34-35 weeks of pregnancy, like all previous ones, are characterized by certain psychological and physical sensations of the woman. The fetus also continues to develop and actively prepare for independent life outside the mother's womb.
There is very little time left before the birth, so it is necessary to prepare all the necessary things for the maternity hospital and take documents with you for the walk, as this may happen earlier than the appointed time.
Analyzes and examinations
The thirty-fifth obstetric week, or the thirty-third from conception, is the eighth month of pregnancy, the middle of the third trimester. Before a scheduled appointment with a gynecologist at this time, the expectant mother must undergo the following tests:
- Analysis of urine;
- blood chemistry;
- analysis for syphilis and HIV.
At the appointment, the doctor, in addition to the usual procedures (weighing, measuring blood pressure, fundal height of the uterus, abdominal circumference, listening to the fetal heartbeat), must take a smear from the patient to rule out various infections. Next, the pregnant woman is sent for CTG and ultrasound.
By the 35th week, the baby is already quite large and will not change its position in the abdomen, so an ultrasound at this time will show what the presentation of the fetus is and what delivery tactics (spontaneous or cesarean section) should be chosen . Plus, experts pay attention to the condition of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid, the presence or absence of umbilical cord entanglement, and the condition of the baby.
Don't tense up
35th week of pregnancy, what month? - this is the end of the 8th month. Pregnancy, anxiety or fear of childbirth, expecting a baby and motherhood - there is a lot to think about and worry about. Meditation, journaling, and talking about it with someone can help ease your worries. Don't hesitate to talk to a professional either. Many mothers use a forum at 35 weeks of pregnancy to exchange useful tips with other women.
What happens in the body of the expectant mother
Throughout pregnancy, changes occur in the body of the expectant mother, and by the end of the eighth month the woman gets used to a lot. However, this does not mean that you should not pay attention to new sensations, since this may cause you to miss a warning signal.
Nature of the discharge
The number of discharges during this period increases slightly. The presence of homogeneous mucus is normal, but bloody discharge most often indicates problems in the body, for example, placental abruption and a threat to the child. If a pregnant woman discovers scarlet spots, she should immediately contact a gynecologist. Also, copious watery discharge is not normal: it may indicate leakage of amniotic fluid. There are tests that can help diagnose this, but again, it's best to see a doctor.
Weight gain
Normally, a pregnant woman should gain about 300 grams per week. Accordingly, by the 35th week the gain will be about 11–12 kilograms.
If the weight you have gained exceeds the norm, you should not immediately limit yourself to food (although this is also worth thinking about). It is quite possible that the extra pounds are water that circulates in the body during pregnancy differently than before. To understand whether there is excess fluid and swelling, just do a small test: in the morning or afternoon, press on your arms or legs. If your finger leaves a dent that does not disappear immediately, it means that excess water is still present and you should limit your salt intake.
Possible troubles
The larger the child and, accordingly, the belly becomes, the more unpleasant and even painful sensations the expectant mother endures. Some of these troubles have serious consequences.
First of all, the growing belly, on the one hand, puts pressure on the pregnant woman’s bladder and intestines, and on the other, props up the stomach, so the woman may suffer from incontinence, constipation, hemorrhoids or heartburn and loss of appetite. In addition, the fetus can interfere with normal blood flow in the mother's body, resulting in varicose veins. Finally, the weight of the baby, placenta and amniotic fluid has a detrimental effect on the expectant mother’s lower back and can cause severe pain or even sciatica. All these problems can be solved by a bandage that will support the abdomen and properly distribute the load, and special compression stockings (however, their use should be agreed with your doctor).
A support bandage will help minimize back pain
As your belly grows and you gain weight, your risk of stretch marks increases significantly. The skin on the abdomen itches and peels, brown stripes appear under the abdomen, on the chest, arms and legs. A special oil for stretch marks or a rich nourishing cream can help with these unpleasant sensations.
To avoid the appearance of stretch marks, it is recommended to use a special oil or nourishing cream.
Experience shows that stretch marks are almost impossible to cure (only with a special laser). Therefore, it is easier to prevent them: use oil or cream in advance, ideally from the first months of pregnancy.
Another trouble that awaits the skin of the expectant mother is chloasma. Pigment spots appear due to hormonal changes in the body and, fortunately, most often disappear after pregnancy without any consequences. However, the expectant mother should refrain from visiting a solarium or prolonged exposure to the sun without protective cream.
After childbirth, pigment spots most often disappear
Tooth decay is partly associated with hormonal changes. In addition, the vitamins necessary for oral health are supplied not only to the mother’s body, but also to the baby, which also negatively affects the condition of the teeth. A visit to the dentist will help solve this problem. Dental treatment during this period is not prohibited.
Changes in the body
At 34-35 weeks, the fetus continues to actively grow, so the woman’s well-being also changes against this background. Pressure on the diaphragm increases, causing shortness of breath. Also, lower back pain is considered normal if it occurs after physical activity and quickly subsides at rest.
These unpleasant sensations are caused by a shift in the center of gravity, as a result of which the woman quickly gets tired and rests more often to relieve the load from her back. There may be a feeling of pain in the pubic area, as the joint of the pelvic bones becomes loose.
After all, the body is already actively producing hormones to increase the elasticity of the birth canal, which will facilitate the process of bringing the baby into the world. In proportion to the growth of the fetus, the uterus also increases, which affects the functioning of adjacent organs. The woman experiences slight tingling in the vagina.
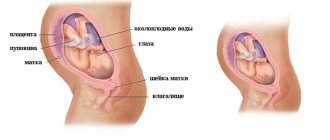
During this period of pregnancy, the uterus is 15 cm above the navel, and the height of its fundus is about 35 cm.
On average, the abdominal circumference increases by 1 cm per week. Therefore, it is recommended that the expectant mother constantly take measurements, which will allow her to track the dynamics. A growing belly causes the skin to stretch. This causes a constant desire to scratch it. If itching is felt only in the abdominal area, then this is normal.
The breasts enlarge, at this stage colostrum is periodically released. The woman's weight gain is also noted. The body most often gets used to such changes without any particular difficulties, but sometimes problems with the functioning of the digestive organs may arise, which is expressed by heartburn, heaviness in the stomach, flatulence and constipation.
There is also a certain clumsiness and limitation in actions. It is already more difficult for the expectant mother to put on shoes, walk long distances and climb stairs. 34-35 weeks of pregnancy are characterized by sleep problems. A woman may experience insomnia because the biological rhythms of mother and baby do not coincide.
The size of the fetus has already noticeably increased and any movement is acutely felt, which interferes with proper rest and it is often very difficult to find a comfortable position for sleeping. For some expectant mothers, at this stage of pregnancy, the stomach has already dropped, so breathing problems disappear, but urination becomes more frequent. The navel already sticks out well and is directed forward, and not upward, as before.
There may be cases of incontinence, especially when a woman laughs, coughs or sneezes. This occurs as a result of the production of relaxants, which help relax the muscles for a favorable pregnancy. Therefore, in order to avoid getting into an awkward situation, a woman should use pads made from natural ingredients.
During this period, the volume of discharge increases. Ideally, they should be of uniform consistency, white or milky in color, and odorless. But the presence of small mucous inclusions is allowed.
Belly shape
There is a myth that the gender of the child can be determined by the shape of the expectant mother’s belly: if the belly is wider and rounder, it means there will be a girl; if the stomach is narrower, but protrudes forward more, it’s a boy.
It is impossible to determine the gender of a child by the shape of the belly.
However, this is not so: the shape of the abdomen depends on the individual characteristics of the woman and on the presentation of the fetus. The most reliable way to find out the sex of the baby is an ultrasound.
The shape of the abdomen depends on the individual characteristics of the mother and the presentation of the fetus
Confident pregnancy
35 weeks of pregnancy is a time of maximum confidence and positive attitude. If some fear of childbirth appears, then you need to drive it away. At night you should watch good movies, don’t forget that music is great for calming, and don’t neglect your vocals. Children love when mom sings.
You need to be sure that everything will be as it should. There's not much time left, you need to have time to enjoy it. If you can’t gain confidence, then you should go to a birthing class.
You feel bolder in company. In addition to the opportunity to communicate, during the courses you will be able to learn a lot of useful information and learn how to behave during contractions. This will also help you gain confidence during childbirth.
Lifestyle of the expectant mother at 35 weeks
If moderate physical activity was previously recommended to a pregnant woman, then at 35 weeks, excessive activity should be abandoned due to the risk of premature birth. But this does not mean that you need to stop moving completely: light gymnastics or yoga, leisurely walks in the fresh air are still welcome. In any case, a woman should listen to her body and focus on her condition and doctors’ recommendations.
Meals at the 35th week should be varied: it is best to include red meat, fish, vegetables and fruits in the diet. Particular attention should be paid to water balance and try to minimize the amount of salt. You need to eat in small portions, but often.
As for intimate life, the opinions of doctors are ambiguous. Some say that sex before the mucus plug comes out is useful, as the cervix softens, others fear that tension in the abdominal muscles can have a detrimental effect on the condition of the fetus and even provoke premature resolution of pregnancy.
Discharge
Normal discharge is clear, light and odorless. If they changed their consistency, they became green, yellow, purulent, bloody and cheesy. This may indicate illness and infection. During pregnancy, this is extremely dangerous not only for the woman, but also for the baby.
Infections can penetrate the placenta and negatively affect the baby, but even if this does not happen during pregnancy, there is a high risk of infection at birth. Therefore, if strange discharge, itching, or inflammation of the genital organs occurs, you should urgently consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Bloody discharge may also indicate the release of a mucus plug, which means labor is approaching. If a lot of fluid has passed, then most likely it is amniotic fluid and you need to call an ambulance immediately.
Late complications
Closer to the end of pregnancy, a woman listens especially sensitively to her body, so as not to miss the first harbingers of the approaching meeting with the baby. However, it is worth paying attention to warning signs so as not to miss the danger.
Arrhythmia
Since the expectant mother’s body endures heavy loads, and the placenta is connected to the woman’s circulatory system, interruptions in the functioning of the heart are quite common. Sometimes arrhythmia does not cause complications and is asymptomatic, but there are cases when the symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia are noticeable and can be dangerous:
Symptoms of arrhythmia:
- increased or decreased heart rate;
- interruptions in heart function;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- fainting.
Severe arrhythmia can lead to fetal hypoxia, placental insufficiency and delayed development of the child. In severe cases, pregnancy is terminated at any stage.
Preeclampsia
Most often, toxicosis worries pregnant women in the first trimester. However, there are cases of late toxicosis - gestosis, which can lead to a number of complications. It can provoke premature birth, cause placental abruption, hypoxia, or even fetal death.
Symptoms of gestosis:
- swelling;
- increased levels of protein in the urine;
- hypertension (high blood pressure).
Moreover, at least one symptom is enough to suspect late gestosis.
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios
The amount of amniotic fluid directly affects the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the baby. Normally, by the 35th week, the volume of amniotic fluid should be about a little over a liter. Accordingly, a decrease or increase in this indicator can have a detrimental effect on the condition of the fetus. If there is a lack of fluid, the necessary nutrients will not reach the baby in the required quantities, and if there is an excess, there is a risk of premature dilatation of the uterus or leakage of amniotic fluid.
The main causes of this complication are considered to be infections and viral diseases, so special tests are prescribed for the pregnant woman. In addition, the amount of amniotic fluid is influenced by the individual characteristics of the mother (for example, obesity or diabetes), Rh conflict or congenital defects of the child.
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios can be determined by the size of the abdomen, the height of the uterine fundus and how well the fetus can be felt and how freely it moves. Hospitalization is required only in extreme cases, for example, with severe polyhydramnios and the risk of premature labor or when infections are detected.
Hypertonicity of the uterus
From about the 20th week of pregnancy, a woman experiences so-called training contractions: the uterus periodically contracts for no apparent reason for 30–60 seconds, after which it relaxes on its own. These same contractions continue until the onset of labor and do not pose a danger; on the contrary, this is how the body prepares for the birth of the baby.
But if the uterus often becomes stone and does not relax for a long time, you should consult a gynecologist. Hypertonicity of the uterus is dangerous due to fetal hypoxia.
Leakage of amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid leakage is often confused with normal discharge or urinary incontinence. It is sometimes difficult to recognize a dangerous complication on your own; if you suspect it, you should see a specialist. Nevertheless, a pregnant woman can still do something.
Leakage differs from discharge in consistency: mucus is more viscous and less transparent. But in any case, if you suspect partial rupture of amniotic fluid, you should use a rapid test, which can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Umbilical cord entanglement
Entanglement with the umbilical cord, which carries nutrients to the fetus, is quite common. And since it becomes increasingly difficult for the baby to move in the womb at the 35th week, he most likely will no longer be able to get rid of the entanglement.
Depending on how many times the umbilical cord wraps around the child’s neck or limb, a distinction is made between single, double or triple wrapping. The first type is not a pathology or an indicator for the use of cesarean section, but the other two can lead to serious consequences:
- absolute hypoxia or suffocation;
- developmental delay;
- placental abruption due to too much tension on the umbilical cord.
In this case, natural childbirth is contraindicated.
Premature aging of the placenta
As mentioned above, at the 35th week, during an ultrasound, the gynecologist pays attention to the condition of the placenta. It is important that its maturity reaches the second degree in the eighth month. With premature aging of the placenta, doctors prescribe drug treatment due to the possible death of the fetus, since nutrients and oxygen will not be able to fully reach the baby.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
ICI is a pathology associated with premature dilatation of the cervix. In the early stages, this threatens miscarriage, and in later stages, premature birth.
Typically, the symptoms of ICI are not pronounced: a feeling of fullness appears, and bleeding may be observed. ICI can be detected using ultrasound.
The cause of the pathology may be disruption of the uterine sphincter due to previous mechanical damage: late abortion, application of obstetric forceps and other surgical operations on the cervix.
The problem of ICN is solved surgically: either after 28 weeks a Meyer ring is installed, or a special suture is placed on the cervix. This operation is performed up to 28 weeks.
Streptococcus
Since a woman’s immune system is weakened during pregnancy and the microflora has undergone changes due to hormonal changes, the expectant mother should beware of infections, including streptococcal ones. Streptococcus bacteria can cause premature birth, placental abruption, impaired fetal development, or death of the child. In addition, intrauterine infection may occur, and the newborn may develop sepsis or meningitis.
It is very difficult to identify streptococcus without pronounced symptoms of the disease - you need to conduct a special test to detect the bacteria in a smear. If the test is positive, antibiotic treatment begins at 35 weeks. During childbirth, medications are also administered to eliminate the risk of infection of the baby.
Intimacy
If there are no contraindications, then sex is allowed during this period. Naturally, sexual intercourse should take place calmly, without sudden penetration and in a position that is comfortable for a pregnant woman. The most suitable one is both partners on their sides, the man behind.
If there is a threat of premature birth, problems with the placenta, or certain pathologies, the doctor may prohibit intimacy. If your water breaks or your mucous plug breaks, you can’t have sex either, as there is a high chance of contracting infections. Of course, complete refusal is necessary in the presence of sexually transmitted diseases and even with such suspicions.
In general, if the pregnancy is going well, there are no problems, then sex will only have a positive effect. Male hormones perfectly help prepare the body for childbirth and, of course, improve the emotional state of the woman in labor.
Baby at 35 weeks: height, weight, belly shape
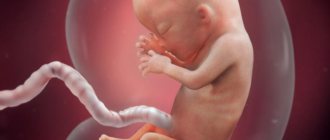
By the 35th week of pregnancy, the fetus is almost completely formed and looks the way the expectant mother will see it after childbirth. Its height is about 47 cm, weight - 1000–2500 grams. Hair continues to grow on the head, but the scalp (lanugo) gradually disappears from the skin of the body: the skin becomes pink and smooth. The baby is actively accumulating subcutaneous fat, its shape is rounded.
At the 35th week of pregnancy, the baby is completely formed in appearance
The child’s body also completes its final preparations for birth: in the eighth month, the adrenal glands are actively developing.
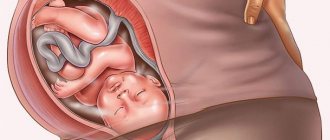
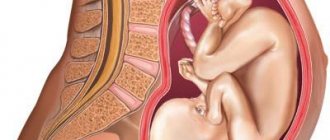
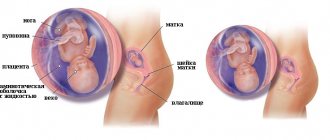
Finally, it is at this time that the fetus takes its final position in the abdomen, and most likely, after the 35th week the presentation will not change. There are cephalic, transverse and pelvic presentations.
Types of fetal presentation
Presentation directly affects the choice of delivery tactics. For the vast majority of women, the child is in the correct position - head position. That is, the baby’s head descends into the mother’s pelvis. With such presentation and the absence of other indications, the doctor allows natural childbirth. Transverse (the baby lies across the abdomen) or pelvic (fetal legs are lowered) presentation is considered incorrect. In such cases, a planned cesarean section is most often prescribed.
Possible positions of the baby in the expectant mother’s belly: cephalic, pelvic and transverse presentation
Fetal movements, D. Pearson test
By the 35th week, the baby reaches such a size that it can no longer move in the mother’s belly as actively as it did before. In order not to worry about this, but also not to miss the alarm signal, women are encouraged to perform the D. Pearson test.
Its essence is as follows: during the day (from 9 am to 9 pm) it is necessary to count the child’s movements over a certain period of time. After recording the moment of the first movement, all, even minor, movements of the child are noted: kicks, rollovers, etc. If 10 movements are noted in 10–20 minutes, then everything is fine with the baby. If the child is more active (more movements during this time) or, conversely, behaves quietly, you need to contact a gynecologist: perhaps the fetus is experiencing oxygen starvation.
Uncomfortable sensations
At the 35th gestational week, a woman in labor experiences unpleasant pain in the abdomen, lower back and legs. The reason for this is the large weight of the child and the hormone relaxin, which begins to be produced to soften bone tissue so that the baby can pass through the birth canal.
For relief, it is recommended for a woman to:
- more time to rest, sit and lie down;
- reduce physical activity;
- wear a special bandage for support;
- perform light exercises and breathing exercises.
It is natural to experience discomfort in the chest area, so you should wear a special bra. Pelvic pain is associated with the preparation of bones for the birth of a child.
Any discomfort should be treated with caution, and if the pain becomes chronic, you should immediately consult a doctor. Some diseases may appear only in the last stages of pregnancy, for example symphysitis, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, cholestasis and others.
Premature birth at 35 weeks
Every pregnant woman knows her PDA (preliminary due date). Normally, resolution of a singleton pregnancy occurs at the 40th week, and the fetus is considered full-term at the 38th week. However, it is not uncommon for birth to occur much earlier.
It is believed that being born in the seventh month is much more dangerous for a child than in the eighth. However, many doctors dispute this: in recent weeks, the baby is actively gaining subcutaneous fat, and his body is finishing preparations for birth. It is very important for the fetus to remain in the womb as long as possible. Therefore, a baby born at 35 weeks has a higher chance of surviving and avoiding complications than babies born earlier.
Causes of premature birth
There are several reasons why labor occurs prematurely.
- Infection. And not only diseases of the genital tract: there are cases where childbirth was also provoked by severe cases of respiratory infections.
- Pathology of the uterus, including isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which is diagnosed in the second trimester.
- Early abortions and miscarriages (especially in the first pregnancy).
- Multiple and polyhydramnios pregnancy.
- Improper lifestyle of the mother (drinking alcohol, smoking, excessive exercise).
- Rhesus conflict.
The expectant mother can avoid some risks on her own; in other cases, medication and hospitalization are required. In any case, in order to know about their condition, pregnant women are advised to register with antenatal clinics as early as possible, not to miss visits to the gynecologist, and to closely monitor their condition.
Harbingers of premature birth
At the 35th week, the baby can already lower his head into the pelvis. At the same time, the stomach will also visually drop (and this will be the first signal that labor will soon begin), and the uterus will put pressure on the cervix, provoking premature dilatation.
In addition, a pregnant woman may be tormented by the training contractions mentioned above. However, if after 10–15 minutes the uterine contractions do not stop, but intensify, and pain appears, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Another sign of the onset of labor is copious watery discharge. They mean that the bladder in which the baby is located has cracked and amniotic fluid is leaking. After the water breaks, the fetus can remain in the mother’s stomach for about 12 hours, after which, if labor does not gain momentum, the woman in labor is sent for an emergency cesarean section.
Other signs of impending labor include:
Weight loss
You may suddenly feel like you've lost some weight. This is due to the removal of excess fluid from the body, swelling is reduced. Changes in the nature of bowel movements are also associated with this. You may need to go to the toilet more often, the consistency of your stool becomes thinner, and many women complain of diarrhea.
Prolapse of the uterine fundus
The baby presses its head against the lower part of the uterus and pulls it down to the entrance to the pelvis. He himself occupies the most convenient position for birth. As a result of these preparations, you will feel how it has become easier to breathe and heartburn has disappeared.
Note that even the most experienced gynecologist will not be able to tell you how soon labor will begin after the appearance of these symptoms.