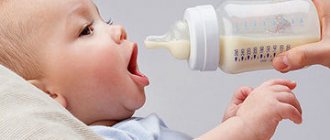
In most cases, the first food for a newborn and infant is breast milk. It contains all the components necessary for the development of a baby at the initial stage of his life. It contains all the vital nutrients, vitamins, minerals, which, on the one hand, are building materials for cells and essential nutrients, and on the other hand, protection and energy for the tissues and cells of the body. At the same time, there is always a threat of a significant decrease in lactation or the impossibility of feeding the baby for medical reasons, and parents are faced with a difficult question - what to feed the child?
Composition of cow's milk
Indeed, in terms of its composition, cow's milk is very valuable. What is contained in 100 grams of the product?
- Proteins – 4.3 g.
- Fats – 1.0 g.
- Carbohydrates – 6.4 g.
- Sodium – 52 mg.
- Potassium – 157 mg.
- Calcium – 136 mg.
- Magnesium – 16 mg.
- Phosphorus – 96 mg.
- Iron – 0.1 mg.
- Vitamins B1, B2, PP, C.
It would seem that for a developing child’s body this is a unique complex of useful substances that contribute to the qualitative growth and development of the baby. There is three times more chlorine, calcium, sodium, phosphorus, and protein in cow's milk than in breast milk. More is not less. But is it really that good?
Let's start thinking logically. Why did nature provide breast milk? In order for a person to feed their offspring with it. Cow's milk, accordingly, is intended for feeding calves. Both products are valuable, this is undeniable, but each in accordance with its purpose. In the first months of its presence in this world, a human baby will breathe life, strength, and energy from its mother’s milk.
What diseases can be transmitted to humans by consuming raw milk?
If milk is not boiled, the risk of contracting many dangerous diseases increases significantly. Possible infection with the following diseases:
- extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis ;
- toxic infections;
- leukemia provoked by a lymphotropic virus;
- streptococcal and staphylococcal gastroenteritis ;
- a number of severe infections - brucellosis , anthrax, foot and mouth disease;
- Q fever;
- arboviral tick-borne encephalitis .
Several centuries ago, children were not fed cow's milk. If the mother could not feed the child, she turned to the nurse for help. According to historical data, cow's milk began to be given to babies only in the eighteenth century.
However, now women do not need to practice this method of feeding. After all, there are a lot of special adapted mixtures containing exactly those substances that the baby needs. Of course, ideally, the newborn should be completely breastfed. But if for certain reasons this is not possible, you should select a suitable formula for feeding.
The benefits of mother's milk
What does mother's milk give to a baby?
- Maximum nutrients in the quantities required for optimal growth and full development. These are lactose, vitamins, enzymes, fats, minerals, iron, water.
- Protection against pathogenic bacteria that multiply in the intestines and cause various diseases.
- Stimulation of brain development. Children fed on mother's milk have good memory and excellent vision.
- A close emotional connection between mother and child, a great feeling of love, warmth, affection.
- Minimal exposure to various diseases, including diabetes, asthma, allergies, and cardiovascular pathologies.
An important advantage of breast milk is that it does not need to be prepared in advance. The product is at the correct temperature and is always available to the child.
Advantages and disadvantages of such feeding
To determine which is better, consider the advantages and disadvantages of each product.
Milk certainly has a number of beneficial properties:
- Contains fats necessary for the human body, rich in vitamins A and B, and useful minerals.
- Calms the nervous system.
- Promotes the development of immunity.
- Helps improve memory.
However, this is a rather heavy product even for an adult body.
Protein in milk
All organs of a newborn are still in the process of development, and therefore cannot fully perform the functions characteristic of an adult’s body. When receiving an excessive amount of protein and minerals contained in cow's milk, the kidneys receive a significant load, the level of which is several times higher than permissible. They are forced to work with special effort. Trying to relieve the body of unnecessary excess substances obtained, they remove liquid in greater quantities than necessary. Accordingly, the baby begins to feel thirsty. Mom, seeing his desire to drink, can give milk again. Thus, a vicious circle is created.
Compared to similar products from other mammals, human milk is characterized by the lowest protein content: 0.8-1.1 g per 100 ml. The valuable element found in breast milk consists of globulins and albumins, which are easily digested in the baby’s body. Protein is also a building material involved in the formation of immunity, the production of antibodies, and the synthesis of hormones and enzymes.
Can babies drink milk after one year?
Of course, if the child has grown up and is already 4-5 years old, he can be given goat and cow milk in reasonable quantities. Of course, provided that the baby has never had any allergic reactions to it. But still, you should not exceed the dose of 400 g per day.
But if the baby has just turned one year old, then it is too early to introduce this product into the diet. And even at two years old, when the necessary enzymes are already in the body, you should not immediately give milk to babies in glasses. After all, the most important rule is that everything needs to be done slowly and gradually.
Mothers who are wondering when they can introduce milk porridge to their baby should take into account that up to two years of age, porridge should be made in water, with the addition of artificial formula or breast milk.
And if it is not recommended to introduce milk porridges to children under one year of age, then closer to two years the child can gradually begin to be given milk porridges.
Casein is harmful to children's bodies
Casein is a cow's milk protein, a fairly large molecule that can injure the mucous membrane and intestinal walls. When it enters the body, histamine is released into the blood. High levels of this substance cause milk allergies. Damage to the intestinal walls can cause bleeding, and then, as a consequence, a drop in hemoglobin levels and the development of iron deficiency anemia.
With constant consumption of cow's milk, there is a risk of intestinal bleeding from ulcers formed on the intestinal mucosa. Breast milk contains tens of times less casein than animal products. Its particles are so small that in the baby’s stomach they form delicate flakes that are easily digested.
What kind of milk is best for children?
In the context of discussing the dangers and benefits of dairy products for children, the question arises about which milk is better to buy for a child - pasteurized “store-bought” or natural, “from a cow”.
Arguing about which baby milk is better, some experts argue that a pasteurized product completely loses all its beneficial properties. And if it has a long shelf life, then this means that the product is completely useless.
However, it is important to take into account that during pasteurization it is mainly pathogenic microorganisms that are destroyed. After all, for flash pasteurization it is heated to 90 degrees, and in other modes the milk is subjected to even lower temperatures.
But drinking it raw is very dangerous, since it may contain any microorganisms. In addition, an animal can be a carrier of a number of infectious diseases, which are asymptomatic in it, but milk can be infectious for humans. And therefore, consuming a raw product is always a risk of contracting tuberculosis , tick-borne encephalitis , brucellosis , etc. Therefore, it is imperative to boil raw milk.
However, pasteurized food should not be considered completely safe and healthy either. antibiotics to protect them from epidemics , which subsequently end up in the milk. Also, many animals are treated with antibiotics for inflammatory processes in the mammary glands that develop due to the use of synthetic hormones to increase productivity.
Accordingly, by constantly consuming such a product, the baby receives certain doses of the antibiotic, which subsequently leads to the development of resistance to antibacterial agents. In addition, antibiotics generally have a negative effect on the condition of the body.
Those who ask whether it is necessary to boil pasteurized milk should know that boiling is not necessary in this case. After all, antibiotics cannot be “removed” in this way. And the remaining beneficial substances will be destroyed by boiling. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether it is necessary to boil pasteurized milk for a child is negative.
By the way, some women who practice pumping also ask whether it is possible to boil breast milk. The answer is similar: the product will lose its beneficial properties after boiling, so you should not boil it.
You can also find recommendations online that children should be given whole milk. Not everyone knows what it is. Whole milk is a product that is not subjected to any processing, except filtering after milking. However, given what whole milk means, this product should not be given to children. After all, the fat content in it is too high, and lack of cleaning is fraught with the risk of contracting dangerous diseases.
Boiling: a must
The question of when can a child be given cow's milk is relevant if the baby is bottle-fed or there is a transfer from breastfeeding to “adult” food. The reason for introducing animal products into the diet may not be only this. For example, many mothers think that their child may not get enough breast milk. It should be understood that with proper breastfeeding, the baby will always have enough milk. Nevertheless, caring mothers are rushing to fill this gap and introduce their babies to a more varied diet, including cow's milk. At what age can children be given this product so that it is not detrimental to their health?
From 9 months (or better yet, when they turn 1 year old) you can start giving children who are on artificial nutrition cow's milk. Of course, it is advisable to prefer formulas adapted for this age, since they contain a balanced complex of essential nutrients. Cow's milk should be given to the child in diluted form and only after preliminary boiling.
Why do you need to boil milk? It is dangerous to drink raw milk from a domestic cow, since there is not always sanitary control over the animal. Some infections may be asymptomatic, or the cow may be a carrier of the infection. In particular, cattle can be a carrier of a dangerous disease - brucellosis, which affects the osteoarticular system, cardiovascular and nervous systems. Therefore, raw dairy products should not be given to young children.
Nutrition of children of the first year of life
why our mothers gave us juice, and what came of it. Still, this material is more like “reasoning” than “advice and recommendations.” I was prompted to create it by a discussion in a parent forum about introducing complementary foods with juices. Unfortunately, the defenders of this method do not provide any other argument other than “we drink and everything is fine” or “our mothers gave us water.” And the arguments of the opposition are studiously ignored, referring to the experience of those very “mothers who gave water.”
Let's talk about them. Why our parents could give water, and why we shouldn’t do it.
This material is especially worth reading for mothers of premature babies. Because, unfortunately, neonatologists very rarely read modern literature, focusing more and more on the knowledge gained from textbooks from the time of the King of the Peas, arguing that rushed babies simply really need “cooping” as early as 2 months.
Okay, I'll stop ranting and start the story.
The method of introducing complementary foods with juice was especially common in the period before the 70s. And not only in Russia, but also in Europe and America. But already in the late 60s, the first recommendations appeared in America and Europe to limit such food activities for children. Russia, as always, is in the rear, observations of the “bourgeois children” have no weight, you need to step on the rake yourself 15 times to understand the meaning of what is happening.
From observations of children aged 6-12 years old who grew up in the wake of early sexual intercourse, information was gathered that such methods can be fraught with long-term consequences. The danger lay in wait not only in the form of immediate allergic manifestations, but also in subsequent reactions of the maturing body. From birth, the child’s gastrointestinal tract, receiving unadapted food (and recommendations to give juices starting from 3 weeks), worked under extreme conditions, “to wear and tear.” And during physiological stressful periods (pre-teenage and adolescence), he simply simply lost his temper, rewarding the child with a bouquet of diseases such as gastritis, pancreatitis, problems with the intestinal mucosa, etc.
And again, turning to that time, let us remember that the main emphasis was on artificial nutrition (and at that time it was considered BETTER to supplement the child with formula than to support breastfeeding, and the mother was recommended to use the services of a nursery as soon as possible in order to return to work shift) - the child needed additional sources of nutrients. This is precisely where the principle of “lesser evil” has become relevant.
Yes, juices as a first complementary food are harmful. But insufficient nutrition due to the lack of breast milk, milk formula of an unbalanced composition with crystalline sugar (and our mothers should remember how they sifted sugar from mixtures with a sieve), cow's milk or kefir, is more dangerous for the child. Nutrient deficiency provokes severe developmental defects, while gastrointestinal problems are, firstly, more distant in time (most often before pre-puberty) and secondly, potentially familiar and theoretically treatable.
And now the numbers. Let me give you an example... m... on iron. More precisely, on its content in various food sources suitable for an infant and the child’s needs for it.
Let me give you an example... m... on iron. More precisely, on its content in various food sources suitable for an infant and the child’s needs for it.
In breast milk, the iron content is insignificant by itself, about 0.04 mg per 100 grams. But iron in breast milk has a unique bioavailability - 50-75%. No other product in the world provides this. Those. the absorbed amount in mcg/100 grams is about 20-30.
In modern adapted mixtures, the content of ferrous sulfate is about 0.2-0.4 mg/100 grams (in enriched mixtures 0.6 mg/100 grams). Taking into account its bioavailability (which is about 20%), the absorbed amount ranges from 40 to 120 mcg/100 grams.
According to WHO, 20 mcg/100 grams is a sufficient amount to meet the needs of a child up to the age of 6-8 months on average. In mixtures in which there are no additional factors stimulating absorption, the iron content, as can be seen, is overestimated.
But in the milk formula that our mothers fed us, the iron content is two times less than in breast milk - 0.02 mg/100 grams. Bioavailability is low - 10%... and the amount of iron absorbed is only 2 mcg/100 grams of the mixture.
Those. for a child who was bottle-fed at that time, the prevention of iron deficiency anemia was VERY relevant. Because from the available food he received less than 1/10 of the required amount.
This was especially true for premature babies, because their own reserves were minimal due to the shortened period of perinatal development, and, as a rule, were depleted to a minimum level by 2 months.
Juices acted as at least some alternative to solving such a problem. Really AT LEAST SOMETHING. Because it is impossible to offer solid food (pieces, purees) to a child of physiological immaturity for complementary feeding. Exceptionally liquid. Such as juices and broths (is the passion of old-school pediatricians to feed a child “soup” already at 4-5 months understandable now?). So, juices... the iron content in fortified apple juice is about 0.4-0.5 mg/100 grams. Bioavailability - 1-2%. those. about 4 mcg/100 grams are absorbed.
Therefore, by the age of physiological decrease in iron reserves in the body (about 4 months), a child who is fed a poor formula should already have a SUFFICIENT amount of another source of iron in the diet - juice. At least these 100 grams of juice per day. But if you give them to a child right away, he will, excuse me, die. That’s why they introduced it as early as possible in order to extend the period of adaptation. Smooth out the stress effect.
Why was the recommendation universal? At that time, and to this day, the prevalence of breastfeeding in Russia is quite low, unfortunately, just as the industrial production of formula did not offer an adequate composition of artificial substitutes. That is why, based on the principle of the lesser evil, guided by the good of the majority, this recommendation was universal. If there is any harm, it will be small compared to the problems of growth defects in a child in the first year due to poor nutrition with unadapted food.
That's all... The main problem is that in the conditions of modern nutrition for children, the advantages of introducing juice have lost their relevance. And when there is no even dubious benefit, then what is left?
And finally: no one claims that “juices are universal evil.” When juices are introduced at the right moment for them, they will act in a new capacity, as stimulants of enzymatic activity for a child receiving a large amount of “heavy” foods - when the child’s diet has already included cereals, vegetables, fruits, meat, fish, dairy products... Simply everything has its time.
How to properly introduce cow's milk into your diet
How to switch a child to cow's milk? Complementary feeding should be started with one teaspoon of milk diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 3. If during the day there is no reaction from the body, then the portion can be gradually increased. After 2.5-3 weeks, the volume of milk consumed can be about 100 ml. Fat content should be within 3-4%. You can gradually reduce the amount of water and eventually remove it completely. If a child has an individual intolerance, you should refuse such a product and stop thinking about the question of when you can give cow’s milk to your child.
The gastrointestinal tract of a child under 2 years of age does not have the necessary enzymes that help fully digest animal products. Therefore, milk allergies are quite common. This happens due to the content of beta globulin in its composition - the main culprit of the rash. Amino acids from mother's milk are absorbed easily and quickly by the child's body, while enzyme systems need to work with increased load to break down foreign acids. Allergies are cumulative in nature, so they may not appear immediately.
Fermented milk products are introduced into a child’s diet before cow’s milk. This is due to the reduced amount of protein and lactose due to the manufacturing process. According to a number of studies, when cow's milk was introduced into the diet of children under 1 year of age, an allergy to this product developed in ¼ of the cases. This circumstance gives grounds to consider cow's milk one of the most allergenic products.
General information
When preparing a diet for a small child, very often mothers, due to inexperience, do not adhere to very important rules.
For example, very often a mother fears that her baby will remain hungry due to the small amount of milk that is produced. Sometimes a mother simply seeks to “feed” the baby, believing that this way he will grow faster. As a result, not knowing what can be given to the baby, his diet is unnecessarily “diversified” with foods that he does not need at all. First of all, it is important to realize the following truth: if the mother breastfeeds the baby correctly, then the baby will have enough feeding. However, not all modern mothers practice breastfeeding Therefore, many inexperienced women often ask more experienced mothers whether it is possible to give a child cow’s milk, whether fermented milk products are healthy for children under one year old, etc. Below we will talk about whether goat’s and cow’s milk is healthy for children of different ages and when to start giving it to his kids.
When can you give cow's milk to your baby?
Human breast milk is optimal for humans, especially in the first half of life. Therefore, parents should have no doubts about whether cow’s milk can be given to a one-month-old baby or not. It is forbidden. At an older age, such liquid can be consumed, but it is better to opt for cottage cheese and fermented milk products.
But what about the proven experience of mothers and grandmothers over the years? In those days, medicine was not so developed; experts could only speculate on the causes of many diseases. Today, science has filled in many gaps, so it suggests being guided only by proven information.
What should parents do? Whether or not to introduce milk into complementary foods is a purely individual matter. But still, if you really want to introduce your baby to such a seemingly useful product, it is better to do this no earlier than 1 year. Until then, be content with mixtures that are adapted to the child’s body and have many more advantages, namely:
- all the vitamins and microelements the child needs;
- stable composition that does not undergo changes;
- minimized likelihood of allergic reactions due to special processing of milk protein;
- convenience and ease of preparation.
What do pediatricians say? Pediatricians unanimously say that cow's milk should not be given to children under one year of age. The most optimal age is after 3 years. It is during this period that the body becomes ready to consume “adult” food, which also includes milk.
Can a nursing mother drink milk?
It is interesting that debates on this matter are still ongoing. Doctors clearly say that in the first month of a baby’s life, a nursing mother should not drink it. As for the next months, there are different opinions on this matter. Some experts say that you can drink it in small portions and dilute it halfway with tea or porridge. At the same time, milk should be introduced into the diet in small portions, carefully observing the child’s reaction.
Many other scientists claim that milk is beneficial for the mother, as it saturates her body and the baby’s body with calcium, which is very important when bones form and grow.
There is also an opinion that it is this product, consumed by the mother, that causes colic in the child. Therefore, it is recommended to introduce more neutral fermented milk dishes into the diet.
But the interdependence of cow's milk consumption and increased lactation is nothing more than a myth. After all, consuming any warm liquid before feeding can give the same effect, increasing the production of mother's milk.
Potential harm of milk for adults and children
Many studies have been devoted specifically to the topic of the influence of this product on the health of children and adults. Based on the results of such studies, scientists have discovered a connection between the consumption of large amounts of dairy products and the development of certain types of cancer in men and women.
If a person eats too much dairy products, the level of galactose in the body exceeds the potential of the enzymes that break it down. This leads to an increased risk of developing ovarian cancer in women.
of prostate cancer is also associated with excessive dairy consumption .
Scientists also refute the previously widespread thesis that milk is useful for the prevention of osteoporosis .