Conjugation jaundice is not an independent disease, but a symptom that develops due to inadequate liver function. Most often diagnosed in newborns who were born prematurely. Typically, the yellowness of the skin disappears by the third week of life.
Conjugated jaundice of newborns is characterized by staining of the baby's skin 3-4 days after birth. The sizes of the liver and spleen are within normal parameters; there are no signs of increased destruction of red blood cells. When the functioning of the system responsible for removing bilirubin improves, the skin acquires a natural color.
We will consider in detail the symptoms of conjunctive jaundice in newborns and their distinctive features, methods of differential diagnosis and causes of development.
What is pathology
Physiological jaundice is an increased level of bilirubin in the blood, which can stain the skin and whites of the eyes. In addition to this symptom, the baby also experiences excessive drowsiness, apathy, and decreased appetite. It appears 3-4 days after birth in the maternity hospital. The condition is not pathological and in most cases goes away on its own without special treatment.
The need for therapy arises if jaundice appears on days 6-7 and does not go away after a week.
The condition is not an independent disease, but only signals the presence of a disorder in the body. Normally, this is an adaptation to the environment after birth; with a protracted process of hemoglobin breakdown, liver malfunctions are suspected.
Symptoms of conjugation jaundice in newborns
The disease most often manifests itself as a change in the color of the mucous membranes and skin on the second or third day of life; they acquire a yellow color. The pathology is not accompanied by an increase in the parenchyma and spleen, but is sometimes accompanied by a change in the baby’s behavior: his appetite decreases, crying becomes prolonged and monotonous.
Physiological jaundice is distinguished from pathological jaundice by the color of the stool: with conjugation disorders, they change color, the urine darkens, and the feces become colorless. Some symptoms indicate pathological disorders of the brain:
- the baby’s mucous membranes, skin and eyeballs become bright orange;
- he often throws his head back and rolls his eyes;
- convulsions occur;
- temperature rises;
- vomits masses of yellowish color.
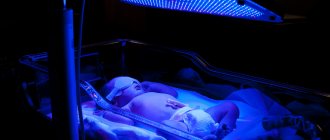
Using a photo lamp
Elevated levels of bilirubin threaten the child’s health, so doctors often prescribe a phototherapeutic course of radiation even in the early stages. It involves the use of ultraviolet lamps with a wavelength of 400-550 nm. The rays are able to penetrate the blood and dissolve bilirubin, as a result of which it loses its toxic properties. Then they are excreted naturally in the feces.
Phototherapy for neonatal jaundice resembles tanning in the sun; the rays have an identical effect on the skin. As treatment progresses, it is very important to monitor changes in bilirubin in the baby’s blood. As soon as it decreases to normal, the procedure is completed. There are several types of radiation:
- LED.
- Fluorescent.
- Halogen.
The doctor decides which lamp is used for neonatal jaundice. The main factor that must be taken into account is its energy resource, because the final result depends on it.
Attention! Only a modern device that is not dangerous to the baby should be used. capable of automatically switching off when overheating or prolonged uncontrolled operation. High-quality equipment is equipped with timers for recording energy output.
When does jaundice go away?
Conjugation disorders are rarely protracted; after 7–10 days, the production of enzymes normalizes, and the concentration of bilirubin decreases to normal levels. In premature infants, jaundice persists longer, up to 21 days. If the skin color remains yellow, the concentration of toxic pigment does not decrease - complications of conjugation jaundice are possible. They are treated for up to 4 months.
This is interesting: Breastfeeding jaundice: causes, symptoms, treatment and consequences for the newborn
Timely removal of intoxication avoids complications. Much depends on the nursing mother: the more often she puts the baby to the breast, the faster he will recover. With rare genetic pathologies of conjugation jaundice, relapses are possible; failure of enzyme production can occur at any age with infectious lesions of the parenchyma.
Indications for use
A phototherapeutic irradiator is used to treat neonatal jaundice in hospitals. The doctor decides to use this method individually, based on the test results and the general condition of the baby. The main indications for the use of a UV irradiator are:
- Pronounced signs of jaundice.
- Early date of birth.
- Insufficient body weight.
- Iron deficiency in the blood.
- Weak appetite and low activity.
- Reduced body temperature.
Treatment under a lamp for jaundice in newborns will not give any result if he has a pathological process in the liver, excessively increased bilirubin or developmental abnormalities. In this case, other methods and an integrated approach to therapy are used.
What is conjugation jaundice?
Pathology occurs due to hereditary factors when the liver does not produce the necessary enzymes that bind bilirubin. It appears in the blood after the natural death of red blood cells. Up to 1% of red blood cells are renewed daily; they contain indirect bilirubin. It is a toxic pigment that transports oxygen and carbon dioxide. In healthy people, it interacts with proteins and forms a complex organic compound. Its destruction occurs in the liver under the influence of enzymes (enzymes), this process is called conjugation. The transformed pigment becomes water-soluble and enters the bile for disposal.
This is interesting: Diet for jaundice: allowed and prohibited foods, sample menu for the week
With conjugation jaundice of newborns, the liver does not produce enzymes in full, the process of processing toxic bilirubin is disrupted, and its concentration in the blood gradually increases. If no measures are taken, the baby’s condition will worsen, and intoxication of the brain nuclei will develop.
Features of the event
A procedure is carried out using an ultraviolet lamp for children against jaundice, in a hospital setting. The baby is completely undressed, leaving the eyes and groin area closed. After which it goes to lie in a special box, where a pleasant blue color glows. The distance of the lamp should be at least 50 cm from the body. This is important to ensure the complete safety of the child. The instructions require the following actions from personnel:
- Bilirubin levels are monitored every 2 hours.
- During breaks, the child must be given clean water to drink, as he intensively loses moisture.
- During the process, medical staff weighs you and monitors your body temperature.
- The photolamp for the treatment of jaundice in newborns is treated with a special antiseptic solution before each use.
- It is not advisable to irradiate a baby at night unless there is an indication for it.
How long phototherapy for newborns with jaundice will last depends on the severity of the problem and the rate of removal of bilirubin from the body. If the yellowing is not severe, it can be treated in other ways.
It is important to know! The therapy does not require separation of mother and child, and allows for frequent feeding breaks. During the process, it is important not to leave the baby alone under the lamp to avoid burns.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis is carried out by a pediatrician in conjunction with an infectious disease specialist; the baby must be in a hospital setting. Be sure to study the mother's medical history. When making a diagnosis, a combination of factors is assessed - the child’s behavior, the level of bilirubin in the body, heredity.
Laboratory tests are carried out - CBC, determination of bilirubin, albumin and other indicators of liver tests. A study of urine and stool is necessary. If bilirubin is excessively high, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed, special attention is paid to the condition of the liver, spleen, gallbladder and biliary tract.
Possible side effects
Light therapy not only brings benefits, but can lead to unwanted side effects. Usually they do not greatly affect the general condition of the baby, but sometimes they lead to health problems. The most common body reactions are:
- increased frequency of bowel movements;
- increased drowsiness and apathy;
- excessive dryness and flaking of the epidermis;
- the appearance of an allergic reaction;
- bronze skin tone;
- headache;
- pain in the eyes and tearing.
The specialist decides how long to lie under the lamp for jaundice in a newborn individually; sometimes continuous stay in the box is indicated. The procedure is stopped if the baby overheats, redness appears on the skin or other symptoms. Side effects are extremely rare and usually do not require additional treatment.
Popular lamp models
Lamps used for neonatal jaundice are considered additional neonatal equipment. They can be halogen, fluorescent, LED. The distribution is also based on the color of the radiation (green, blue, mixed). In hospitals and maternity hospitals, irradiators on tripods are used. At home, portable structures are used, which can be rented or purchased at medical equipment stores. The following table describes the technical characteristics of several models that are used for light therapy.
| Indicators/characteristics | BabyGuard U-1133 | BabyGuard Y-1135 | BabyGuard U-1131/U-1132 | OFTN 03 Izhevsk |
| Availability of blue lamp | + | — | + | + |
| Availability of fluorescent lamp | — | + | + | — |
| Adjusting the stand height | + | + | + | — |
| Adjusting the lamp angle | + | + | — | — |
| Availability of built-in timer | + | — | — | + |
| Temperature regulator | + | + | — | + |
| Mobile design | + | + | + | + |
| For the treatment of jaundice | + | + | + | + |
| For the treatment of indirect hyperbilirubinemia | — | — | + | + |
The first three models described in the table have stands on which they are mounted. The Izhevsk model OFTN 03 is presented in the form of a plastic incubator, which contains a fabric hammock. The blue lamp is located at the bottom. The hammock allows ultraviolet waves to pass through and protects the baby's body from overheating. The design is equipped with timers that allow you to set the duration of the procedure and control the lamp resources. It is important to remember that phototherapy should only be carried out as prescribed by a specialist and under his supervision.
Contraindications and restrictions
Phototherapeutic exposure is a safe method of treatment, so there are practically no categorical contraindications. But there are a number of clinical situations when the procedure is prescribed with caution due to the high likelihood of side effects. The main conditions under which it is prohibited to use a photo lamp are:
- Eye pathologies. In this case, prolonged exposure to UV radiation on a newborn leads to the development of complications and a decrease in visual acuity. Therefore, the procedure is performed only with protective tight glasses.
- Skin diseases. The epidermis, sensitive to ultraviolet rays, may become inflamed during the procedure. Therefore, if absolutely necessary, it is prescribed only for a short time.
- Neurological disorders. Ultraviolet radiation has a stimulating effect, so for many diseases of the central nervous system, irradiation is not recommended.
- Hormonal disorder. Phototherapy causes excessive production of a number of hormones. In case of endocrine disruption, it is prohibited.
- Tuberculosis or lung diseases. There is a high risk of developing serious complications.
Phototherapy is not prescribed by a pediatrician for acute conditions, hyperthermia, tumor processes and a tendency to bleeding. Otherwise, the procedure becomes a trigger for a number of complications or serious deterioration of the condition.
Treatment of physiological jaundice at home
It happens that jaundice of newborns appears after discharge from the parental home. Adults should not panic; it is quite possible to cope with the problem on your own at home.
The child needs to be provided with quality walks in the fresh air and air baths (under indirect rays of the sun). In the summer, the baby is allowed to be laid out completely undressed in the shade for 1-2 hours. In winter, air baths are arranged at home. We must not forget about breastfeeding, this will allow you to get rid of excess bilirubin and make it easier and faster to adapt to unfamiliar conditions.
When treating at home, it is important to understand how to use the equipment correctly. If you have any questions, it is important to seek specialist advice. It is possible that in order to monitor the child’s condition, he will have to be taken to the laboratory every day to be tested for bilirubin levels.
If the baby gets worse, he is taken to the hospital; to speed up recovery, the mother is recommended to express milk and feed the baby. He needs to drink enough fluids. Jaundice can be treated quickly enough with the help of phototherapy, except for complex and advanced cases, in which it is impossible to do without the mandatory help of doctors.
Phototherapy at home
Many parents do not want to constantly visit the clinic for a session. They wonder if it is possible to do radiation at home. This is permitted subject to the following rules:
- The whole process requires strict control; the parent is not allowed to leave the room even for 5 minutes.
- The lamp should be installed no closer than half a meter above the child.
- The visual organ and groin area are qualitatively protected from exposure.
- The baby's position changes every 2 hours.
- Temperature measurements must be taken hourly.
- Before starting the course, you must take tests and consult a doctor.
A photolamp for the treatment of jaundice in newborns can be rented, or you can buy a device for personal use. It is impossible to carry out the procedure on your own, without the advice of a specialist, since the cause of yellowing can be serious diseases, which are aggravated by the action of UV rays.
A lamp for the treatment of jaundice in newborns is used in pediatrics for the purpose of relieving jaundice and rehabilitation. It is also used when a child has hematomas or hemorrhages on the body, or if preparation for an upcoming operation is necessary. It is carried out in a hospital or at home, depending on the condition of the baby. The duration of exposure and the duration of the course are determined by the doctor, taking into account all key factors. Therapy will be ineffective if the cause of yellowing of the skin is hidden in impaired liver function.
When does phototherapy stop?
First of all, lamps for the treatment of jaundice should be turned off if symptoms of overheating of the child appear. This includes an increase in the baby's body temperature or severe redness of the skin. The latter may also indicate a burn. Also, an indication for discontinuation of treatment is a decrease in the level of total bilirubin and the absence of an increase in its unconjugated fraction. At the same time, the baby’s skin and sclera become less yellow than during the pathological condition.
Is it possible to cure jaundice in another way?
Depending on the cause of jaundice, a treatment plan is determined. If the symptom is associated with large hemorrhage under the periosteum, the effect of phototherapy is short-lived. After the puncture, light treatment is prescribed, the remaining blood drops well.
Too high a bilirubin level is determined in hemolytic disease. In such cases, in addition to phototherapy, exchange blood transfusion and administration of immunoglobulins are prescribed.
When jaundice is associated with intrauterine infections, the first step should be to eliminate the underlying disease. For congenital malformations of the gastrointestinal system, in addition to phototherapy, surgical correction is indicated.
When a child suffers from jaundice associated with hereditary pathologies, he is prescribed a course of special medications, sometimes without a donor liver transplant.
Symptoms
The clinical picture develops in several phases. The first phase is typical for the first few days of a baby's life. There is a depression in the activity of the central nervous system, motor activity sharply decreases, muscle tone of the upper and lower extremities is noticeably reduced. The child cannot independently make sucking movements, and breathing periodically stops.
The second phase of the disease develops 4–5 days from the onset of symptoms and lasts several days or even weeks. It is characterized by an excessive increase in the tone of the muscles of the arms and legs, hyperthermia. A spasm of the back and neck muscles appears, which causes the child to take an unnatural arched position, and an unnatural high-pitched cry occurs, which experts call a “brain cry.” Doctors also note a positive Graefe symptom - when the child rotates his head, the eyeball moves downward, and a wide white stripe remains above the iris. This symptom is also called the “setting sun” symptom.
The third phase of kernicterus resembles a period of recovery, but this is only apparent well-being. The fourth phase develops closer to 6–8 months of life. It manifests itself in a number of neurological complications and consequences:
- cerebral palsy;
- paresis and paralysis;
- involuntary pathological movements of arms and legs, grimaces;
- a sharp decrease in hearing acuity up to complete deafness;
- impaired mental function;
- disruption of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus.
Important! In premature babies, pathology does not develop in phases. They are characterized by depression of the central nervous system and decreased muscle tone. In the future - a violation of physical and mental development.
Causes
The main molecule involved in blood transport is hemoglobin. Few people know that there are several varieties of it. In adults, hemoglobin A predominates, and in children, fetal hemoglobin (F) predominates. During the prenatal period, hemoglobin F is the main carrier of oxygen for the fetus. Compared to hemoglobin A, it is more effective as an oxygen carrier, but is less resistant to large fluctuations in pH and other negative environmental factors affecting the body. An increase in bilirubin levels is normal for a newborn. Yellowing of the skin and visible areas of the mucous membranes indicates the active breakdown of immature red blood cells and the accumulation of bilirubin in the surrounding tissues.
Physiological jaundice is a normal reaction of the newborn body to contact with the environment. It develops in the vast majority of children and is a kind of adaptation to new living conditions. Physiological jaundice can be expressed differently in all children, but, as a rule, it occurs 2-3 days after birth and goes away on 8-9 days. The level of bilirubin with physiological jaundice in newborns may increase. A similar reaction is observed in more than half of healthy children. According to some reports, the percentage of children with physiological jaundice that occurs after birth reaches 70%. Gradually, hemoglobin A begins to predominate, and bilirubin accumulated in the skin and mucous membranes is destroyed and excreted by the kidneys and liver.
Hemoglobin
Initially, the oxygen carrier in the developing fetus is fetal hemoglobin. It begins to be synthesized already at 1 week of pregnancy. Fetal hemoglobin replaces embryonic hemoglobin in the middle of the 2nd month. Be that as it may, fetal hemoglobin does not disappear completely and is contained in the blood in a small concentration throughout the entire intrauterine development.
At the time of birth of the child, the content of fetal hemoglobin reaches 80% percent. Over time, this figure decreases and by the end of the first year of life it is 1.5%, which corresponds to the content in adults.