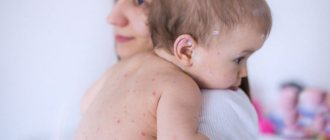
Chickenpox is a fairly contagious infectious disease caused by the herpes virus, which belongs to the third type. The main characteristic symptom is a rash that appears on the mucous membranes and skin, causing severe itching.
The period of first manifestations does not always coincide with the period when a person is dangerous to the people around him. Therefore, it is very important to know when chickenpox is contagious in children. Let's try to figure out this issue so as not to “catch” this disease.
What is chickenpox and how does it manifest?
By and large, chickenpox is the most popular infectious disease, which most often occurs in childhood. This pathology is distinguished by the fact that it manifests itself as a small rash and all sorts of other symptoms inherent in intoxication.
Chickenpox comes in varying degrees of severity, from mild to the most severe, resulting in quite serious consequences.
THIS IS INTERESTING! Previously, in Rus', when laboratory tests were not common and modern vaccines did not exist, chickenpox and rubella were considered childhood diseases.
People knew that it was better to get over such diseases in childhood, so that there would be no further complications. This fact especially concerned girls, as future mothers.
If one of the children fell ill with rubella or chickenpox, then in the locality they tried to gather the children together and lock them in one room for a couple of hours. As a result, children suffered from childhood diseases at an early age.
In younger age groups, chickenpox is easily tolerated. At the same time, the infection leaves behind a lifelong immunity and can only manifest itself in cases of immunodeficiency. Most people get chickenpox only once in their life. Chickenpox manifests itself as follows:
- general condition deteriorates significantly; feeling unwell; body temperature rises, chills occur;
- loss of appetite;
- sleep is disturbed;
- skin rashes and itching appear.
Who needs to take extra care?
Chicken pox itself is not considered dangerous by doctors: in most children it goes away without any consequences. Chickenpox is more difficult for infants and children over 12 years of age. Also, special caution should be exercised by weakened individuals and people with immunodeficiency conditions (AIDS, psoriasis, cancer).
Breastfed babies get sick less often than bottle-fed babies
After chickenpox, chronic pathologies and other problems can become aggravated and complicated. Children 4-7 years old need to be protected, as they most often become infected with herpes virus infection. Infants under two months of age usually become ill when bottle-fed in utero.
If the baby is breastfed, then the likelihood of infection is minimal, since the antibodies of a vaccinated or recovered woman are transferred to the child. If the mother has not had smallpox before, she needs to be especially careful.
Chickenpox can lead to the following complications:
- pneumonia;
- encephalitis;
- scars and cicatrices in place of vesicles;
- myocarditis (poses a danger to the life of a small patient);
- hepatitis;
- stomatitis;
- otitis;
- arthritis;
- myositis;
- infection, purulent inflammation of the skin (elements of the rash are itchy, so the child can comb them with dirty hands and introduce pathogens);
- bacterial keratitis (when pathogens penetrate the mucous membrane of the eyes);
- inflammation of the foreskin in boys;
- thrombophlebitis;
- bursitis;
- vulvitis and vaginitis in girls;
- chickenpox croup.
Serious complications due to chickenpox develop in approximately 5% of children.
Incubation period
This period is a certain period of time, which is counted from the entry of the virus into the human body until its first manifestations. After this, viruses begin to multiply in the cells of the mucous membrane, accumulate and gradually leak into the blood. After the pathogen has spread throughout the body, it begins to settle in the cells and provoke a rash.
Generally, the incubation period is two weeks.
Depending on a huge number of factors and the functioning of the immune system, this period can reach three weeks or one.
In general, chickenpox infection occurs very quickly, due to the high degree of contagiousness. In other words, it is enough to be in the same room with the patient for just a few minutes, and the virus finds a carrier. The virus thoroughly penetrates the nasopharynx and oral mucosa and begins to multiply. But in the first stages there are no symptoms. This period is called incubation.
Quarantine for chickenpox in child care institutions (kindergarten, school) is 21 days. During this period after exposure, chickenpox may appear in other children or adults who have not previously had the disease and have been in contact with the patient.
Contagiousness of chickenpox throughout the entire period of the disease
From the moment the threat of infection appears, caused by a large accumulation of the chickenpox pathogen in the saliva and mucus of the patient, and throughout the entire period of the disease, the person continues to be infectious. Why?
The fact is that when symptoms of infection appear, the degree of infectiousness increases due to an increase in the concentration of the virus in the fluid secreted by the patient. However, when a characteristic sign of the disease appears, an additional threat appears.
The rash, according to the stages of development, exhibits a polymorphic character and changes. The first elements of the rash - roseola, within 24 hours turn into papules - small nodules that form in the central part of the roseola, which within 48 hours transform into vesicles (vesicles filled with clear liquid). The liquid contained in the vesicles contains an even greater concentration of the infectious agent. The vesicles can burst, which leads to a massive release of the infectious pathogen into the air. In this case, there is also a possibility of infection if microscopic particles of the “bubble” liquid get onto the mucous tissues of a healthy person when breathing.
How long is a person contagious with chickenpox? As a rule, the appearance of the last foci of exanthema, on average, occurs 4-12 days after the appearance of the first elements of the rash, indicating a rapid recovery of the patient, but at this moment it is also contagious. We took the figure “4-12 days” from calculations, establishing the minimum period of rash in children (in childhood, the period of rash lasts 4-6 days), and the maximum period of rash in adults (in adult members of society, a rash can form within 7-12 days). Consequently, a person is contagious throughout the entire period of chickenpox rashes plus 1-3 days before them.
What is the contagious period
At various stages of the disease, a person is able to secrete infection in various ways. So, before determining the contagious period for chickenpox, it is worth noting that large quantities of the pathogen are found in saliva, and with the appearance of a rash, also in the blisters. When they burst, they can infect others. During this period, chickenpox can be transmitted by airborne droplets.
The duration of this period can vary significantly; it all depends on the severity of the disease and ranges from nine days to three weeks.
How many days is chickenpox contagious?
In general, this period can be divided into three stages:
Video on the topic
A pediatrician explains when chickenpox is contagious and how you can catch it:
Thus, a child with chickenpox is contagious for about two weeks. This period depends on the strength of the baby’s defenses, the characteristics of his body, the timeliness and correctness of treatment. In people with immunodeficiency, smallpox can last quite a long time and cause severe complications. The child becomes non-infectious 5-6 days after the end of the appearance of the rash on the body.
How contagious is chickenpox after the rash?
Naturally, many parents and adults are concerned about the question of how long after the first rash appears a person remains contagious.
Experts have found that during chickenpox, the patient is able to infect others for five to seven days after the last rash appears.
After this, the virus is no longer released into the environment. Thanks to the use of coloring antiseptics, it is significantly easier to determine the moment of onset of infection. Since it is easy to distinguish between processed and newly appeared bubbles.
When uncolored vesicles do not appear for two days, you can begin to count down the healing period.
A method to avoid infection
In fact, you can only become infected with chickenpox from a sick person, by direct contact with him or by being nearby. There is also a minimal risk of catching the infection during a fleeting meeting with a patient with chickenpox or simply sitting at home, since the virus is able to penetrate through open windows, ventilation, etc. Therefore, in order to protect yourself from this disease, it is necessary to avoid contact with infected people who have obvious signs of the disease. It seems that everything is simple, but...
You can become infected from a person suffering from herpes zoster (a secondary manifestation of the chickenpox virus), which manifests itself in the form of unilateral herpes-like rashes on the body, which is often not possible to notice. And as we found out above, chickenpox is contagious even before the appearance of symptoms and characteristic exanthema. So how can you protect yourself from infection?
Today, in medical practice, preventive vaccination against chickenpox is widely used, using a live vaccine containing a weakened strain of VZV Oka (Varicella zoster virus). When this vaccine is administered to a healthy person, an immune response is provoked, including the production of specific antibodies that bind or neutralize the infectious agent. This method, after completing the full course of vaccination (for children - 1 dose, for adults - 2), allows you to develop stable immunity against this infection, which will function for 10 years, and after revaccination - for life. In addition, the introduction of a live vaccine eliminates the possibility of developing herpes zoster.
By the way, you can become infected with chickenpox from people who have recently undergone a course of preventive vaccination.
Do not be ill.
When does chickenpox stop being contagious in children?
The answer to this question is very important, especially when a child is sick. After all, it is important to determine when it is permissible to resume contact with other children.
Naturally, skin rashes are considered visible landmarks for determining such a moment. The moment new bubbles stop appearing, this is an important signal that the baby is beginning to recover.
The disease ceases to be contagious a week after the last rash appears. After this period, the person is no longer dangerous to others.
Returning to the garden or society before this date is not only unethical in relation to other people, but it also threatens a new outbreak of the disease. In addition, the patient must restore physical strength and appearance after chickenpox at home, in a normal, quiet environment. If there is a rash, but no fever, chills, or muscle pain, then you can take a walk, but do not contact other people.
How many days do you need to be at home?
Previously, it was believed that children and adults who had contact with a person with chickenpox became infectious on the 10th day of the period, and were subject to isolation for the entire duration of the disease, starting from that day.
Infectious disease doctors are of the opinion that an infected person becomes infectious on the 17th day of the period. It turns out that the minimum period of isolation is 2 weeks. With the active phase of the rash in 5 days and 5 days of waiting after it, plus the incubation period.