most cases, a doctor comes to calls due to laryngospasm.
If the symptoms of laryngospasm appeared in an adult, then this occurred against the background of an upper respiratory tract disease. Most cases occur with a moderate degree of laryngeal spasm, so to provide emergency assistance it will be enough to go to an ambulance and drink a soda solution at home.
Emergency care for laryngospasm - actions to alleviate the condition
05/31/2018 Laryngospasm is a pathological condition that can manifest itself under the influence of various negative factors and diseases.
Laryngospasm is a condition in which there is a spasm of the tone of the smooth muscles of the larynx, as well as slight swelling of its mucous membrane. This leads to partial or complete closure of the gap.
This pathology can develop in children and adults, but it is most common in childhood. Emergency care for laryngospasm can save the lives of loved ones or others if carried out correctly.
Surgery
If the ongoing drug therapy does not produce results or the severity of the attack requires more radical measures, surgical intervention is required. For laryngospasm, 2 types of surgery are performed:
- Tracheal intubation
- Tracheotomy
In the first case, the child is provided with air flow through the introduction of a special tube through which oxygen enters the lungs and breathing is restored. The second type of operation is performed only when the patient is hospitalized. Under anesthesia, the trachea is dissected to provide air flow. The further treatment and recovery regimen depends on the root cause of the attack and the presence of contraindications in the child.