What is diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis is irritation of the baby’s skin, accompanied by redness (hyperemia), itching, inflammation of the affected areas due to prolonged contact with a wet diaper or diaper, urine or feces, or improper care of the newborn’s delicate skin.
Absolutely all newborns and toddlers who actively use diapers are susceptible to diaper dermatitis. According to statistics, about 60% of young children suffer from this seemingly mild disease, which is scary for its complications, especially for newborns.
Diaper dermatitis in newborns is a phenomenon that almost every new parent has encountered.
Human skin is its largest organ, which is the primary barrier to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses into the body.
Children's skin is thin, they do not actively participate in the body's immunity precisely because of its imperfection, and sometimes they cause the development of serious diseases associated with diaper dermatitis, due to its high traumatism and vulnerability.
Types of diaper dermatitis
There is no generally accepted classification of the types of diaper dermatitis, so most often when determining its types, they rely on its localization and the factors that caused its occurrence.
Types of diaper dermatitis by localization:
- Perianal. Affects the child's anal area. The main reasons for its appearance are considered to be a change in the acidity of the stool, the introduction of complementary foods, and prolonged diarrhea. It may manifest itself as slight redness of the skin with pronounced bright red erythema, with papular and pustular lesions. If treated incorrectly, high skin ulceration occurs.
Types of diaper dermatitis depend on its location and associated complications
- Genital dermatitis has a clear localization and affects girls to a greater extent due to physiological characteristics. Its development is influenced by the composition of urine.
- Intertrigo is diaper dermatitis, which is caused by friction of skin on skin, usually the inguinal and buttock folds, contact with feces or urine, which, due to their aggressive composition, corrode the injured skin.
- Edge dermatitis, or chafing, occurs where the edges of the diaper touch the skin. With timely treatment, it goes away quite quickly without complications.
Factorial types of diaper dermatitis:
- Candidal dermatitis is characterized by the involvement of a secondary infection in the form of Candida fungi in the disease process. In a healthy state, the skin can easily repel the attacks of a fungal infection.
Normally, a certain amount of fungi of this family is present on the human body and mucous membranes, but with a decrease in immunity and a violation of the integrity of the skin, the fungus multiplies quickly. In addition, the area under the diaper has excellent conditions (humidity and temperature) for their lightning-fast reproduction.
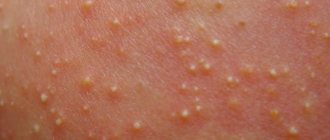
Rashes with candidal dermatitis have a bright red tint, with raised edges, there are single or group pustules, the skin is moist and weeping. In addition to the typical area of rashes, they can spread to other areas of the body.
- Impetigo is a diaper dermatitis caused by coccal infections that multiply in the baby's groin area in the diaper area. It can be bullous (accompanied by the appearance of blisters) and non-bullous (characterized by the presence of red scars with yellow crusts). Localized in the abdomen, thighs and groin.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by a bright red rash with a yellow crust on top. A distinctive feature is the pronounced oily sheen of the rash due to increased sebum production.
- Atopic dermatitis can occur in all areas of the body, including the diaper area. It is a papular scaly rash with jagged edges, which is accompanied by severe itching.
To establish the exact subtype of diaper dermatitis, a visual examination of the child is sufficient. If the treatment is not effective, then a smear is taken for microflora from the affected area.
Classification
In the International Classification of Diseases, diaper dermatitis is assigned a code - ICD 10 .
Depending on the location of the rash, the following subtypes are distinguished:
- Dermatitis in the area of the cervical folds: forms after regular regurgitation of food masses. Once they get under the diaper, they actively irritate the skin.
- Dermatitis around the anus (perianal). The irritating effect is exerted by the enzymatic activity of feces and the infant’s nutritional habits: artificial feeding, introduction of the first complementary foods.
- Dermatitis in the area of the inguinal folds.
- Isolated dermatitis of the genital organs (the cause of development can only be determined by conducting a detailed urine test).
Depending on the type of damage, there are three main forms of the disease: abrasions, marginal dermatitis and intertrigo.
When abraded, the skin of newborns turns red and is injured only at the point of contact with the diaper. Once the source of damage is eliminated, the symptoms go away on their own. Edge diaper dermatitis is clinically similar to the form described above, but the rash appears around the perimeter of the chafing edges of the diaper. With intertrigo, the skin in the deep folds of the groin and thighs becomes slightly red.
A much less common form of dermatitis is seborrheic. The rash is characterized by a bright red color and is covered with yellowish scales. The skin under the diaper is first affected, and then the redness spreads to other areas of the body.
There is also a type of disease called impetigo (staphylococcal dermatitis). Affects the groin and buttocks area. It is divided into two subtypes: bullous (accompanied by the formation of blisters), non-bullous (resembles crusty scars).
Stages and degrees of diaper dermatitis
Film dermatitis in newborns suggests its different manifestations at certain stages.
Diaper dermatitis has 3 stages:
- loss of the stratum corneum of the dermis of its protective role due to maceration, friction, exposure to the skin of urine, feces, change in the PH of the skin to alkaline;
- loss of the barrier functions of the epidermis due to the addition of pathogenic microorganisms and fungi to the primary symptoms, for example, after infection with candidal dermatitis, after 72 hours the fungus is detected inside the body;
- normalization of the condition of the epidermis after drug or therapeutic treatment.
Diaper dermatitis in newborns very quickly passes from one stage to another due to the addition of staphylococcal infection and Candida type fungi to the initial symptoms.
In this regard, diaper dermatitis has varying degrees of disease:
- A mild degree of the disease is characterized by slight redness and a mild rash in the form of spots and pimples. The localization of the rash is limited, most often it is located in the perineum, buttocks and upper thighs. At this stage, it is important to start treatment, then the symptoms will disappear after 2 to 3 days without a trace.
- Medium degree - redness becomes brighter, rashes become more varied. In addition to increasing the area of the rash, papules with purulent contents may form, and areas of skin with an erosive surface may appear, which increases the likelihood of a secondary infection.
- A severe degree is characterized by the addition of a secondary infection, while the redness of the skin has a persistent red or purple color, the affected areas swell, become wet (exudate) and become covered with ulcers to a greater extent. The child may have a fever and loss of appetite.
Parents of a newborn child should closely monitor his condition and mood. During times of illness or discomfort, children become especially whiny and capricious. When a child’s behavior changes, it is necessary to exclude all possible causes, including diaper dermatitis.
Symptoms
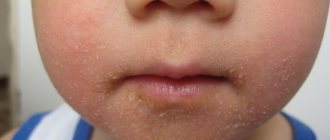
The main sign of the disease is redness of the skin in the groin, buttocks, and thighs. Areas of skin that regularly come into contact with diapers may become blistered and peeling. At an advanced stage, pustules and swelling form. When consuming artificial mixtures, an alkaline reaction appears in the stool, which increases the likelihood of irritation around the anus.
The process of diaper dermatitis is characterized by an alternating nature. The intensity of symptoms increases with changes in diet, lack of hygiene, and increased humidity levels.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, there are three degrees of severity of diaper dermatitis:
- Mild degree. Moderate redness of the skin, rare rashes, and peeling are noted.
- Average degree. Erosions and papules appear. Infiltrate accumulates between the folds. There is a risk of secondary infection.
- Severe degree. The newborn has rashes in the form of blisters filled with serous fluid. Erosion and infiltrates form. Quickly spreads to other parts of the body.
In some cases, diaper dermatitis indicates the development of concomitant diseases.
If there is an elevated temperature, purulent scars, swelling and cyanosis of the baby’s skin, it is necessary to show it to a pediatrician. It is also necessary to consult with a specialist in cases where long-term home treatment does not help get rid of symptoms.
Symptoms of diaper dermatitis
The main symptoms of diaper dermatitis in infants are severe redness and disruption of the integrity of the epidermis in the diaper area - buttock, thigh, groin. Redness may be accompanied by a rash, single or group papules, the skin peels or, on the contrary, gets wet.
Localization of inflammation - inguinal folds, surface of the buttocks, anal area, inner thighs. That is, those places where the skin can come into contact with disposable and reusable diapers.
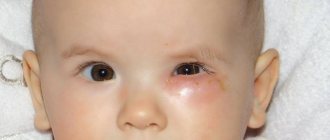
If such inflammation was found in other parts of the baby’s body, then the cause should be sought in another disease, since diaper dermatitis does not occur except in the groin and buttock areas. Diaper dermatitis is characterized by red, almost purple, large spots without clear contours or boundaries.
Side symptoms of diaper dermatitis are manifested in the child’s capriciousness, burning (the child cries) before or after urination, decreased appetite, lethargy, and increased temperature in severe cases of the disease. Hospitalization for diaper dermatitis is not required.
Treatment
Therapy for diaper rash is carried out in a comprehensive manner using various medical and folk remedies. Strict adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician is also required.
Therapeutic
In addition to drug treatment, parents must create favorable conditions for successful recovery from pathology. The main rule is personal hygiene: you need to bathe your baby every day and change diapers regularly.
It is also important to monitor your child's nutrition. If complementary foods are already being introduced into the diet, then this must be done with extreme caution. If the baby is bottle-fed, you need to carefully select the formula to avoid a negative reaction from the body.
Medication
Before treating diaper dermatitis with any means, you need to perform a number of important steps:
- Rinse the baby's genitals and buttocks well with warm water.
- Use hypoallergenic soap as a hygiene product.
- Dry the skin, but under no circumstances rub the skin with a towel, just pat dry.
- Take an air bath by wiping the affected area with a cotton swab soaked in a decoction of chamomile or string.
- Apply the medication prescribed by your doctor to dry skin.
Which medicine to use is decided by the attending physician, depending on the cause of diaper dermatitis.
Creams and ointments
If weeping lesions occur in the folds of the skin, it is recommended to use products containing zinc. These include ointments for diaper dermatitis such as Sudocrem, Tsindol cream, and Zinc ointment. Thanks to the presence of this element in the composition, local medications dry out the skin, suppress the inflammatory process, and relieve swelling.
To combat diaper rash, young mothers are advised to purchase Pantestin gel. It will help destroy pathogenic microorganisms and cure inflammation. The creams “D-Panthenol” and “Bepanten” have also proven themselves well: they allow the epidermis to recover faster and cope with the pathological process.
Another effective cream for treating skin with diaper disease is “Drapolen”. It softens the epidermis, kills germs, and accelerates healing. To dry and soften the skin, you can use Biolan ointment, which includes panthenol and zinc oxide.
When fungal diaper dermatitis develops, treatment is carried out using antifungal local medications.
Powders
To dry wet lesions with diaper dermatitis, it is recommended to use special baby powders. They can be found in any children's store or pharmacy. Products should not contain dyes, flavors or other harmful components.
The following brands of powder for diaper dermatitis and diaper rash are very popular among young mothers: “JOHNSON`s BABY”, “Mir Detstva”, “Baneotsin”, “Karapuz”. They are hypoallergenic and ideally dry the skin of newborns.
Causes of diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis in newborns is a multifactorial disease, the main causes of which include:
1. Physical factor:
- rare diaper changes;
- non-compliance with the temperature regime, overheating of the child;
Failure to observe hygiene, including intimate hygiene, in newborns provokes diaper dermatitis
- failure to comply with hygiene standards;
- An incorrectly selected diaper size contributes to skin chafing.
Physical factors only trigger the disease process, then chemical and biological factors influence the affected areas.
2. Chemical factor:
- skin irritation from the child’s waste products;
- change in PH of feces due to dysbacteriosis or prolonged diarrhea;
- lack of vitamins in the child’s diet - zinc, biotin and B vitamins.
3. Biological factor:
- infection of microtraumas with fungal and streptococcal infections;
- rarely congenital or acquired allergic reactions and diseases.
Diagnosis of diaper dermatitis
If the child’s parents or staff suspect that the baby has diaper dermatitis, then there is no delay in making a diagnosis.
Diaper dermatitis in a newborn, as a diagnosis, is established based on a visual examination of the child’s skin, a survey of parents and the general clinical picture.
If the doctor suspects the addition of a secondary infection, then additional tests are necessary:
- General blood analysis. Taking capillary blood from a finger to determine the general condition of the child and his ability to resist infections, as well as identifying the inflammatory process.
- Bacteriological seeding of material from injured areas of the skin to identify the causative agent of infection. Laboratory assistants remove particles of the epidermis from the most affected areas and place them in a nutrient medium to identify pathogenic organisms. Tank seeding makes it possible to accurately identify the pathogen and select antibiotics to suppress or destroy it.
- Stool analysis to determine pH and exclude dysbacteriosis.
All 3 analyzes are considered in combination; each individually cannot give a complete picture of the course of the child’s illness. The collection of material and its analysis can be carried out in a children's clinic.
When to see a doctor
Parents of a child can diagnose diaper dermatitis on their own - just pay closer attention to the folds of skin in the groin area and monitor the baby’s mood, sleep and appetite.
You should contact your pediatrician if symptoms of diaper dermatitis worsen.
But still, no one is immune from the occurrence of diaper dermatitis. At the initial stage, when the disease is mild, parents can cope on their own by following the ABCDE method.
If the symptoms of the disease have not disappeared after 3 days and its progress is observed, then you must immediately contact your doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis, exclude secondary infection, prevent complications and prescribe adequate treatment.
Only a pediatrician, based on his knowledge and experience, can and has the right to prescribe medication to a child. It is not permissible to prescribe medications to a child and treat him with them yourself, as this can cause the death of the baby or cause irreparable harm to his health.
Symptoms
Diaper dermatitis occurs in areas of skin contact with feces and urine - buttocks, genitals. What does this type of dermatitis look like? At the initial stage, redness, blisters, and peeling appear on the skin. If the pathology is left unattended, the blisters can turn into ulcers with pus, spread to the back and abdomen, and severe swelling appears.
Signs of diaper dermatitis:
- the rash does not go away for more than 4 days, has a clear border, peeling layers of the epidermis are visible;
- the baby becomes restless, constantly reaching for the diaper, trying to take it off;
- Often the disease occurs when new foods are introduced into the child’s diet.
Important! A distinctive feature of ordinary diaper dermatitis from other types (candidiasis, seborrheic, atopic) is that with this type of dermatitis the folds of the skin are almost never affected.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of an external examination, the results of a clinical blood test, and a stool test for dysbacteriosis to determine the specific type of pathogen.
When is it necessary to urgently take your child to the doctor? Sometimes diaper dermatitis can be a symptom of serious pathologies. Urgent medical attention is needed if the baby has a fever, the rash turns purple-blue, or the child has purulent discharge and ulcers.
Prevention of diaper dermatitis
The best treatment for a disease is its prevention or prevention.
The most effective system for preventing diaper dermatitis is called ABCDE, from the first letters of the English words:
- Air - air. Regular air baths help reduce the time of contact of the baby’s skin with the diaper and rubbing parts, as well as normalize the temperature of the skin.
- Barrier - barrier. Pediatricians around the world recommend using barrier methods with every diaper change. Zinc oxide or petroleum jelly, which are included in creams and pastes, create a barrier to moisture entering the baby's skin during urination or bowel movements.
In addition, such creams do not interfere with the healing of already affected areas of the skin and contribute to the regression of skin rashes. Creams and pastes should be applied in a sufficient layer to the surface of those areas that come into contact with the diaper or where the impact of waste products on them is greatest.
- Cleansing - cleansing. Cleansing the baby's skin should be done after every diaper change or bowel movement. Particular attention should be paid to the folds of the groin area and gluteal folds. Pediatricians do not recommend using soap every time you wash your face, as it greatly dries the skin, causing microcracks, and therefore injury to the epidermis.
Warm water is enough to effectively cleanse the skin. To control, you can use wet wipes without alcohol or fragrances. After water procedures, the diaper area must be thoroughly blotted with a well-absorbing cloth or special small towels for the child’s groin area.
Diapers should be selected according to the age and weight of the baby - this will help avoid the occurrence of diaper dermatitis
- Diapering - changing a diaper. Timely diaper change is one of the most important points in the prevention of diaper dermatitis. The child should not wear a diaper for more than 3 hours, even if it seems dry to the mother, during the day, and at night there should be at least one change.
When a baby defecates, the diaper should be changed immediately. Wearing disposable diapers does not prevent diaper dermatitis, at least this theory has not yet been proven by scientists, but one cannot deny their high absorbent properties, due to which the time of skin contact with the baby’s waste products is significantly reduced.
- Education – training. Parents and caregivers in hospitals and other institutions should be informed about the care of the baby's skin in the diaper area.
Ensure that it is changed as quickly as possible and that special barrier creams and pastes are applied. If possible, ensure that the child stays without a diaper for as long as possible - taking air baths.
With proper skin care in the diaper area, the clinical manifestations of diaper dermatitis regress on the 3rd day.
If there is no positive effect during therapeutic treatment or if the treatment is protracted, it is recommended to resort to the use of medications, especially if a secondary fungal or bacterial infection is associated.
Causes
The main cause of diaper dermatitis is prolonged skin contact with a wet diaper. Urine does not evaporate; inflammation begins against the background of the skin being exposed to uric acid and other substances that are part of urine and feces. The simultaneous impact of urine and feces on the skin is also important - this leads to an increased damaging effect.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of film dermatitis:
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- allergic reaction to detergents and chemical products;
- individual intolerance to children's cosmetics;
- poor quality diapers that do not allow air to pass through;
- concomitant pathologies, diathesis;
- incorrect diaper size, and, as a result, mechanical friction of the skin;
- contact with microbes.
Candidiasis diaper dermatitis occurs in children as a result of skin damage by fungi of the genus Candida after antibacterial therapy; it often occurs in babies who are bottle-fed.
The cause of the disease can be some features of the body - atopic predisposition, high ammonia content in the urine, weak immunity, diarrhea.
Important! Many people think that diaper irritation occurs, but in fact, high-quality diapers can significantly reduce the incidence of the disease and the degree of its manifestation.
Treatment methods for diaper dermatitis
Treatment methods for diaper dermatitis in newborns and children of the first year of life are divided into medicinal and therapeutic:
- Therapeutic methods include the prevention of diaper dermatitis, hygiene and proper care of the baby's skin under the diaper, including regular air baths.
- Drug treatment is prescribed by the attending physician after diagnosing the disease, as well as when a secondary infection has occurred or the child has a weak immune response to the ongoing disease.
Medications
The most important factors when choosing a drug for the treatment of diaper dermatitis with secondary infections is the identification of their causative agent, usually Candida fungi, staphylococcal and streptococcal infections.
Based on the diagnosis, the pediatrician prescribes antimicrobial or antifungal drugs along with ointments for the speedy regeneration of the damaged epidermis. In addition, in order to reduce itching and swelling of the skin, the pediatrician may prescribe antihistamines.
| Purpose of the drug | Name, release form | price, rub. | Application | Course duration, days |
| Antifungal drugs | Nystatin, ointment | from 49 rub. | Apply to affected areas 1 - 2 times. /d. | 7 — 14 |
| Clotrimazole 1%, cream | from 57 rub. | 10 -14 | ||
| Pimafucin 1%, cream | from 187 rub. | 7 — 11 | ||
| Sertamicol 2%, cream | from 402 rub. | 5 — 7 | ||
| Antimicrobials | Mupirocin 2% (supirocin), ointment | from 562 rub. | Apply to affected areas 2 - 3 times. /d. | 10 |
| Fusidic acid 2% (fusiderm), cream | from 327 rub. | 7 — 10 | ||
| Antihistamines | Finistil, drops | from 327 rub. | The daily dosage is calculated by the pediatrician taking into account the child’s weight. The daily dosage is divided into 3 doses. Taken as prescribed by a doctor under his supervision. | |
| Zyrtec, drops | from 220 rub. | |||
| Zodak, drops | from 199 rub. | |||
| Wound healing, anti-inflammatory, emollient drugs | D-Patnenol, ointment | from 168 rub. | Apply after each diaper change, linen change or water procedure to the affected areas of the skin. | Daily |
| Bepanten, ointment | from 438 rub. | |||
| Drapolene, cream | from 293 rub. | |||
Traditional methods
Traditional methods are advisable to use for minor redness, at the initial stage of diaper dermatitis or as a preventive measure.
To do this, decoctions of string, chamomile flowers, which have an anti-inflammatory effect, or oak bark, which contains tannins that dry out the skin, are added to the bath.
Bathing your baby in medicinal herbs will help prevent diaper rash
To prepare the infusion, you need to take 2 tbsp. l. dry raw materials (grass, flowers, bark), pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for 30 seconds. Then strain and add the broth to the bathtub.
Other methods
During an acute illness with complications, it is not recommended to wash a child with hygiene products containing alkalis (they dry out the skin), or to use wet wipes, especially those containing alcohol. These remedies will not reduce inflammation and irritation, but will only cause pain to the baby.
To treat affected areas after urination or defecation, doctors recommend using a weak pinkish solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) or a pharmaceutical solution of furatsilin.
A weak (!) solution of potassium permanganate is used to treat damaged baby skin
Preparation of potassium permanganate solution:
- powder (2 - 3 grains) is diluted in 50 ml of warm water in a separate container;
- after the grains are completely dissolved, 2/3 of the concentrate is carefully poured into the bathing container until a faint pink tint is obtained, it is important to ensure that undissolved grains do not get into the child’s water, this can cause a serious chemical burn;
- the remainder of the concentrate is disposed of.
Possible complications
The main complications of diaper dermatitis occur when the affected skin becomes infected.
If untimely or improperly treated, the infection can penetrate into the deep layers of the skin and cause:
- abscess - purulent inflammation of tissues caused by their “melting” and the formation of a purulent cavity;
- infiltrate – concentration in the tissues of cellular organisms mixed with blood and lymph;
- candidal or fungal dermatitis;
- impetigo.
Diaper dermatitis in newborns and young children should not be taken too lightly.
Due to a weak immune response, the course of the disease may progress too quickly, causing serious complications.
Secondary infections with diaper dermatitis are especially dangerous.
They are responsible for the deterioration of the child’s quality of life and long-term health problems, weakening of the immune system.
Therefore, if the child’s parents are unable to cope with the symptoms of diaper dermatitis on their own, or the treatment is sluggish and not productive, and the disease has frequent intervals, then you should immediately contact a pediatrician for additional research and adequate treatment.
Article design: Natalie Podolskaya
Cosmetic preparations for illness
If the disease has become serious or is difficult to treat with air therapy alone, Komarovsky urges parents to consult a pediatrician. The doctor will select external medications that will relieve the child of the disease in a short time.
Medicines that can cure diaper dermatitis can take the following forms:
- cream;
- ointment;
- powder;
- extremely rarely - baby oil.
One of the most popular remedies designed to combat diaper dermatitis is Bepanten cream or ointment. This drug not only treats the disease, but also prevents it. Bepanten can be used from the first day of a baby's life. It is applied to clean and dry skin of children in a thin layer. Treatment involves positive dynamics in the shortest possible time. It won't be the next day that parents will notice the first changes.
Bepantent has the following properties:
- moisturizing;
- regenerating;
- restorative;
- protective.
Komarovsky strongly recommends treatment with this drug in a course. You should not stop using Bepanten as soon as the filmic dermatitis has completely disappeared; you need to use the drug for at least a month.
Sudocrem is an external preparation that can relieve not only dermatitis, but also a number of other skin diseases that occur in children.
The product is recommended for use even by allergy sufferers from the very first days of life. Sudocrem not only relieves inflammation on the skin, but also quickly relieves itching and burning in damaged areas.
Diaper dermatitis in children goes away in a short time. The main substance of the drug – zinc oxide – contributes to this. This component creates a barrier that protects the skin from external factors, without causing a greenhouse effect.
For children with sensitive skin prone to allergic reactions, separate treatment regimens are selected. The pediatrician will prescribe several medications at once that need to be combined. Usually the complex consists of a moisturizing cream and a product that contains zinc - this is a drying substance. The third drug can be an external antiseptic or an ointment with antihistamine properties.
Previously, diaper dermatitis was treated mainly only with powders. They absorb excess moisture on the skin and have a calming effect. Today, pediatricians are increasingly refusing to use these products, because they often cause excessive dry skin, allergic reactions, and inflammation. The most popular manufacturers of baby powder are Bubchen, Johnson's Baby, and My Sunshine.
All drugs must be tested before full use. A new product for the baby is applied in a small amount to the thigh or shoulder area. You need to monitor your skin reaction throughout the day. If no unpleasant symptoms appear, then the product can be used. This method will protect your baby from a serious allergic reaction.